Edps gdpr principles attacks – EDPS GDPR principles, the bedrock of data protection in the digital age, are under constant attack. From data breaches and phishing scams to ransomware and denial-of-service attacks, malicious actors are constantly seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in organizations’ data security frameworks. These attacks not only violate the core principles of the EDPS GDPR, but also pose significant legal and reputational risks for organizations.
The challenges are real, and the stakes are high. Understanding the types of attacks, their impact, and the strategies for mitigation is crucial for organizations to effectively protect personal data and ensure compliance with the EDPS GDPR.
Understanding EDPS GDPR Principles
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enforced by the European Data Protection Supervisor (EDPS), establishes a comprehensive framework for data protection, encompassing a set of core principles that guide the handling of personal data. These principles are fundamental to ensuring the responsible and ethical use of personal information, safeguarding individual rights and fostering trust in data processing activities.
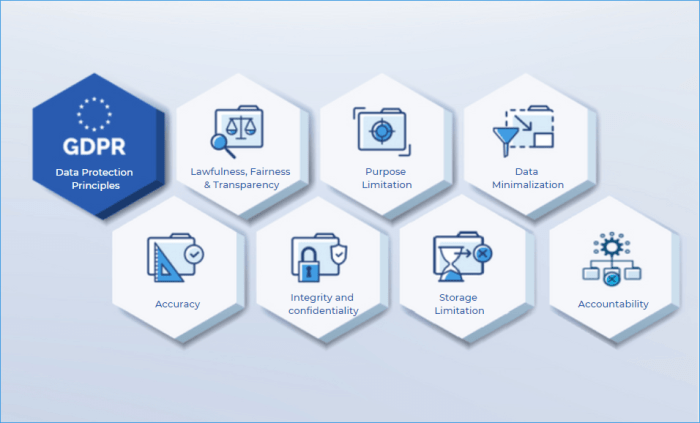
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
The GDPR emphasizes the importance of ensuring that the processing of personal data is lawful, fair, and transparent. This means that individuals must be informed about how their data is being used and have a clear understanding of the legal basis for its processing. For example, individuals should be notified about the purpose of data collection, the types of data being processed, the recipients of the data, and the duration of storage. This principle promotes accountability and empowers individuals to exercise their rights over their personal data.
Purpose Limitation
The principle of purpose limitation dictates that personal data should be collected for specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes. This means that data should only be processed for the stated purpose and not for any other, unrelated purpose. For instance, if data is collected for marketing purposes, it should not be used for profiling or decision-making without explicit consent. This principle prevents the misuse of personal data and safeguards individuals from potential harm.
Data Minimization
The principle of data minimization requires that only the necessary personal data is collected and processed. This means that organizations should avoid collecting excessive or unnecessary data, only gathering information that is relevant to the stated purpose. This principle helps to reduce the risk of data breaches and minimizes the potential impact of any data security incidents.
Accuracy
The GDPR emphasizes the importance of maintaining accurate and up-to-date personal data. This means that organizations have a responsibility to ensure that the data they process is accurate and to correct any errors promptly. This principle promotes data integrity and prevents the use of outdated or inaccurate information for decision-making.
Storage Limitation
The principle of storage limitation dictates that personal data should not be stored for longer than necessary. This means that organizations should have clear retention policies and procedures in place to ensure that data is deleted or anonymized once it is no longer needed for the stated purpose. This principle helps to minimize the risk of data breaches and reduces the potential impact of any data security incidents.
Integrity and Confidentiality
The GDPR emphasizes the importance of protecting the integrity and confidentiality of personal data. This means that organizations must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This principle promotes data security and safeguards individuals from potential harm.
Accountability
The principle of accountability requires that organizations demonstrate compliance with the GDPR principles. This means that organizations must have appropriate policies, procedures, and controls in place to ensure that they are processing personal data in accordance with the law. This principle promotes transparency and ensures that organizations are held responsible for their data processing activities.
Challenges in the Digital Age
The EDPS GDPR principles pose significant challenges in the context of data protection in the digital age. The rapid evolution of technology, the increasing volume and complexity of data, and the interconnected nature of digital systems create new challenges for data protection.
Relevance to Cyberattacks
The EDPS GDPR principles are highly relevant to the protection of personal data from cyberattacks. The principles of data minimization, storage limitation, and integrity and confidentiality are particularly important in this context. By minimizing the amount of data collected and stored, organizations can reduce the potential impact of a data breach. By implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction, organizations can strengthen their defenses against cyberattacks. The principle of accountability also plays a crucial role, as it requires organizations to demonstrate compliance with the GDPR principles and to be held responsible for any data breaches.
Common Types of Attacks Targeting GDPR Compliance
Data protection is a critical aspect of any organization, especially in the context of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). GDPR mandates robust data security measures to protect personal information, and attackers are constantly seeking vulnerabilities to exploit. This section delves into common attack types targeting GDPR compliance, their impact on data protection principles, and potential mitigation strategies.
Data Breaches, Edps gdpr principles attacks
Data breaches are a common threat that can have severe consequences for GDPR compliance. These breaches involve unauthorized access to or disclosure of personal data. They can occur through various methods, including:
* Malicious hacking: Attackers gain unauthorized access to systems through vulnerabilities in software or network security.
* Insider threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data may intentionally or unintentionally leak or misuse information.
* Physical theft: Laptops, mobile devices, or physical storage media containing personal data can be stolen.
* Data leakage: Sensitive information may be unintentionally shared or exposed through misconfigured systems, unsecure file sharing, or insecure cloud storage.
Data breaches can violate multiple GDPR principles, including:
* Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: If data is breached due to negligence or lack of appropriate security measures, the organization may be deemed to have failed to process data lawfully, fairly, and transparently.
* Purpose limitation: If data is accessed or disclosed for purposes beyond those for which it was collected, this violates the principle of purpose limitation.
* Integrity and confidentiality: Breaches compromise the integrity and confidentiality of personal data, as unauthorized access and disclosure can lead to data alteration or misuse.
* Accountability: Organizations are accountable for ensuring the security of personal data, and a breach may indicate a failure to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures.
Here is a table summarizing the impact of data breaches on GDPR principles and potential mitigation strategies:
| Attack Type | Impact on GDPR Principles | Mitigation Strategies |
|—|—|—|
| Data Breach | Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency; Purpose limitation; Integrity and confidentiality; Accountability | Implement robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments. Train employees on data security best practices. Implement strong access controls and data loss prevention mechanisms. |
Organizations should strive to prevent data breaches by implementing comprehensive security measures, but they should also have a robust incident response plan in place to minimize the impact of any breach that occurs.
Impact of Attacks on Data Protection
Data breaches and attacks on organizations’ data protection systems can have devastating consequences for individuals whose personal information is compromised. These attacks not only violate privacy but also lead to significant financial, emotional, and reputational harm.
Consequences for Individuals
Successful attacks on data protection systems can result in various forms of harm to individuals, including:
- Identity Theft: Stolen personal data, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card details, can be used by attackers to impersonate individuals and commit fraud. This can lead to financial losses, damage to credit scores, and difficulties obtaining loans or credit.
- Financial Loss: Unauthorized access to financial information can result in direct financial losses, such as stolen funds from bank accounts or fraudulent transactions. Individuals may also incur costs related to identity theft recovery, such as credit monitoring services and legal fees.
- Emotional Distress: The exposure of sensitive personal information can cause significant emotional distress, anxiety, and feelings of vulnerability. Individuals may experience fear of identity theft, reputational damage, and social stigma.
- Discrimination: The misuse of personal data can lead to discrimination based on sensitive information such as race, religion, or health status. This can affect access to employment, housing, and other opportunities.
- Reputational Damage: The disclosure of personal information can damage an individual’s reputation, leading to social isolation, job loss, and difficulty in personal relationships.
Legal and Reputational Risks for Organizations
Organizations face significant legal and reputational risks in the event of a GDPR violation due to an attack:
- Heavy Fines: The GDPR imposes substantial fines on organizations that fail to comply with its provisions. These fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of the organization’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
- Legal Action: Individuals whose personal data has been compromised can file legal action against organizations for damages. This can result in significant financial settlements and legal costs.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, decreased brand value, and negative media coverage. This can negatively impact future business prospects and revenue.
- Loss of Business: Customers may lose trust in an organization that has suffered a data breach and choose to do business with competitors. This can lead to a decline in sales and revenue.
Real-World Examples of Data Breaches
Several real-world examples demonstrate the devastating impact of data breaches on both individuals and organizations:
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): This massive data breach affected over 147 million individuals in the United States, exposing sensitive personal information such as Social Security numbers, birth dates, and credit card details. Equifax faced significant legal penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses as a result of the breach.
- Yahoo Data Breaches (2013, 2014): Yahoo experienced two major data breaches that compromised the personal information of billions of users. These breaches resulted in substantial legal settlements, reputational damage, and a decline in user trust.
- Cambridge Analytica Scandal (2018): This scandal involved the misuse of Facebook user data by Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm, to influence elections. The scandal resulted in significant regulatory scrutiny of Facebook and raised concerns about the use of personal data for political purposes.
Strategies for Mitigating Attacks and Ensuring Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a high bar for data protection, and organizations need to proactively defend against attacks that target GDPR compliance. A robust strategy is essential to mitigate risk, ensure compliance, and protect sensitive data.
Building a Comprehensive Data Security Framework
A comprehensive data security framework is the cornerstone of GDPR compliance. This framework should be designed to address the specific risks and vulnerabilities faced by an organization, taking into account the EDPS GDPR principles.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess data security risks, including potential attacks on GDPR compliance. Identify vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation efforts. Examples include assessing the impact of a data breach on individuals, analyzing potential attack vectors, and evaluating the effectiveness of existing security controls.
- Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Only collect and process data that is necessary for specific, legitimate purposes. This principle reduces the attack surface and limits the potential impact of a data breach. Examples include implementing data minimization policies, conducting regular data audits, and ensuring data is only processed for its intended purpose.
- Data Security Controls: Implement robust technical and organizational controls to protect data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Examples include access control mechanisms, encryption, data loss prevention measures, and secure data storage and disposal procedures.
- Data Retention and Deletion: Establish clear policies for data retention and deletion, ensuring that data is only stored for as long as necessary. This principle minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures compliance with GDPR requirements. Examples include implementing data retention policies, regularly reviewing data retention schedules, and securely deleting data when it is no longer needed.
- Data Integrity and Confidentiality: Ensure that data is accurate, complete, and kept confidential. Implement controls to prevent unauthorized modification or deletion of data. Examples include data validation procedures, data quality monitoring, and robust access control measures.
- Data Breach Notification: Establish a clear process for responding to data breaches and notifying relevant authorities and individuals affected. This process should be timely and transparent, ensuring compliance with GDPR notification requirements. Examples include creating a data breach response plan, conducting thorough investigations, and providing clear and concise notifications to individuals affected.
Data Protection Best Practices
- Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. This includes encrypting databases, files, and communication channels. Examples include using strong encryption algorithms like AES-256, implementing encryption at the database level, and encrypting data during transmission over public networks.
- Access Control: Implement strong access control mechanisms to restrict access to data based on roles, permissions, and need-to-know principles. Examples include implementing role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication, and access logs to track user activity.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. This includes monitoring data transfers, blocking unauthorized data transfers, and identifying and preventing data leaks. Examples include implementing DLP software, configuring rules to identify and block sensitive data transfers, and integrating DLP solutions with existing security infrastructure.
- Incident Response: Develop and test a comprehensive incident response plan to address data breaches and other security incidents effectively. This plan should include procedures for containment, investigation, remediation, and notification. Examples include establishing a dedicated incident response team, conducting regular incident response drills, and documenting procedures for responding to different types of incidents.
The Importance of Data Governance and Awareness: Edps Gdpr Principles Attacks
Data governance plays a crucial role in safeguarding personal data and ensuring compliance with the EDPS GDPR principles. A robust data governance framework establishes clear policies, procedures, and responsibilities for managing personal data, minimizing the risk of attacks and fostering a culture of data protection within the organization.
Data Governance and EDPS GDPR Compliance
Data governance policies and procedures are essential for organizations to comply with the EDPS GDPR principles. A well-defined data governance framework helps organizations:
- Identify and categorize personal data: Organizations must have a comprehensive understanding of the personal data they collect, process, and store. This includes identifying the types of data, its purpose of collection, and the legal basis for processing.
- Implement appropriate technical and organizational security measures: Data governance policies should Artikel the necessary security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Ensure accountability and transparency: Organizations are responsible for demonstrating their compliance with GDPR principles. Data governance policies should clearly define roles and responsibilities for data protection, including data controllers, data processors, and data protection officers.
- Manage data retention and deletion: Data governance policies should establish clear guidelines for data retention periods and procedures for secure data deletion. This ensures that personal data is only retained for as long as necessary and is deleted securely when no longer required.
- Respond to data breach incidents: Data governance policies should Artikel procedures for handling data breach incidents, including reporting obligations, incident response plans, and communication protocols.
Data Privacy Awareness Training
Data privacy awareness training for employees is crucial for mitigating the risk of attacks targeting GDPR compliance. Training programs should cover the following key areas:
- Understanding GDPR principles: Employees should be educated about the key principles of the GDPR, including the rights of data subjects and the obligations of data controllers and processors.
- Recognizing and preventing data breaches: Employees should be trained to identify potential data breaches and understand the risks associated with mishandling personal data.
- Data security best practices: Training should cover best practices for handling personal data, including password security, secure data storage, and data encryption.
- Reporting data breaches: Employees should be aware of the procedures for reporting data breaches and the importance of promptly reporting any suspected incidents.
The Future of Data Protection and Security
The landscape of data protection and security is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, emerging threats, and evolving regulatory frameworks. As we look ahead, it’s crucial to understand the trends and challenges that will shape the future of data protection in the context of the EDPS GDPR.
Emerging Trends and Challenges
The EDPS GDPR has established a robust framework for data protection, but its effectiveness hinges on the ability to adapt to emerging trends and challenges. These include:
- The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming industries, but they also introduce new data protection challenges. AI systems often rely on vast datasets for training, raising concerns about data privacy and potential biases. The EDPS GDPR’s principles of data minimization and purpose limitation must be carefully considered in the context of AI and ML.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing: The proliferation of IoT devices and the shift towards edge computing create new attack surfaces and complicate data security. Organizations must ensure that data collected and processed by IoT devices is protected, while also complying with the EDPS GDPR’s requirements for data security and transparency.
- Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats: Data breaches remain a significant threat, and the sophistication of cyberattacks continues to evolve. Organizations need to implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. The EDPS GDPR’s requirements for data security and breach notification are crucial in mitigating the impact of breaches.
Potential Future Attack Vectors
As technology advances, so do the tactics used by attackers. Future attack vectors may include:
- Sophisticated Social Engineering Attacks: Attackers are increasingly using sophisticated social engineering techniques to gain access to sensitive data. This could involve impersonating trusted individuals or organizations to trick users into revealing confidential information.
- Exploitation of Emerging Technologies: New technologies like quantum computing and blockchain could introduce new vulnerabilities. Attackers may exploit these technologies to bypass existing security measures or create new forms of attacks.
- Targeted Attacks on Critical Infrastructure: Attackers may target critical infrastructure like power grids, transportation systems, or healthcare facilities, potentially causing widespread disruption and data loss.
The Evolving Role of Technology in Safeguarding Data
Technology plays a vital role in safeguarding data, and its role will continue to evolve in the future:
- Advanced Security Technologies: Organizations will increasingly rely on advanced security technologies like zero-trust security, threat intelligence, and automated security orchestration to detect and respond to threats.
- Data Privacy Enhancing Technologies: Technologies like differential privacy and homomorphic encryption can help protect data privacy while enabling data analysis and sharing.
- Blockchain and Decentralized Data Storage: Blockchain technology offers potential benefits for data security and integrity, as it can provide a secure and transparent way to record and track data transactions.
Preparing for Future Threats and Maintaining GDPR Compliance
Organizations must proactively prepare for future threats and ensure ongoing GDPR compliance:
- Develop a Comprehensive Data Protection Strategy: Organizations need a comprehensive data protection strategy that addresses all aspects of data processing, including data collection, storage, use, sharing, and deletion.
- Invest in Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Training: Employees must be trained on data protection principles, cybersecurity best practices, and the importance of data privacy.
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments and Audits: Regular security assessments and audits are essential to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with the EDPS GDPR.
- Stay Informed About Emerging Threats and Technologies: Organizations must stay informed about emerging threats and technologies to adapt their data protection measures accordingly.
In a world where data is constantly under threat, a proactive approach to data protection is essential. By implementing robust data security frameworks, embracing emerging technologies, and fostering a culture of data privacy awareness, organizations can effectively mitigate the risk of attacks and ensure compliance with the EDPS GDPR. The future of data protection relies on our ability to stay ahead of the curve, adapting to evolving threats and continuously strengthening our defenses.
While we’re all buzzing about the new BlackBerry slider smartphone expected to arrive by November , let’s not forget the importance of protecting our data. EDPS GDPR principles are essential for safeguarding our privacy in the digital age, especially as we embrace new technologies. Understanding and upholding these principles is crucial for a secure and responsible digital future.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News