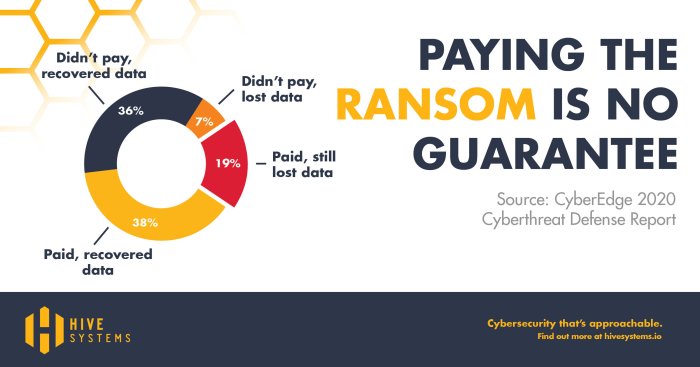
Should we ban ransom payments? It’s a question that’s been swirling in the cybersecurity world for years. On one hand, paying criminals encourages them to continue their malicious activities. On the other, refusing to pay could mean losing valuable data and facing crippling downtime. This debate isn’t just about ethics; it’s about the very future of digital security.
The rise of ransomware has forced businesses and individuals alike to confront a stark reality: cybercriminals are increasingly targeting our data, holding it hostage for profit. This has sparked a heated discussion about whether we should pay these criminals, or if a tougher stance is needed. The implications are far-reaching, impacting everything from the economy to the way we approach cybersecurity.
The Ethics of Ransom Payments
The issue of paying ransoms to criminals is a complex one, fraught with ethical considerations. While the immediate goal of paying a ransom is to secure the release of a victim, the act itself raises questions about morality, justice, and the potential consequences for society as a whole.
Moral Implications of Paying Ransoms
The moral implications of paying ransoms are deeply rooted in the principles of right and wrong. On one hand, paying a ransom can be seen as a desperate act of compassion, driven by the desire to save a life. However, critics argue that paying ransoms encourages criminal activity by rewarding perpetrators and incentivizing future attacks. This creates a vicious cycle where criminals are motivated by the potential for financial gain, and victims are left vulnerable to extortion.
Ethical Considerations of Paying Ransoms vs. Refusing
The decision to pay a ransom is often a difficult one, involving a complex interplay of ethical considerations and practical realities. Paying a ransom may seem like the only way to secure a victim’s release, but it can also send a message that paying criminals is acceptable. This can lead to an increase in kidnappings and other criminal activities, as criminals become emboldened by the prospect of financial reward.
Refusing to pay a ransom, on the other hand, carries the risk of the victim being harmed or even killed. This decision is often driven by a desire to stand firm against criminal demands and prevent the encouragement of further criminal activity. However, it can also be a risky and potentially tragic choice.
Impact of Ransom Payments on Victims and Their Families
The impact of ransom payments on victims and their families is often profound and long-lasting. Beyond the immediate trauma of being kidnapped, victims may suffer from psychological distress, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression. The financial burden of paying a ransom can also be devastating, leaving families in dire financial straits.
Furthermore, the act of paying a ransom can be a source of shame and guilt for victims and their families. They may feel as though they have been complicit in the criminal act, and the experience can erode their sense of security and trust in the world.
The Economic Impact of Ransom Payments
Ransom payments are a significant economic burden, impacting both individuals and organizations. While the immediate cost of paying a ransom might seem like the only financial consequence, the reality is far more complex. This section explores the various economic ramifications of ransomware attacks and the ripple effects they have on different sectors.
The Financial Impact on Individuals
Paying a ransom can have a devastating financial impact on individuals. Victims often face substantial financial losses, including the cost of the ransom itself, the cost of recovering lost data, and the potential loss of income due to downtime. This financial strain can be particularly crippling for individuals who may not have the financial resources to absorb such losses.
- For example, a small business owner might be forced to close their business temporarily while they recover from a ransomware attack, leading to a loss of revenue and potentially even bankruptcy.
- Individuals who are victims of ransomware attacks targeting personal computers might have to pay a ransom to regain access to their files, which could include important documents, photos, or other sensitive data.
The Economic Impact on Organizations
Ransomware attacks can have a profound impact on organizations of all sizes, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. The economic consequences of ransomware attacks go far beyond the cost of the ransom itself, including:
- Lost Productivity: Organizations might experience significant downtime while they attempt to recover from a ransomware attack. This downtime can lead to a loss of productivity and revenue, as employees are unable to work.
- Recovery Costs: The process of recovering from a ransomware attack can be costly, involving the purchase of new hardware and software, the hiring of IT professionals, and the potential need to rebuild lost data.
- Reputational Damage: Ransomware attacks can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and potential business opportunities.
- Legal and Regulatory Costs: Organizations may face legal and regulatory fines if they fail to comply with data protection regulations in the wake of a ransomware attack.
Industries Particularly Vulnerable to Ransomware Attacks
Certain industries are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks due to their reliance on sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and other healthcare providers are prime targets for ransomware attacks, as they hold sensitive patient data and rely on critical infrastructure for patient care.
- Finance: Financial institutions are also vulnerable to ransomware attacks, as they hold sensitive financial data and rely on critical infrastructure for financial transactions.
- Education: Educational institutions are increasingly becoming targets for ransomware attacks, as they hold sensitive student and faculty data and rely on critical infrastructure for online learning and administrative operations.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies are vulnerable to ransomware attacks, as they rely on critical infrastructure for production and distribution. A ransomware attack could disrupt operations, leading to production delays and financial losses.
- Energy: Energy companies are also vulnerable to ransomware attacks, as they rely on critical infrastructure for power generation and distribution. A ransomware attack could disrupt power supply, leading to significant economic losses.
The Costs Associated with Ransomware Attacks
| Cost Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Ransom Payment | The amount of money paid to the attackers to regain access to encrypted data or systems. | A company might pay a ransom of $1 million to regain access to its critical data. |
| Recovery Efforts | The costs associated with recovering from a ransomware attack, including data recovery, system restoration, and IT support. | A company might spend $500,000 on data recovery and system restoration after a ransomware attack. |
| Lost Productivity | The loss of revenue and productivity due to downtime caused by a ransomware attack. | A company might lose $1 million in revenue due to a ransomware attack that disrupts its operations for a week. |
| Reputational Damage | The loss of customer trust and business opportunities due to a ransomware attack. | A company might lose $1 million in revenue due to a decline in customer trust after a ransomware attack. |
| Legal and Regulatory Costs | The costs associated with legal and regulatory fines for data breaches and non-compliance. | A company might face a fine of $1 million for failing to comply with data protection regulations after a ransomware attack. |
The Effectiveness of Banning Ransom Payments
The idea of banning ransom payments to deter ransomware attacks is appealing, but its effectiveness is a complex issue with potential benefits and drawbacks. While it may seem like a straightforward solution, the reality is more nuanced, and the effectiveness of such a ban hinges on various factors, including the specific implementation and the broader cybersecurity landscape.
Potential Benefits of Banning Ransom Payments
Banning ransom payments could potentially deter ransomware attacks by reducing the financial incentive for attackers. This could lead to a decrease in the number of attacks and the severity of their impact.
“By making it more difficult for attackers to profit, a ban on ransom payments could discourage them from targeting victims in the first place.”
This approach could also encourage organizations to prioritize preventative measures, such as robust cybersecurity defenses, data backups, and employee training, to minimize their vulnerability to attacks.
Potential Drawbacks of Banning Ransom Payments
While a ban on ransom payments may seem like a straightforward solution, it comes with its own set of challenges. One of the main concerns is the potential for attackers to find alternative ways to monetize their attacks. For instance, they could resort to extortion tactics, demanding other forms of payment, such as cryptocurrency or sensitive data, or they could simply delete or destroy the data, causing significant damage.
Another drawback is the difficulty of enforcement. It is challenging to prevent organizations from paying ransoms, especially when they are facing significant financial losses or the threat of critical data loss. Additionally, banning ransom payments could create a false sense of security, leading organizations to neglect essential security measures.
Examples of Policies Restricting Ransom Payments
Several countries and organizations have implemented policies restricting ransom payments. For instance, the United States government has issued guidance discouraging ransom payments, emphasizing the importance of reporting attacks to law enforcement and focusing on prevention.
The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) has also adopted a similar stance, urging organizations to prioritize preventative measures and avoid paying ransoms whenever possible.
Alternative Strategies for Dealing with Ransomware Attacks
While banning ransom payments might seem like a simple solution, it is crucial to explore alternative strategies for dealing with ransomware attacks.
- Robust Data Backups: Implementing regular and comprehensive data backups is a fundamental step in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks. Having backups allows organizations to restore their systems and data even if they are compromised.
- Incident Response Plans: Developing and regularly testing incident response plans is crucial for handling ransomware attacks effectively. These plans Artikel steps for containing the attack, recovering data, and restoring operations.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about ransomware threats, phishing attacks, and best practices for cybersecurity is essential for preventing attacks.
- Cybersecurity Investments: Organizations need to invest in robust cybersecurity solutions, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security software, to protect their systems from ransomware attacks.
The Role of Law Enforcement
Law enforcement agencies play a crucial role in combating ransomware attacks. They are responsible for investigating attacks, identifying and apprehending the perpetrators, and working to prevent future attacks. However, this task presents significant challenges, requiring a multifaceted approach.
Challenges Faced by Law Enforcement
Investigating and prosecuting ransomware criminals poses a significant challenge for law enforcement agencies. This is due to the transnational nature of these crimes, the sophisticated techniques used by criminals, and the difficulty in tracing the flow of ransom payments.
- Transnational Nature of Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks often originate from countries with different legal frameworks and extradition treaties, making it difficult for law enforcement to collaborate and apprehend suspects.
- Sophisticated Techniques Used by Criminals: Ransomware criminals employ sophisticated techniques to conceal their identities and locations, making it difficult for law enforcement to track their activities.
- Difficulty in Tracing Ransom Payments: Ransom payments are often made using cryptocurrencies, which are difficult to trace and track. This makes it challenging for law enforcement to identify the beneficiaries of the payments.
Potential Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
To deter ransomware attacks, law enforcement agencies need to collaborate with governments, businesses, and individuals. This collaboration can lead to the development of effective legal and regulatory frameworks that address the vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware criminals.
- Strengthening International Cooperation: Enhancing international cooperation between law enforcement agencies is crucial to sharing intelligence, tracking down criminals, and extraditing suspects.
- Improving Cybercrime Legislation: Updating and strengthening existing cybercrime legislation to specifically address ransomware attacks, including penalties for those who engage in these activities.
- Promoting Cybersecurity Awareness: Educating individuals and organizations about best practices for preventing ransomware attacks, such as using strong passwords, updating software regularly, and backing up data.
- Developing Technical Countermeasures: Investing in research and development of technical countermeasures to disrupt ransomware operations, such as tools to detect and block ransomware attacks and to recover encrypted data.
The Impact on Cybersecurity
Banning ransom payments is a controversial topic with potential ramifications for cybersecurity practices. While it might seem like a straightforward solution to curb ransomware attacks, the impact is multifaceted and requires careful consideration.
The Impact of Banning Ransom Payments on Cybersecurity Practices
The primary argument for banning ransom payments is that it would discourage ransomware attacks by removing the financial incentive for attackers. However, this approach has its drawbacks. Cybercriminals are adaptable and might find alternative ways to monetize their activities, such as stealing data and selling it on the dark web or launching denial-of-service attacks. Moreover, banning ransom payments could lead to organizations becoming more complacent about their cybersecurity posture, believing that they are less vulnerable to attacks. This could result in a decrease in investments in cybersecurity measures, making organizations more susceptible to attacks.
Improving Cybersecurity Posture to Mitigate Ransomware Attacks
Organizations can take several steps to improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of ransomware attacks, regardless of whether ransom payments are banned or not. These measures include:
- Implementing strong password policies: Enforce the use of complex passwords and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This is a critical step in safeguarding against unauthorized access and mitigating the risk of ransomware attacks.
- Regularly patching systems: Software vulnerabilities are often exploited by attackers, so it is crucial to patch systems regularly to address security flaws and prevent exploitation. Keeping systems updated with the latest security patches is essential for minimizing the risk of successful ransomware attacks.
- Conducting regular security audits: Conducting regular security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure. This proactive approach allows for the identification and remediation of potential risks before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Implementing a robust backup and recovery plan: Even with strong cybersecurity measures, there is always a risk of a ransomware attack. A robust backup and recovery plan allows organizations to restore data quickly and efficiently in the event of an attack, minimizing downtime and data loss. This is a critical aspect of disaster recovery and ensures business continuity in the face of ransomware attacks.
- Investing in cybersecurity training for employees: Employees are often the weakest link in an organization’s cybersecurity defenses. Providing cybersecurity awareness training can educate employees about common ransomware threats and how to avoid them. This includes teaching them to recognize phishing emails, avoid suspicious links, and report any suspicious activity to the IT department. Training employees to be vigilant about cybersecurity threats is a crucial aspect of preventing ransomware attacks.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Cybersecurity awareness training is essential for individuals and organizations to combat ransomware attacks effectively. It empowers individuals to identify and avoid phishing scams, recognize suspicious links, and understand the importance of strong passwords and multi-factor authentication. This knowledge helps prevent ransomware infections in the first place.
“Cybersecurity awareness training is not a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices.”
Training should include practical examples of phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and common ransomware attacks. It should also cover the importance of reporting suspicious activity and following security protocols.
The Future of Ransomware: Should We Ban Ransom Payments
Ransomware has evolved from a nuisance to a significant threat to businesses and individuals alike. As technology advances, so too do the tactics used by ransomware attackers, making it crucial to understand the future trajectory of this cybercrime.
Potential Evolution of Ransomware Attacks
The future of ransomware attacks will likely see a convergence of sophisticated techniques and emerging technologies.
- More Targeted Attacks: Attackers will likely focus on high-value targets, such as critical infrastructure, government agencies, and financial institutions. This will involve meticulous reconnaissance and customized attack vectors.
- Increased Use of AI and Machine Learning: Attackers will leverage AI and ML to automate their operations, improve the effectiveness of their attacks, and evade detection. This could include AI-powered phishing campaigns, automated malware development, and self-propagating ransomware.
- Exploitation of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Attackers will exploit newly discovered vulnerabilities in software and systems before vendors have a chance to patch them. This will require a proactive approach to security, including regular patching and vulnerability assessments.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): RaaS will continue to grow, enabling individuals with limited technical skills to launch sophisticated ransomware attacks. This will lower the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, increasing the volume and complexity of attacks.
- Double Extortion: Attackers will increasingly combine data encryption with data theft, demanding payment to both decrypt data and prevent the stolen data from being leaked or sold on the dark web. This will add another layer of pressure on victims to pay the ransom.
Emerging Technologies to Combat Ransomware Attacks, Should we ban ransom payments
Emerging technologies hold the potential to counter the evolving threat of ransomware.
- Advanced Threat Detection and Response (ATDR): ATDR solutions leverage AI and ML to analyze network traffic and identify malicious activity, allowing for faster detection and response to ransomware attacks.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can be used to create immutable records of data, making it more difficult for attackers to tamper with or steal data. This can also be used for secure data storage and recovery.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero Trust security assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict authentication and authorization for access to resources. This can help to prevent lateral movement within a network and limit the impact of a ransomware attack.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity by breaking current encryption methods and enabling faster and more efficient threat detection.
Timeline of Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks have a long and evolving history, reflecting the changing landscape of cybercrime.
- 1989: The first known ransomware attack, known as the “AIDS Trojan,” targeted users with a ransom demand of $189.
- Early 2000s: Ransomware attacks became more common, targeting individuals and small businesses. These attacks often involved encrypting files and demanding payment for decryption.
- 2013: The emergence of the CryptoLocker ransomware, which used sophisticated encryption techniques and spread rapidly, marked a significant escalation in ransomware attacks.
- 2017: The WannaCry ransomware attack, which exploited a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows, infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, causing significant disruption and financial losses.
- 2020-Present: Ransomware attacks continue to evolve, becoming more sophisticated and targeting larger organizations, critical infrastructure, and government agencies. The use of double extortion tactics and ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has further increased the threat.
The question of whether to ban ransom payments is complex and multifaceted. There are no easy answers, and the debate will likely continue for years to come. But one thing is clear: we need to take a proactive approach to cybersecurity, investing in robust defenses and fostering a culture of vigilance. By doing so, we can reduce the risk of falling victim to ransomware and protect our digital world from the growing threat of cybercrime.
Banning ransom payments is a hot topic, but the real question is: how do we help businesses protect themselves in the first place? That’s where platforms like Catalog come in. By providing a secure and streamlined B2B commerce experience, Catalog empowers small businesses to thrive, making them less vulnerable to cyberattacks and ransomware threats.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News