Cruise hits the brakes on driverless uaw makes progress and more ev backpedaling – Cruise Hits the Brakes on Driverless, UAW Gains Ground, and More EV Backpedaling takes center stage, a whirlwind of shifts in the automotive industry is shaking things up. From Cruise’s stalled autonomous ambitions to the UAW’s growing unionization efforts and a wave of EV backpedaling, the road ahead for the future of transportation is becoming increasingly uncertain.
Cruise, once a frontrunner in the autonomous driving race, has hit a major snag. Recent setbacks have forced the company to re-evaluate its driverless ambitions, raising questions about its future prospects. Meanwhile, the UAW is making significant strides in its push to unionize the auto industry, potentially reshaping labor relations within the sector. And then there’s the growing trend of major automakers scaling back or altering their electric vehicle plans, fueled by market fluctuations, technological challenges, and economic concerns. These developments paint a complex picture of the evolving automotive landscape, leaving many wondering what the future holds for driverless cars, electric vehicles, and the workers who build them.
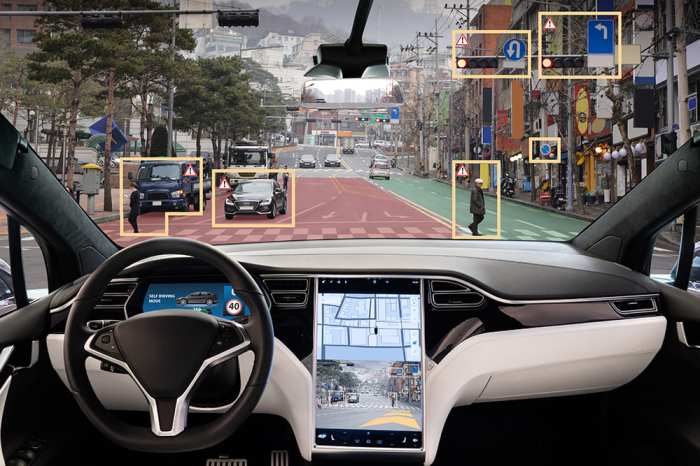
Cruise’s Driverless Ambitions Stall
Cruise, the self-driving car company backed by General Motors, has recently hit a roadblock in its pursuit of fully autonomous driving. After years of aggressive expansion and ambitious goals, the company has made a strategic decision to “hit the brakes” on its driverless ambitions. This shift in strategy has sent ripples through the industry and raised questions about the future of autonomous driving.
Reasons for the Shift
The decision to scale back driverless ambitions is driven by a combination of factors. Cruise has faced several challenges in its pursuit of fully autonomous driving. These include:
- Regulatory hurdles: Obtaining permits and approvals for driverless operations has been a complex and time-consuming process. Regulations vary significantly from city to city, and obtaining the necessary licenses has proven to be a major obstacle.
- Technological limitations: Despite significant advancements, self-driving technology still faces limitations in navigating complex and unpredictable real-world scenarios. Situations involving heavy traffic, adverse weather conditions, and unexpected pedestrian behavior continue to pose challenges for autonomous systems.
- Cost concerns: Developing and deploying driverless technology is a costly endeavor. The need for extensive testing, infrastructure investments, and ongoing maintenance has put a strain on Cruise’s financial resources.
- Public perception: There are ongoing concerns about the safety and reliability of driverless vehicles. Public trust in this technology remains a key factor in its widespread adoption.
UAW Makes Progress in Unionization Efforts: Cruise Hits The Brakes On Driverless Uaw Makes Progress And More Ev Backpedaling
The United Auto Workers (UAW) union has recently achieved notable progress in its efforts to organize workers within the automotive industry, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) sector. These advancements are significant, as they could reshape labor relations in a rapidly evolving industry.
Impact of Unionization
The UAW’s success in organizing EV workers could have a significant impact on the future of labor relations in the automotive industry. Here’s why:
* Improved Working Conditions: Unions typically advocate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions for their members. This could lead to a more attractive work environment for EV workers, potentially reducing turnover and increasing worker satisfaction.
* Increased Job Security: Unionization often brings with it greater job security for workers. This can be particularly important in a rapidly evolving industry like EV manufacturing, where technological advancements and changing market demands can lead to job uncertainty.
* Greater Influence on Industry Practices: Unions can exert influence on industry practices, potentially shaping issues such as safety standards, environmental regulations, and worker training programs. This could lead to a more sustainable and equitable EV manufacturing sector.
Challenges and Opportunities
The UAW faces both challenges and opportunities as it continues to push for unionization in the EV sector.
* Challenges:
* Anti-Union Sentiment: Some employers may resist unionization efforts, potentially leading to legal battles and contentious negotiations.
* Rapid Technological Change: The rapid pace of innovation in the EV industry could make it difficult for unions to keep up with evolving technologies and workforce needs.
* Geographic Dispersion: EV manufacturing is often geographically dispersed, making it challenging for unions to organize workers across multiple locations.
* Opportunities:
* Growing EV Market: The rapid growth of the EV market creates a large potential workforce that unions can target for organization.
* Public Support for Unions: Public support for unions is generally high, particularly among younger generations who are more likely to support labor rights.
* Alliance with Other Labor Groups: The UAW can collaborate with other labor groups to create a united front in advocating for worker rights in the EV sector.
Electric Vehicle Backpedaling
The automotive industry, once seemingly on a headlong rush towards an electric future, is experiencing a wave of recalibration. Major automakers are scaling back or adjusting their EV plans, prompting speculation about a shift in the industry’s trajectory. This “backpedaling” on EV commitments raises questions about the future of electric vehicles and the factors driving this change.
Reasons for EV Backpedaling
The recent adjustments in EV strategies are driven by a complex interplay of market forces, technological challenges, and economic considerations.
- Market Demand Uncertainty: While EV adoption is increasing, the pace of growth has been slower than initially anticipated by some manufacturers. Consumer concerns about range, charging infrastructure, and the higher cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered vehicles have contributed to this slower adoption rate.
- Economic Headwinds: The global economic landscape has shifted significantly in recent years, with rising inflation, supply chain disruptions, and increased interest rates impacting consumer spending. These economic challenges have led some automakers to prioritize cost-cutting measures, which may involve scaling back EV investments.
- Technological Challenges: Despite significant advancements, EV technology still faces challenges, including battery range, charging time, and battery production costs. Automakers are facing pressure to deliver on consumer expectations for long-range EVs with fast charging capabilities while keeping production costs manageable.
- Shifting Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment surrounding EVs is evolving rapidly. Some governments have reduced subsidies for EV purchases, while others have introduced stricter emissions standards for gasoline-powered vehicles, creating a complex and uncertain regulatory landscape for automakers.
The Future of Autonomous Driving and Electric Vehicles
The intersection of autonomous driving and electric vehicles represents a transformative shift in transportation, promising a future with increased safety, efficiency, and sustainability. While these technologies are still in their early stages of development and adoption, their potential impact on society is undeniable.
Potential Milestones in Autonomous Driving and Electric Vehicle Development and Adoption
The development and adoption of autonomous driving and electric vehicles will likely unfold in a series of stages, each marked by significant advancements and changes in public perception. Here’s a potential timeline of key milestones:
- Near Term (2023-2028): Increased availability of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) in passenger vehicles, including lane-keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and automated parking. Expansion of electric vehicle models and charging infrastructure, with growing consumer adoption in urban areas. Limited deployment of autonomous vehicles in controlled environments, such as private shuttles and ride-hailing services in specific cities.
- Mid-Term (2029-2035): Widespread adoption of ADAS features in most new vehicles, leading to a significant reduction in traffic accidents. Continued expansion of electric vehicle models and charging infrastructure, with increasing consumer adoption in suburban and rural areas. Larger-scale deployment of autonomous vehicles in specific geographies, including public transportation systems and ride-hailing services.
- Long Term (2036-2045): Full autonomy becomes a reality, with widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles in various sectors, including personal transportation, public transit, and commercial logistics. Electric vehicles become the dominant mode of transportation, with widespread charging infrastructure and advanced battery technologies. Significant societal and economic shifts, including changes in urban planning, employment, and energy consumption patterns.
Factors Shaping the Future of Autonomous Driving and Electric Vehicles
The future of autonomous driving and electric vehicles will be shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Government Regulations: Governments worldwide are actively developing regulations for autonomous driving and electric vehicles, addressing safety, liability, and infrastructure needs. The clarity and effectiveness of these regulations will significantly influence the pace of adoption. Examples include: the US Department of Transportation’s Automated Driving Systems 4.0, the European Union’s General Safety Regulation for Automated Vehicles, and China’s Guidelines for the Development of Intelligent Connected Vehicles.
- Consumer Demand: The ultimate success of these technologies depends on consumer acceptance and demand. Factors influencing consumer adoption include cost, range, safety, convenience, and environmental impact. Examples include: Tesla’s success in building a large customer base for its electric vehicles, and the growing popularity of ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft, which demonstrate consumer appetite for convenient and affordable transportation options.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and battery performance will drive the development of more advanced and reliable autonomous driving and electric vehicle systems. Examples include: the development of lidar and radar systems with improved range and accuracy, and advancements in battery technology that increase range and reduce charging time.
Benefits and Challenges of Autonomous Driving and Electric Vehicles, Cruise hits the brakes on driverless uaw makes progress and more ev backpedaling
The widespread adoption of autonomous driving and electric vehicles presents both potential benefits and challenges. The following table summarizes some of the key considerations:
| Category | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Reduced traffic accidents due to human error. Improved road safety for vulnerable road users, such as pedestrians and cyclists. | Ensuring the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicle systems. Addressing potential ethical dilemmas in decision-making algorithms. |
| Efficiency | Reduced congestion and improved traffic flow. Increased utilization of vehicles, reducing the need for individual car ownership. | Adapting existing infrastructure to accommodate autonomous vehicles. Managing the transition from human-driven to autonomous vehicles. |
| Sustainability | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions from transportation. Improved air quality in urban areas. | Ensuring the sustainability of battery production and disposal. Addressing potential environmental impacts of increased vehicle use. |
| Accessibility | Increased mobility for individuals with disabilities. Improved transportation options for underserved communities. | Addressing potential disparities in access to autonomous vehicles and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. |
| Economy | Creation of new jobs in the automotive and technology sectors. Increased productivity and economic growth. | Potential job losses in traditional transportation sectors. Addressing the potential impact on insurance and liability models. |
The automotive industry is at a crossroads. The future of autonomous driving, electric vehicles, and the workforce that powers them remains uncertain. While Cruise grapples with its driverless setbacks, the UAW’s unionization efforts gain momentum, and EV backpedaling raises concerns, the industry is forced to navigate a complex landscape of technological advancements, market forces, and evolving consumer demands. The road ahead is filled with both opportunities and challenges, and the direction the industry takes will shape the future of transportation for generations to come.
It seems like the future of self-driving cars is taking a detour, with Cruise hitting the brakes on its driverless ambitions and the UAW making progress in securing worker rights. Meanwhile, the EV revolution is also experiencing some backpedaling. But amidst these shifts, one platform is opening its doors to a wider audience – substack now lets anyone publish posts even if they dont have a newsletter.
This move could provide a fresh platform for independent voices to share their perspectives on the future of technology, including the ever-evolving landscape of autonomous vehicles and electric transportation.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News