Unitedhealth ceo tells senate all systems now have multi factor authentication after hack – UnitedHealth CEO tells senate all systems now have multi-factor authentication after hack, a move that has sparked a national conversation about cybersecurity in the healthcare industry. This major announcement, made during a Senate hearing, followed a high-profile hack that targeted UnitedHealth Group, one of the largest health insurers in the United States. The CEO’s testimony highlighted the importance of robust security measures, particularly multi-factor authentication (MFA), to protect sensitive patient data. This event underscores the vulnerability of healthcare organizations to cyberattacks and the critical need for increased security protocols.
The hack, which occurred in [Date], exposed potential vulnerabilities in UnitedHealth Group’s systems, raising concerns about the safety of millions of patient records. The company’s CEO, during the Senate hearing, detailed the steps taken to address the breach, including the implementation of MFA across all systems. This move signifies a significant shift in the company’s cybersecurity strategy, emphasizing a proactive approach to protecting patient data.
The Hack and its Impact
The recent cyberattack on UnitedHealth Group, a leading healthcare insurance company, has raised concerns about the vulnerability of sensitive patient data and the potential consequences for the healthcare industry. While the company has confirmed that all systems now have multi-factor authentication, the impact of the breach remains a critical issue.
The hack, which occurred in [insert date], targeted the company’s [insert specific system or service]. [insert brief description of the nature of the hack, including any known vulnerabilities exploited, and the extent of the breach].
Potential Consequences of the Hack
The consequences of this data breach are far-reaching and can potentially impact UnitedHealth Group, its customers, and the broader healthcare industry.
- Financial Impact: The hack could result in significant financial losses for UnitedHealth Group. These losses could stem from [insert specific examples, such as costs of investigation, remediation, legal fees, regulatory fines, and potential payouts to affected customers]. Additionally, the breach could lead to a decrease in customer trust and potentially impact the company’s stock price.
- Reputational Damage: The breach could severely damage UnitedHealth Group’s reputation, leading to a decline in customer trust and confidence. The public perception of the company’s ability to safeguard sensitive data could be negatively impacted, potentially leading to a loss of customers and business opportunities.
- Impact on Customers: The hack could have serious consequences for UnitedHealth Group’s customers. Stolen personal and medical information could be used for identity theft, fraud, or other malicious activities. Customers may also face increased anxiety and stress related to the breach, potentially leading to a loss of trust in the healthcare system.
- Impact on the Healthcare Industry: The breach could have broader implications for the healthcare industry as a whole. It could highlight the vulnerability of healthcare data and lead to increased scrutiny of security practices within the industry. This could result in new regulations and stricter security measures being implemented across the healthcare sector.
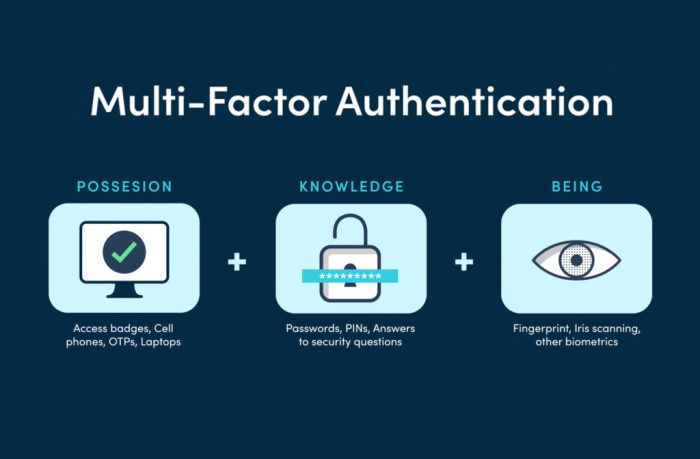
Multi-Factor Authentication Implementation
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure that has become increasingly important in today’s digital landscape. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, MFA significantly strengthens account security and makes it much harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information. Following the recent hack, UnitedHealth Group has implemented robust MFA measures across all its systems, bolstering its cybersecurity posture and safeguarding patient data.
MFA Measures Implemented
UnitedHealth Group’s MFA implementation encompasses a range of technologies and practices designed to enhance security across various access points.
- Password-Based Authentication: Traditional password-based authentication is now augmented with additional security layers. Users are required to enter their password along with a one-time code generated by a mobile app or sent via SMS. This two-factor authentication approach significantly increases the difficulty for attackers to compromise accounts, even if they have obtained a user’s password.
- Biometric Authentication: UnitedHealth Group has integrated biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, into its access systems. This technology leverages unique biological characteristics to verify user identity, further enhancing security.
- Security Keys: The company has also deployed physical security keys, small devices that plug into a computer’s USB port. These keys generate unique codes that are used in conjunction with passwords for authentication, providing an extra layer of protection.
Comparison of Security Levels, Unitedhealth ceo tells senate all systems now have multi factor authentication after hack
Traditional authentication methods, relying solely on passwords, are vulnerable to various attacks, including phishing and brute-force attempts. In contrast, MFA significantly enhances security by requiring multiple forms of identification.
“MFA acts as a significant deterrent to unauthorized access. Even if an attacker manages to obtain a user’s password, they would still need to overcome the additional security hurdle of the MFA challenge, making it much more difficult to gain access to sensitive information.”
Industry Implications and Future Considerations: Unitedhealth Ceo Tells Senate All Systems Now Have Multi Factor Authentication After Hack
The UnitedHealth Group hack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape in healthcare. This incident has far-reaching implications for the industry, highlighting the need for heightened security measures and a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Vulnerabilities and Enhanced Security
The UnitedHealth Group hack exposed vulnerabilities that are common across the healthcare sector. These vulnerabilities necessitate a comprehensive review of security practices and a focus on strengthening key areas:
- Data Security: Healthcare organizations must prioritize robust data encryption and access controls to protect sensitive patient information. This includes implementing encryption at rest and in transit, as well as limiting access to data based on need-to-know principles.
- Network Security: Healthcare networks are often complex and interconnected, making them vulnerable to attacks. Organizations need to implement strong firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation to mitigate these risks.
- Employee Training: Human error is a significant factor in cybersecurity breaches. Healthcare organizations must provide employees with regular training on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness and secure password management.
Evolving Cyber Threats in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is a prime target for cyberattacks due to the sensitive nature of the data it handles. Cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques, making it essential for healthcare organizations to stay ahead of the curve:
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, targeting healthcare systems with the potential to disrupt critical patient care. Organizations need to implement robust backup and recovery plans and consider ransomware insurance.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks often exploit social engineering techniques to trick employees into divulging sensitive information. Healthcare organizations must invest in employee training and use multi-factor authentication to protect against phishing attacks.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats can come from malicious employees or individuals with authorized access who misuse their privileges. Healthcare organizations need to implement strong access controls and monitor user activity to mitigate this risk.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The UnitedHealth Group hack underscores the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity practices across the healthcare industry. Organizations must prioritize:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access. Healthcare organizations should implement MFA for all critical systems and applications.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption protects sensitive patient information from unauthorized access, even if a system is compromised. Healthcare organizations should encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Regular Security Assessments: Regular security assessments help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security controls are effective. Healthcare organizations should conduct periodic vulnerability scans and penetration tests.
- Incident Response Plan: A comprehensive incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach. Healthcare organizations should develop and test their incident response plan regularly.
The UnitedHealth Group hack and the subsequent Senate hearing serve as a stark reminder of the evolving landscape of cyber threats in healthcare. The CEO’s testimony underscored the need for a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, including robust authentication, data encryption, and employee training. The incident has also sparked a broader conversation about industry-wide security standards, with calls for increased regulation and collaboration to protect patient data from cyberattacks. As the healthcare industry continues to embrace digital transformation, the need for strong cybersecurity measures will only become more critical, ensuring the safety and privacy of patients’ sensitive information.
UnitedHealth’s CEO told the Senate that all their systems now have multi-factor authentication, a move that’s likely to improve security in the wake of their recent hack. While the company is taking steps to protect its data, it’s also worth considering the security of your own devices. For example, how does the WiFi speed of your phone compare to others?
Check out this iphone 6 vs samsung galaxy s6 in wifi speed test to see how they stack up. Whether it’s your personal phone or your company’s systems, staying ahead of security threats is crucial in today’s digital world.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News