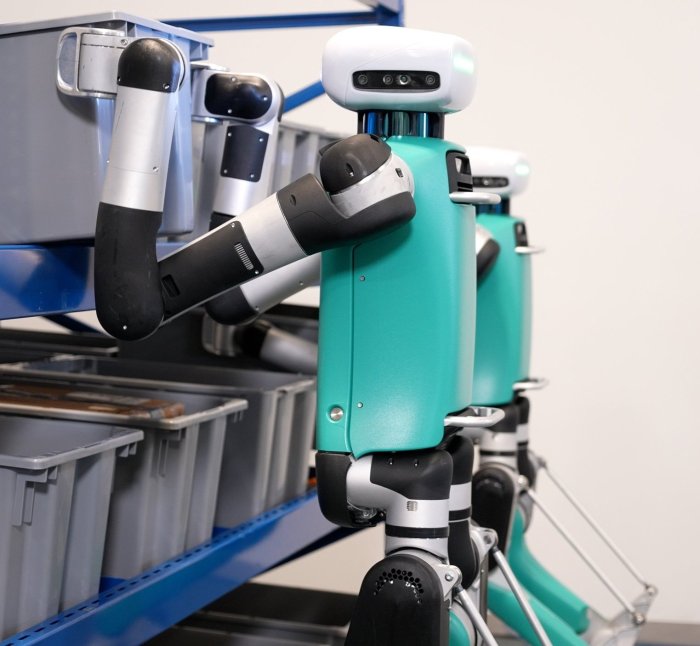
Agility is using large language models to communicate with its humanoid robots – Agility: Using Large Language Models to communicate with its humanoid robots, is a fascinating concept that’s rapidly changing the landscape of robotics. Imagine a future where robots can understand and respond to human language in a natural and intuitive way, thanks to the power of large language models. This technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to customer service and beyond.
The rise of humanoid robots, with their human-like appearances and capabilities, is already making waves in various sectors. From assisting surgeons in complex procedures to providing companionship to the elderly, these robots are proving their value. But what if we could take this interaction to the next level, allowing robots to communicate with humans in a way that feels natural and seamless? That’s where large language models come in.
The Rise of Humanoid Robots
The world is witnessing a surge in the development and deployment of humanoid robots, machines designed to resemble and mimic human form and capabilities. These robots are increasingly venturing beyond the realm of science fiction and into real-world applications, impacting various industries and aspects of our lives.
The increasing presence of humanoid robots is driven by several factors, including advancements in artificial intelligence, robotics, and sensor technology. These robots are becoming more sophisticated, capable of performing complex tasks and interacting with their environments in increasingly human-like ways.
Applications of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are finding applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Humanoid robots can perform repetitive and dangerous tasks on assembly lines, enhancing efficiency and safety. They can also work alongside human workers, collaborating on complex tasks. For example, in the automotive industry, robots are used for welding, painting, and assembly tasks, freeing up human workers for more specialized roles.
- Healthcare: Humanoid robots are being developed to assist healthcare professionals with tasks such as patient care, surgery, and rehabilitation. For instance, robots can provide companionship to elderly patients, assist with medication delivery, and perform basic tasks like fetching objects.
- Customer Service: Humanoid robots can serve as customer service representatives, providing information, answering questions, and assisting customers with purchases. For example, retail stores are using robots to greet customers, answer inquiries, and provide product information.
- Education: Humanoid robots can be used as teaching assistants, providing interactive learning experiences and personalized instruction. They can also serve as companions for children with special needs, providing social interaction and emotional support.
- Exploration: Humanoid robots are being developed for use in hazardous environments, such as disaster zones, space exploration, and underwater environments. They can perform tasks that are too dangerous or difficult for humans to perform, such as search and rescue operations.
Advantages of Humanoid Robots
The use of humanoid robots offers several advantages over traditional machines:
- Versatility: Humanoid robots are designed to interact with the world in a way that is similar to humans, making them more adaptable to a variety of tasks and environments. Their human-like form allows them to navigate complex spaces, use tools designed for humans, and interact with human-designed interfaces.
- Safety: Humanoid robots can be programmed to perform tasks safely, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries to human workers. Their ability to sense and react to their surroundings allows them to avoid obstacles and hazards.
- Efficiency: Humanoid robots can work tirelessly without breaks, increasing productivity and reducing downtime. They can also perform repetitive tasks with high accuracy, reducing errors and improving quality.
- Cost-effectiveness: In the long run, humanoid robots can be cost-effective, as they can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. They can also perform tasks that are too expensive or dangerous for humans to perform.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While humanoid robots offer numerous advantages, their deployment also presents challenges and ethical considerations:
- Job Displacement: One of the primary concerns is the potential for job displacement, as robots become increasingly capable of performing tasks currently done by humans. This raises questions about the future of work and the need for retraining and reskilling programs.
- Safety and Security: As robots become more autonomous, it is crucial to ensure their safety and security. Malfunctioning robots or hacking could pose risks to human safety and data security.
- Ethical Implications: The increasing use of humanoid robots raises ethical questions about their role in society. For example, how should we treat robots? Do they have rights? How do we ensure that robots are used ethically and responsibly?
- Social Impact: The widespread adoption of humanoid robots could have a significant impact on human relationships and social interactions. It is important to consider the potential consequences of robots becoming more integrated into our lives.
The Role of Large Language Models: Agility Is Using Large Language Models To Communicate With Its Humanoid Robots
Large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the way we interact with machines, particularly in the realm of humanoid robots. Their ability to understand and generate human-like text makes them ideal for bridging the communication gap between humans and robots.
LLMs possess several key capabilities that make them suitable for interacting with humanoid robots. These capabilities include:
Understanding Natural Language
LLMs are trained on massive datasets of text and code, enabling them to understand the nuances of human language. This includes comprehending context, identifying intent, and interpreting complex sentence structures. For instance, an LLM can understand the difference between “turn left” and “turn left at the next intersection,” allowing a robot to navigate effectively.
Generating Natural Language
LLMs can generate coherent and grammatically correct text in response to prompts. This enables robots to communicate effectively with humans in a natural and engaging manner. For example, a robot equipped with an LLM could respond to a user’s question about the weather with a detailed and informative answer.
Learning and Adapting
LLMs are constantly learning and adapting based on new data. This allows them to improve their understanding of human language and behavior over time. As robots interact with humans, LLMs can learn their preferences, habits, and communication styles, leading to more personalized and effective interactions.
Examples of LLM Applications in Humanoid Robots, Agility is using large language models to communicate with its humanoid robots
LLMs can be used in various ways to enhance communication and understanding between robots and humans:
- Personalized Assistance: An LLM can help a robot understand a user’s needs and preferences, providing personalized assistance in tasks like scheduling appointments, setting reminders, or finding information.
- Interactive Storytelling: Robots equipped with LLMs can engage in interactive storytelling, creating narratives tailored to the user’s interests and preferences.
- Language Translation: LLMs can facilitate communication across language barriers, allowing robots to interact with users who speak different languages.
- Emotional Understanding: LLMs can analyze tone and sentiment in human language, enabling robots to understand and respond appropriately to emotions.
Benefits of Using LLMs for Natural Language Processing in Humanoid Robots
LLMs offer several benefits for natural language processing in the context of humanoid robots:
- Enhanced Communication: LLMs enable robots to communicate with humans in a natural and intuitive way, improving the user experience.
- Increased Understanding: LLMs can understand complex language, allowing robots to interpret human instructions and requests accurately.
- Improved Responsiveness: LLMs can process language quickly, enabling robots to respond to user queries and requests in real time.
- Personalization: LLMs can learn and adapt to individual users, providing personalized experiences and assistance.
Integration Approaches for LLMs in Humanoid Robots
There are different approaches to integrating LLMs with humanoid robots:
- Cloud-Based Integration: LLMs can be hosted in the cloud and accessed by robots through an API. This approach allows for scalability and easy updates but may require a stable internet connection.
- On-Device Integration: LLMs can be deployed directly on the robot’s hardware. This approach provides faster response times and offline functionality but requires more computational resources.
- Hybrid Integration: A combination of cloud-based and on-device integration can be used to optimize performance and functionality.
Applications of Agility
The agility of using large language models (LLMs) for communication with humanoid robots opens up a wide range of possibilities, transforming how we interact with and utilize these advanced machines. This agility allows for seamless communication, enabling robots to understand complex instructions, adapt to changing environments, and learn from their interactions with humans.
Examples of Agile Applications
The ability of LLMs to translate human language into actionable commands for robots creates a multitude of applications. For example, imagine a scenario where a humanoid robot is tasked with assisting a chef in a busy kitchen. The chef, with their hands covered in flour, might simply say, “Please grab me the whisk from the top shelf.” The LLM, integrated with the robot, would process this request, understand the context, and instruct the robot to locate and retrieve the whisk. This seamless communication allows for efficient collaboration between humans and robots in various settings.
Potential Applications Across Sectors
| Sector | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| Healthcare |
|
| Manufacturing |
|
| Customer Service |
|
Tasks Humanoid Robots Can Perform More Effectively with LLMs
- Navigating complex environments: LLMs can help robots interpret their surroundings, understand spatial relationships, and navigate through obstacles. For example, a robot could use an LLM to plan a route through a crowded shopping mall or a cluttered warehouse.
- Understanding and responding to natural language: LLMs can enable robots to engage in conversations, understand human emotions, and respond appropriately. This could be beneficial in customer service, education, and companionship roles.
- Learning and adapting to new tasks: LLMs can facilitate the transfer of knowledge and skills from humans to robots, allowing them to learn new tasks and adapt to changing circumstances. This would enable robots to perform a wider range of tasks and become more versatile.
- Providing personalized assistance: LLMs can allow robots to tailor their responses and actions to individual preferences and needs. This could be particularly useful in healthcare, where robots could provide customized care plans and support to patients.
Technical Challenges and Future Directions
The integration of large language models (LLMs) with humanoid robots presents a unique set of technical challenges. These challenges stem from the need to bridge the gap between the abstract world of language and the physical world of robotics. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of agility and its transformative impact on society.
Natural Language Understanding
Natural language understanding (NLU) is a critical aspect of enabling effective communication between LLMs and robots. LLMs excel at processing and generating human-like text, but they often struggle to interpret the nuances of natural language, particularly in the context of real-world scenarios. For example, a robot might misinterpret a command like “Bring me the red cup” if it cannot distinguish between different shades of red or if it encounters multiple cups.
- Contextual Understanding: Robots need to understand the context of a command to interpret it accurately. For example, “Put the book on the table” might mean different things depending on the location of the robot and the specific book in question.
- Ambiguity Resolution: Natural language is often ambiguous. A robot needs to be able to resolve ambiguity in commands and questions. For instance, “Bring me the book” could refer to any book in the room.
- World Knowledge Integration: Robots need to integrate world knowledge into their understanding of language. For example, a robot needs to understand the relationship between objects and their properties.
Robot Perception
Humanoid robots need to perceive their surroundings to navigate, interact with objects, and understand the context of their actions. This requires sophisticated sensors and algorithms for visual, auditory, and tactile perception.
- Sensor Fusion: Integrating data from multiple sensors, such as cameras, microphones, and touch sensors, is crucial for building a comprehensive understanding of the environment.
- Object Recognition and Tracking: Robots need to be able to recognize and track objects in real time, allowing them to interact with them effectively.
- Scene Understanding: Robots need to understand the relationships between objects in a scene, allowing them to plan actions and make decisions.
Communication Protocols
Effective communication between LLMs and robots requires robust communication protocols that can handle real-time data transfer and ensure reliable message delivery.
- Low-Latency Communication: Robots need to receive instructions and respond quickly, especially in dynamic environments.
- Data Compression and Optimization: Transferring large amounts of data between the LLM and the robot can be resource-intensive.
- Error Handling and Resilience: Communication systems need to be robust and resilient to errors, ensuring that the robot can continue to function even if there are communication disruptions.
The integration of large language models with humanoid robots marks a significant leap forward in artificial intelligence. This fusion has the potential to reshape our world, creating a future where robots are not just tools but collaborators, assistants, and even companions. As we continue to push the boundaries of AI, the agility of using large language models for communication with humanoid robots will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of technology and human interaction.
Agility’s humanoid robots are getting pretty chatty these days, thanks to their integration with large language models. But while they’re busy learning how to hold conversations, the internet’s buzzing with something else entirely – fallout 4 speculation increases after fallout necklace goes on sale. It seems like everyone’s hoping for a new installment in the beloved post-apocalyptic franchise, and a recent necklace release has only fueled the fire.
Maybe Agility’s robots will even make an appearance in the wasteland one day!
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News