Enterprise Tech Generative AI 2023: Revolutionizing Industries is more than just a buzzword. It’s a paradigm shift, a force reshaping how businesses operate and innovate. From crafting personalized marketing campaigns to automating complex tasks, generative AI is weaving itself into the fabric of enterprise tech, promising unprecedented efficiency and a future brimming with possibilities.
Imagine a world where AI can generate realistic product prototypes, write compelling marketing copy, and even analyze financial data with lightning speed. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of generative AI in action. This technology is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s here, and it’s already transforming the way we work, interact, and innovate.
The Rise of Generative AI in Enterprise Tech
Generative AI, a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content like text, images, audio, and video, is rapidly gaining traction in the enterprise tech landscape. Its ability to automate complex tasks, improve efficiency, and unlock new opportunities is driving businesses across various industries to embrace this transformative technology.
Key Drivers of Generative AI Adoption
The increasing adoption of generative AI in enterprise tech is driven by several key factors:
- Advancements in AI technology: Recent breakthroughs in deep learning and natural language processing (NLP) have enabled the development of powerful generative AI models that can produce high-quality outputs across diverse domains.
- Growing availability of data: The abundance of data generated by businesses provides a rich training ground for generative AI models, enabling them to learn patterns and generate outputs that closely resemble real-world data.
- Reduced costs and increased efficiency: Generative AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic initiatives. This leads to significant cost savings and improved efficiency across various business processes.
- Competitive advantage: Companies that leverage generative AI to create innovative products and services can gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Challenges Generative AI Addresses, Enterprise tech generative ai 2023
Generative AI is effectively addressing various challenges faced by businesses across different industries:
- Content creation: Generative AI can automate content creation tasks such as writing marketing copy, generating product descriptions, and creating social media posts. This allows businesses to produce high-quality content at scale, reducing time and effort.
- Customer service: Generative AI-powered chatbots can provide instant responses to customer queries, resolving issues efficiently and improving customer satisfaction. These chatbots can also learn from past interactions and personalize responses, creating a more engaging customer experience.
- Data analysis: Generative AI can help businesses extract insights from large datasets by identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies. This enables businesses to make data-driven decisions and improve their overall performance.
- Product development: Generative AI can assist in designing new products and services by generating innovative ideas and prototypes. This allows businesses to accelerate product development cycles and bring new offerings to market faster.
Examples of Generative AI in Enterprise Tech
Numerous enterprise tech companies are using generative AI to improve their operations and products:
- Google: Google’s AI-powered chatbot, Bard, is being used to generate personalized responses to customer queries and provide assistance with various tasks.
- Microsoft: Microsoft’s DALL-E 2 model is used for generating realistic images from text descriptions, enabling businesses to create marketing materials and product mockups more efficiently.
- Amazon: Amazon uses generative AI to personalize product recommendations for customers, improving the shopping experience and driving sales.
- Netflix: Netflix leverages generative AI to create personalized movie and TV show recommendations for its subscribers, improving engagement and customer satisfaction.
Key Technologies and Trends in Generative AI: Enterprise Tech Generative Ai 2023
Generative AI is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, creating new possibilities across various industries. This section delves into the core technologies powering generative AI and explores emerging trends shaping its future.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
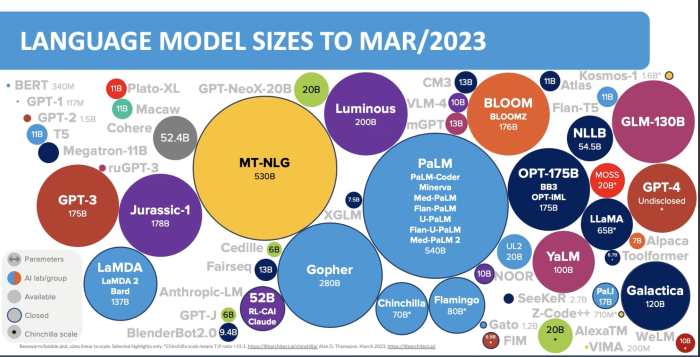
LLMs are a cornerstone of generative AI, particularly in natural language processing (NLP). These models are trained on massive datasets of text and code, enabling them to understand and generate human-like text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way.
“LLMs are trained on massive datasets of text and code, enabling them to understand and generate human-like text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way.”
Examples of LLMs include:
- GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) by OpenAI, renowned for its ability to generate realistic and coherent text.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) by Google, excels in understanding the context of words in a sentence.
- LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) by Google, designed for conversational AI applications.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs are a type of deep learning model that uses two neural networks, a generator and a discriminator, to generate new data that resembles the training data. The generator creates new data, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between real and generated data. This adversarial process leads to the generator becoming increasingly skilled at creating realistic data.
GANs have found applications in:
- Image generation: Creating realistic images of objects, faces, and scenes.
- Video generation: Producing realistic videos, including deepfakes.
- Data augmentation: Generating synthetic data to enhance the training of other machine learning models.
Diffusion Models
Diffusion models are a class of generative models that learn to reverse a noisy process to generate data. They start with a random noise distribution and gradually remove noise until they reach a realistic data distribution.
Diffusion models are particularly effective in:
- Image generation: Generating high-quality images, often surpassing GANs in terms of image realism.
- Text-to-image synthesis: Creating images based on text descriptions.
- Audio generation: Producing high-fidelity audio, such as music and speech.
Transformers
Transformers are a type of neural network architecture that has revolutionized natural language processing. They excel at understanding long-range dependencies in text, making them highly effective for tasks like machine translation, text summarization, and question answering.
Key features of transformers include:
- Attention mechanism: Allows the model to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence.
- Parallel processing: Enables efficient processing of large amounts of data.
- High accuracy: Achieves state-of-the-art results on various NLP tasks.
Multimodal AI
Multimodal AI refers to AI systems that can process and understand information from multiple sources, such as text, images, audio, and video. This capability allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the world and enables AI to perform tasks that require integrating information from different modalities.
Examples of multimodal AI applications include:
- Image captioning: Generating descriptive captions for images.
- Video understanding: Analyzing videos to extract information about objects, events, and emotions.
- Virtual assistants: Integrating speech, text, and visual information to provide a more natural and engaging user experience.
Explainable AI
Explainable AI (XAI) focuses on making AI systems more transparent and understandable. This is crucial for building trust in AI systems and ensuring their responsible use. XAI aims to provide insights into how AI models make decisions, enabling users to understand the reasoning behind the model’s output.
XAI techniques include:
- Feature attribution: Identifying the features that contribute most to a model’s prediction.
- Decision trees: Visualizing the decision-making process in a tree-like structure.
- Rule-based explanations: Explaining predictions based on a set of rules.
Responsible AI
Responsible AI is an ethical framework that guides the development and deployment of AI systems. It emphasizes the importance of fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy. Responsible AI principles aim to ensure that AI systems are used for good and do not perpetuate biases or harm individuals or society.
Key aspects of responsible AI include:
- Bias mitigation: Identifying and addressing biases in AI models.
- Privacy protection: Ensuring the responsible use of personal data.
- Transparency and accountability: Making AI systems transparent and holding developers accountable for their actions.
Challenges and Opportunities in Enterprise Generative AI Adoption
Generative AI, with its ability to create novel content, has the potential to revolutionize how businesses operate. However, implementing this technology in an enterprise setting comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Data Quality and Availability
The performance of generative AI models heavily depends on the quality and quantity of data they are trained on. Organizations need to ensure that their data is accurate, complete, and representative of the tasks they want the AI to perform.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Removing errors, inconsistencies, and redundancies in data is crucial. This process can be time-consuming and require specialized expertise.
- Data Bias and Fairness: Generative AI models can inherit biases from the training data. Organizations must be mindful of potential biases and implement measures to mitigate them. For example, if a model is trained on a dataset that underrepresents certain demographics, it may generate biased outputs.
- Data Privacy and Security: Generative AI models often require access to sensitive data. Organizations must ensure that appropriate security measures are in place to protect this data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Model Bias and Fairness
Generative AI models are susceptible to inheriting biases from the data they are trained on. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Bias Mitigation Techniques: Organizations can implement techniques like data augmentation, adversarial training, and fairness-aware algorithms to minimize bias in their models. These techniques aim to balance the data representation and ensure the model learns from a more diverse and inclusive set of examples.
- Transparency and Explainability: Understanding how a model makes decisions is crucial for identifying and mitigating bias. Organizations need to invest in tools and techniques that provide insights into the model’s internal workings. This transparency allows for the detection and correction of biased outcomes.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Generative AI models can be vulnerable to attacks that compromise their integrity or lead to the leakage of sensitive information.
- Data Poisoning: Malicious actors can inject biased or misleading data into the training dataset, influencing the model’s outputs and potentially leading to harmful consequences.
- Model Evasion: Attackers can craft inputs that fool the model into generating unintended outputs. This can be used to bypass security measures or generate malicious content.
- Data Leakage: Generative AI models may inadvertently leak sensitive information during the training process or when generating outputs. Organizations need to implement robust security measures to prevent such leaks.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating generative AI models into existing enterprise systems can be a complex process that requires careful planning and execution.
- API Integration: Generative AI models are often accessed through APIs. Organizations need to ensure that their systems can seamlessly integrate with these APIs and handle the data flow effectively.
- Workflow Automation: Generative AI models can automate tasks, but integrating them into existing workflows requires careful consideration of how the model’s outputs will be used and managed.
- Data Compatibility: The data used by generative AI models may need to be transformed or formatted to be compatible with existing systems. This can involve data cleansing, transformation, and mapping.
Lack of Skilled Professionals
Implementing and managing generative AI requires specialized skills and expertise. Finding and retaining skilled professionals can be a challenge for many organizations.
- Training and Development: Organizations need to invest in training programs to equip their workforce with the skills necessary to develop, deploy, and manage generative AI models.
- Talent Acquisition: Organizations need to attract and retain talented professionals with expertise in AI, machine learning, and data science. This can involve offering competitive salaries, benefits, and opportunities for professional development.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Generative AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more creative and strategic work.
- Content Creation: Generative AI can create various types of content, including articles, blog posts, social media updates, and marketing materials, significantly reducing the time and effort required for content creation.
- Code Generation: Generative AI models can assist developers in writing code, generating boilerplate code, and suggesting solutions to coding problems, improving coding efficiency and reducing errors.
- Process Optimization: Generative AI can analyze data and identify opportunities to optimize business processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Enhanced Customer Experiences
Generative AI can personalize customer interactions, provide tailored recommendations, and create more engaging experiences.
- Personalized Recommendations: Generative AI can analyze customer data and preferences to provide personalized product recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and driving sales.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Generative AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant customer support, answer questions, and resolve issues, improving customer service efficiency and satisfaction.
- Content Personalization: Generative AI can personalize content, such as marketing emails and website content, based on individual customer preferences, leading to more engaging and effective interactions.
New Revenue Streams
Generative AI can open up new avenues for revenue generation by enabling businesses to create new products and services.
- AI-Powered Products: Businesses can leverage generative AI to create new products and services that leverage AI capabilities, such as personalized content creation tools, AI-powered design platforms, or AI-driven customer service solutions.
- AI-Driven Services: Businesses can offer AI-powered services, such as AI-assisted content creation, AI-driven marketing campaigns, or AI-powered data analysis, generating new revenue streams.
Competitive Advantage
Businesses that adopt generative AI early can gain a competitive advantage by leveraging its capabilities to innovate and differentiate themselves.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Generative AI can accelerate product development and bring new products and services to market faster, giving businesses a competitive edge.
- Improved Customer Engagement: Generative AI can enhance customer experiences, leading to increased customer loyalty and retention, giving businesses a competitive advantage.
- Reduced Costs: Generative AI can automate tasks, reduce operational costs, and improve efficiency, leading to a competitive advantage in terms of cost and pricing.
The Future of Generative AI in Enterprise Tech
Generative AI is poised to revolutionize enterprise technology, transforming how businesses operate and interact with their customers. Its ability to create new content, automate tasks, and enhance decision-making processes presents a vast array of possibilities for innovation and efficiency.
The Evolution of Generative AI Technologies
The rapid advancement of generative AI technologies is driven by breakthroughs in deep learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. This progress will lead to even more powerful and versatile applications in the coming years.
- Enhanced Generative Models: Expect to see the development of more sophisticated generative models capable of producing higher-quality and more nuanced outputs. These models will be trained on larger and more diverse datasets, leading to more realistic and contextually relevant results.
- Multimodal Generative AI: The integration of different AI modalities, such as text, image, and audio, will enable the creation of more immersive and interactive experiences. Imagine AI systems that can generate personalized narratives, interactive product demos, or even realistic virtual assistants.
- Explainable Generative AI: The black-box nature of many generative AI models has raised concerns about transparency and accountability. Future advancements will focus on developing explainable AI systems that can provide insights into the decision-making process, enhancing trust and understanding.
Applications of Generative AI in Enterprise Tech
The potential applications of generative AI in enterprise tech are vast and far-reaching, spanning across various industries and functions.
- Content Creation: Generative AI can automate the creation of marketing materials, product descriptions, website content, and even code. This can free up human resources to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Customer Service: Generative AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized and efficient customer support, resolving queries and issues in real-time.
- Data Analysis and Insights: Generative AI can analyze large datasets to identify patterns, generate insights, and predict future trends, enabling better decision-making and risk management.
- Product Design and Development: Generative AI can assist in product design, prototyping, and optimization, accelerating the development process and creating innovative solutions.
- Personalized Experiences: Generative AI can create personalized experiences for customers, such as tailored product recommendations, customized marketing campaigns, and personalized learning programs.
Ethical and Societal Implications
The widespread adoption of generative AI raises important ethical and societal concerns that need to be addressed proactively.
- Bias and Discrimination: Generative AI models are trained on vast amounts of data, which may contain biases and reflect societal inequalities. It’s crucial to ensure fairness and mitigate potential discriminatory outcomes.
- Job Displacement: The automation capabilities of generative AI may lead to job displacement in certain sectors. Strategies for retraining and upskilling the workforce will be essential to manage this transition.
- Misinformation and Deepfakes: Generative AI can be used to create highly realistic synthetic content, including fake news, images, and videos. This raises concerns about the spread of misinformation and the potential for manipulation.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of generative AI requires access to large datasets, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Robust safeguards and regulations are needed to protect sensitive information.
As generative AI continues to evolve, its impact on enterprise tech will only deepen. Businesses that embrace this technology will unlock a world of possibilities, from boosting productivity to creating entirely new revenue streams. However, navigating the ethical and practical challenges of AI is crucial. By fostering responsible development and prioritizing data privacy, we can harness the transformative power of generative AI to create a future where innovation thrives, and businesses flourish.
Enterprise tech in 2023 is all about generative AI, and that means everyone’s looking for the best way to harness its power. One interesting approach is to bring the cloud on-prem, and oxide is the latest startup to try and bring the power of the cloud on prem. This could be a game-changer for businesses that need the performance and security of on-premises infrastructure while still leveraging the benefits of cloud-based AI.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News