Face ID Technology in 2018 iPhones: 2018 Iphones Stick With Same Face Id Sensors
Face ID, introduced in the iPhone X in 2017, revolutionized smartphone security. In 2018, Apple continued to refine this technology, incorporating it into the iPhone XR, iPhone XS, and iPhone XS Max. These models leveraged the same fundamental Face ID technology as the iPhone X, but with enhancements for improved performance and accuracy.
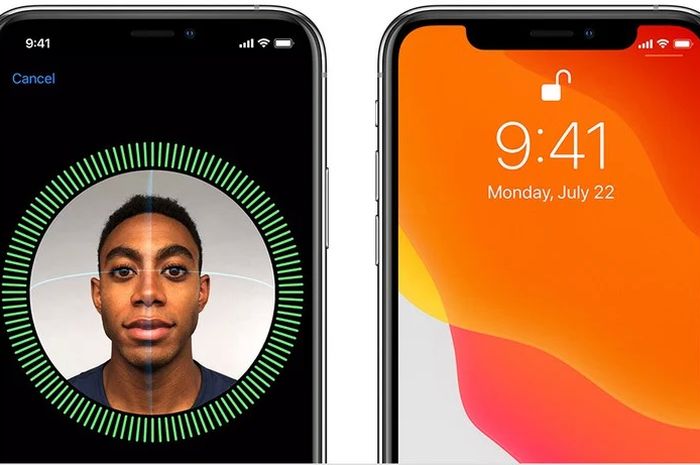
How the Face ID Sensor Works
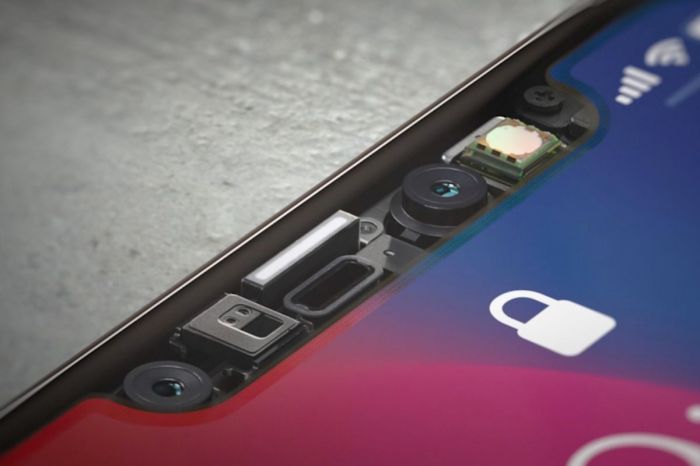
The Face ID sensor, located at the top of the iPhone, utilizes a complex system of hardware and software. It comprises a dot projector, an infrared camera, and a flood illuminator.
* Dot projector: This component projects a pattern of infrared dots onto the user’s face, creating a depth map.
* Infrared camera: This camera captures an image of the user’s face in infrared light, allowing for recognition even in low-light conditions.
* Flood illuminator: This component illuminates the user’s face with infrared light, enhancing the accuracy of the depth map.
The Face ID sensor combines these elements to create a 3D map of the user’s face. This unique map is then compared to the stored facial data, unlocking the phone if a match is found.
Comparison to Previous Models
While the core technology remained the same, the 2018 iPhone models featured several improvements to Face ID. These enhancements included:
* Faster processing: The A12 Bionic chip, introduced in the 2018 models, enabled faster processing speeds, resulting in quicker face recognition.
* Improved accuracy: The Face ID sensor in the 2018 iPhones was more accurate, capable of recognizing faces from wider angles and under more challenging lighting conditions.
* Enhanced security: The Face ID technology in the 2018 iPhones was further fortified with enhanced security features, making it even more difficult to spoof.
Security Implications of Using the Same Face ID Sensor Across Multiple Models
The use of the same Face ID sensor across multiple iPhone models raised concerns about potential security vulnerabilities. While Apple implemented robust security measures, there was a theoretical possibility that someone could create a 3D mask that could bypass the Face ID system. However, Apple actively worked to address such concerns, constantly improving the security of Face ID with each software update.
Reasons for Sticking with the Same Sensor
Apple’s decision to retain the same Face ID sensor in their 2018 iPhones, despite advancements in facial recognition technology, was a strategic move driven by several factors. This decision was a balance of benefits and drawbacks, ultimately leading to a path of maintaining consistency in their flagship feature.
Benefits of Maintaining Consistency
Maintaining consistency in Face ID technology across iPhone models offered several advantages for Apple. The benefits of using the same sensor can be categorized into the following:
- Improved User Experience: Users familiar with the existing Face ID system could seamlessly transition to newer iPhones without having to learn a new facial recognition process. This consistent experience fostered user trust and satisfaction.
- Enhanced Security: Apple’s commitment to robust security was strengthened by maintaining the established Face ID technology. The proven reliability of the sensor, along with the company’s security protocols, provided a higher level of confidence in protecting user data.
- Reduced Development Costs: Developing a new Face ID sensor would have incurred significant research and development expenses. Reusing the existing technology allowed Apple to allocate resources to other areas of innovation and product improvement.
Potential Drawbacks of Not Upgrading the Face ID Sensor
While maintaining consistency had its benefits, there were potential drawbacks associated with not upgrading the Face ID sensor:
- Missed Opportunities for Advancement: New technologies, like 3D facial mapping and improved algorithms, could have enhanced the accuracy and security of Face ID. By not upgrading, Apple potentially missed opportunities to push the boundaries of facial recognition technology.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Competitors were actively incorporating advanced facial recognition features into their devices. Maintaining the same sensor could have positioned Apple as lagging behind in the technological race.
- Reduced User Appeal: Users might have been attracted to newer and more sophisticated facial recognition features offered by competitors. This could have negatively impacted the appeal of Apple’s iPhones.
Cost Comparison: Developing a New Sensor vs. Using the Existing One
The decision to stick with the same Face ID sensor was likely influenced by a cost-benefit analysis. Developing a new sensor would have involved significant upfront investments in research, development, and testing. The cost of these activities would have been substantial, potentially impacting the overall profitability of the iPhone line. In contrast, reusing the existing sensor allowed Apple to allocate resources to other areas of product development, like improving camera technology or enhancing software features.
Impact on User Experience
Sticking with the same Face ID sensor in 2018 iPhones means users get to experience the same familiar and reliable facial recognition technology they’ve come to expect. This consistency provides a smooth user experience, as there’s no need to re-learn how to use the feature. However, there are potential limitations and challenges that users might encounter, and it’s important to analyze these to understand the overall impact on user experience.
Potential Limitations and Challenges
While Face ID has been a successful feature, using the same sensor in 2018 iPhones presents some potential limitations and challenges for users. Here are some key points to consider:
- No Significant Improvements: Users might not experience significant improvements in Face ID performance compared to previous models. This could lead to a sense of stagnation, especially considering the rapid pace of technological advancements in the smartphone industry.
- Limited Adaptability to Changing Facial Features: Face ID might struggle to recognize users if their facial features change significantly, such as after gaining or losing weight, growing a beard, or wearing glasses or makeup. While the system is designed to adapt to some changes, it may not be able to handle drastic transformations.
- Security Concerns: While Face ID is considered secure, there are always concerns about potential vulnerabilities. Using the same sensor in 2018 iPhones might raise concerns about whether the technology is sufficiently robust against evolving security threats.
User Feedback and Reviews
User feedback and reviews regarding the Face ID performance in 2018 iPhones are generally positive. Many users praise the speed, accuracy, and convenience of the feature. However, some users have reported challenges with Face ID, particularly in situations involving significant changes in facial features or challenging lighting conditions.
Comparison to Other Smartphone Models
Compared to other smartphone models with facial recognition, Face ID in 2018 iPhones generally performs well. While some competitors offer faster unlocking speeds or more advanced features, Face ID remains a reliable and secure option. It’s important to note that the user experience can vary depending on the specific model and software implementation.
Technological Advancements in Face ID
Since the introduction of Face ID in 2017, Apple has continuously refined and improved its facial recognition technology. These advancements aim to enhance the accuracy, security, and user experience of Face ID.
Performance Enhancements
Performance improvements in Face ID have focused on increasing the speed and accuracy of facial recognition. These advancements have been achieved through a combination of hardware and software upgrades.
* Faster Processing: Newer iPhone models feature more powerful processors that can handle complex facial recognition algorithms more efficiently, leading to faster unlocking times.
* Improved Infrared Sensors: The infrared sensors used in Face ID have been upgraded to capture more detailed facial data, resulting in more accurate facial recognition.
* Enhanced Machine Learning: Apple’s machine learning algorithms have been continuously trained on larger datasets of facial images, improving the system’s ability to recognize faces in different lighting conditions, with varying expressions, and even when wearing accessories.
Security Enhancements
Security improvements in Face ID have focused on making the system more resistant to spoofing attempts. These advancements have been achieved through a combination of hardware and software upgrades.
* More Secure Encrypted Storage: Face ID data is stored securely on the device, encrypted with a unique key. This makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to access the data.
* Advanced Anti-Spoofing Techniques: Newer iPhones incorporate advanced anti-spoofing techniques, including the use of depth sensing technology to detect 3D objects and prevent spoofing attempts using photographs or masks.
* Real-time Facial Analysis: Face ID continuously analyzes facial features in real-time, ensuring that the person unlocking the device is the authorized user.
Comparison with 2018 iPhones
Newer iPhone models offer significant improvements in Face ID performance and security compared to the 2018 iPhones. These improvements include:
* Faster Unlock Speeds: Newer iPhones can unlock significantly faster than the 2018 models due to more powerful processors and optimized algorithms.
* Enhanced Accuracy: The improved infrared sensors and machine learning algorithms in newer iPhones lead to more accurate facial recognition, even in challenging lighting conditions or when wearing accessories.
* More Secure Anti-Spoofing: Newer iPhones feature more advanced anti-spoofing techniques, making them more resistant to spoofing attempts using photographs or masks.
Potential Future Developments, 2018 iphones stick with same face id sensors
Future advancements in Face ID technology could include:
* Integration with Augmented Reality: Face ID could be integrated with augmented reality (AR) applications, allowing users to interact with virtual objects using their facial expressions.
* Enhanced Security Features: Future versions of Face ID could incorporate advanced security features, such as iris scanning or voice recognition, to further enhance the security of the system.
* Wider Applications: Face ID could be used in a wider range of applications, such as unlocking doors, making payments, and accessing secure areas.
2018 iphones stick with same face id sensors – The decision to stick with the same Face ID sensor in 2018 iPhones was a calculated one, likely driven by a combination of factors. While some users might have desired a more advanced sensor, Apple’s focus on consistency and cost-effectiveness played a significant role. Ultimately, the choice to stick with the tried-and-true technology allowed Apple to maintain a high level of security and user experience while keeping costs down. This decision highlights the delicate balance between innovation and practicality in the tech world, a balance that continues to shape the future of smartphones.
While the 2018 iPhones are sticking with the same Face ID sensors, it’s worth noting that Apple’s commitment to water resistance is still going strong. Check out this pro surfer who put an iPhone 7 through the ultimate test pro surfer tests iphone 7 water resistance – and it still survived! So, even if you’re not a pro surfer, you can rest assured that your iPhone is ready for whatever life throws at it, even if it’s a splash of water.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News