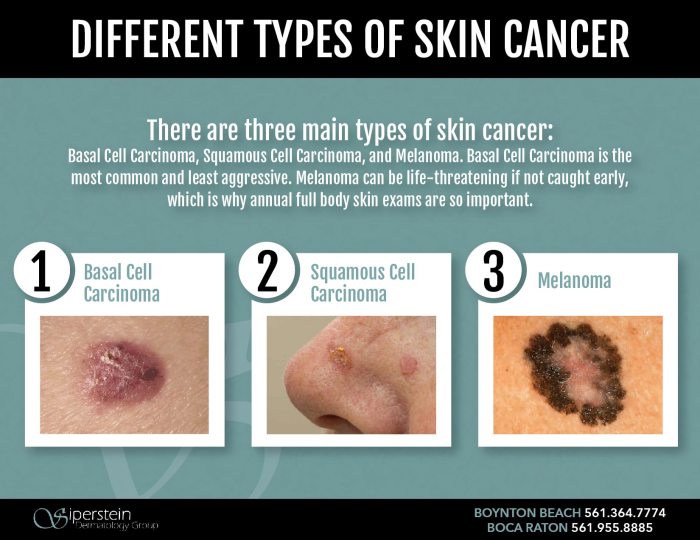
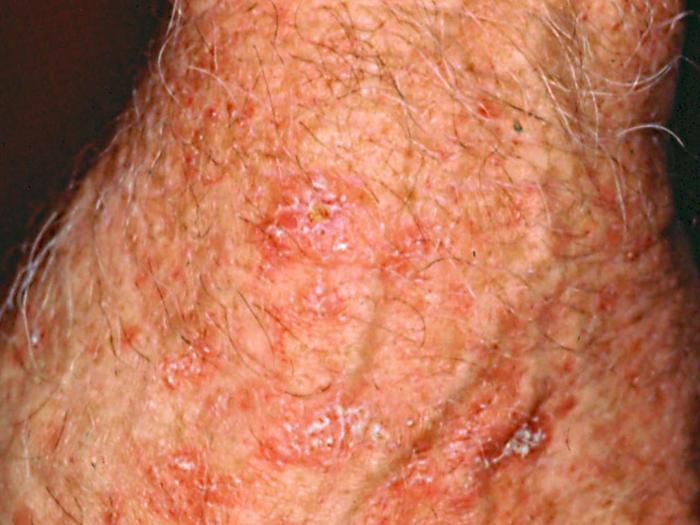
Satellite Technology and Cancer Detection
The potential of satellite technology to revolutionize cancer detection is an exciting area of research. While current technology may not be able to diagnose cancer directly from space, the advancements in satellite imaging offer a unique perspective on early detection and monitoring.
Satellite Imaging Capabilities
Satellite imaging has come a long way, boasting impressive resolution and data acquisition capabilities. Modern satellites can capture images with resolutions down to a few centimeters, allowing for detailed observations of the Earth’s surface. This level of detail is crucial for identifying changes in skin pigmentation and other potential signs of skin cancer. Satellites also have the advantage of covering vast areas quickly, enabling the monitoring of large populations and remote regions.
Potential Benefits of Satellite Imaging for Cancer Detection
The use of satellites for cancer detection presents several potential benefits:
* Accessibility: Satellites can reach remote areas and underserved populations, making early detection services more accessible to individuals who might otherwise lack access to traditional healthcare facilities.
* Coverage: Satellites can monitor large populations simultaneously, potentially identifying individuals at risk of developing skin cancer who might not have sought medical attention.
Comparison of Satellite Imaging and Traditional Methods
Satellite imaging offers unique advantages over traditional methods for cancer detection, but it also has limitations:
- Strengths:
* Wide Coverage: Satellites can cover vast areas, enabling large-scale screening for skin cancer.
* Accessibility: Satellite imaging can reach remote areas, providing access to healthcare for underserved populations.
* Non-Invasive: Satellite imaging is non-invasive, unlike biopsies, which can be painful and require tissue samples. - Limitations:
* Resolution: While satellite resolution is improving, it may not be sufficient for detecting all types of skin cancer.
* Accuracy: Satellite imaging alone may not be accurate enough for diagnosis, requiring further investigation by dermatologists.
* Privacy Concerns: Data privacy concerns must be addressed when using satellite imaging for medical purposes.
Technical Feasibility and Challenges: This Satellites Camera Could Potentially Scan Your Skin For Cancer
The concept of using satellites to scan for skin cancer, while intriguing, presents significant technical hurdles. The technology required to capture high-resolution images of the skin from space, coupled with the challenges of atmospheric interference and body movement, necessitates innovative solutions and careful consideration.
Sensor Types and Data Processing
The success of satellite-based skin cancer detection hinges on the ability to capture high-resolution images of the skin with sufficient detail to identify potential cancerous lesions. This requires specialized sensors capable of detecting subtle variations in skin pigmentation, texture, and morphology.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This technique involves capturing images across a wide range of wavelengths, providing detailed information about the chemical composition of the skin. This can help differentiate between normal and cancerous tissues based on their unique spectral signatures.
- Multispectral Imaging: This approach captures images in multiple specific wavelengths, providing information about different skin features. This can help identify changes in pigmentation, texture, and vascular patterns that may indicate cancer.
- Polarimetric Imaging: This technique measures the polarization of light reflected from the skin, providing information about the surface structure and composition. This can help detect subtle changes in skin texture that may indicate cancerous growth.
The data captured by these sensors needs to be processed using advanced algorithms to identify potential cancerous lesions. These algorithms should be trained on large datasets of skin images, including both normal and cancerous examples, to ensure accurate detection.
Challenges in Image Acquisition
Capturing high-resolution images of the skin from space presents several challenges:
- Atmospheric Distortion: The Earth’s atmosphere can distort and scatter light, reducing the clarity of images. This can be particularly problematic for capturing images of the skin, which requires high resolution and detail.
- Body Movement: Even small movements of the body can blur images, making it difficult to accurately assess skin features. This challenge is exacerbated by the long distances involved in satellite imaging.
- Image Resolution: Achieving the necessary resolution to detect subtle changes in skin features from space requires advanced imaging technology and powerful processing capabilities.
Hypothetical System Architecture
A hypothetical satellite-based skin cancer detection system could be designed with the following components and functionalities:
- Satellite Platform: The satellite would house the imaging sensors, data processing unit, and communication systems. It would be positioned in a low Earth orbit to ensure optimal image acquisition.
- Imaging Sensors: The satellite would be equipped with specialized sensors, such as hyperspectral, multispectral, or polarimetric cameras, to capture high-resolution images of the skin.
- Data Processing Unit: This unit would process the raw image data, applying advanced algorithms to identify potential cancerous lesions. It would also filter out noise and distortions introduced by atmospheric conditions and body movement.
- Ground Station: This station would receive the processed image data from the satellite and transmit it to a medical imaging center for further analysis and interpretation.
- Medical Imaging Center: This center would employ qualified medical professionals to review the images and make a diagnosis based on the identified potential lesions. They would also communicate the findings to the patient and their primary care physician.
This hypothetical system architecture highlights the complex interplay of technology and expertise required to implement a satellite-based skin cancer detection system.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The prospect of using satellite imagery for medical diagnosis, specifically for skin cancer detection, raises significant ethical and privacy concerns. While the potential benefits of early detection are undeniable, careful consideration must be given to the potential misuse or misinterpretation of such sensitive data.
Data Privacy and Informed Consent
The use of satellite imagery for medical diagnosis involves collecting and analyzing personal data, raising crucial questions about data privacy and informed consent. The images captured by satellites could contain sensitive information about individuals, including their location, appearance, and even potentially their health status.
- Data Collection Transparency: It is essential to ensure transparency regarding the collection and use of satellite data for medical purposes. Individuals should be informed about the types of data being collected, the purpose of the collection, and how their data will be used and protected.
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent from individuals before using their satellite data for medical diagnosis is crucial. This process should involve providing clear and understandable information about the potential risks and benefits of participating in such a program.
- Data Security and Anonymization: Robust measures must be in place to protect the privacy and security of collected data. Anonymization techniques should be employed to prevent the identification of individuals from the satellite imagery, while ensuring that the data remains useful for medical analysis.
Potential Benefits and Risks
The potential benefits of early detection through satellite-based skin cancer screening are substantial. Early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes and increase survival rates. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the risks associated with misinterpretation and misuse of satellite data.
- Misinterpretation of Data: Satellite imagery may not always provide a clear and accurate picture of skin lesions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis or unnecessary interventions.
- False Positives and Negatives: The sensitivity and specificity of the technology must be carefully evaluated to minimize false positives and negatives, which could lead to unnecessary anxiety or delayed diagnosis, respectively.
- Potential for Misuse: The data collected from satellite imagery could be misused for purposes other than medical diagnosis, potentially leading to discrimination or privacy violations.
Guidelines for Responsible Data Collection and Use, This satellites camera could potentially scan your skin for cancer
To address the ethical and privacy concerns surrounding satellite-based skin cancer detection, a set of guidelines for responsible data collection and use is essential. These guidelines should encompass:
- Transparency and Informed Consent: Clearly inform individuals about the purpose, scope, and risks associated with using satellite imagery for medical diagnosis, obtaining informed consent before collecting and using their data.
- Data Security and Anonymization: Implement robust data security measures to protect the confidentiality and integrity of collected data. Anonymization techniques should be employed to prevent the identification of individuals from the imagery.
- Accuracy and Validation: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technology by conducting rigorous testing and validation studies. The technology should be able to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions with high accuracy.
- Ethical Oversight: Establish an independent ethical review board to oversee the development and implementation of the program, ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines and data privacy regulations.
This satellites camera could potentially scan your skin for cancer – The idea of using satellites to detect skin cancer is still in its early stages, but the potential is undeniable. While there are technical hurdles and ethical concerns to overcome, the possibility of early detection and improved accessibility for skin cancer screening is a game-changer. Imagine a future where satellites act as our guardians, watching over our health from above. It might be a while before this futuristic vision becomes a reality, but the journey is certainly worth watching.
Imagine a future where a satellite orbiting Earth could scan your skin for cancer. While that might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, it’s actually a real possibility being explored by researchers. And while we’re dreaming about the future, Apple is rumored to be refreshing the iPad Mini with an A8 processor , which could make it a powerful tool for accessing and analyzing this kind of cutting-edge medical technology.
Who knows, maybe one day you’ll be able to use your iPad Mini to check for skin cancer, right from your own home.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News