Windows 10 Minimum Hardware Requirements Overview
Before diving into the world of Windows 10, it’s crucial to understand the minimum hardware requirements. Knowing these requirements helps ensure a smooth and efficient operating experience. If your computer doesn’t meet the minimum specs, you might encounter performance issues, crashes, or even incompatibility with certain features.
Minimum Hardware Requirements for Windows 10
Microsoft has officially Artikeld the minimum hardware requirements for running Windows 10. These specifications represent the bare minimum needed for the operating system to function.
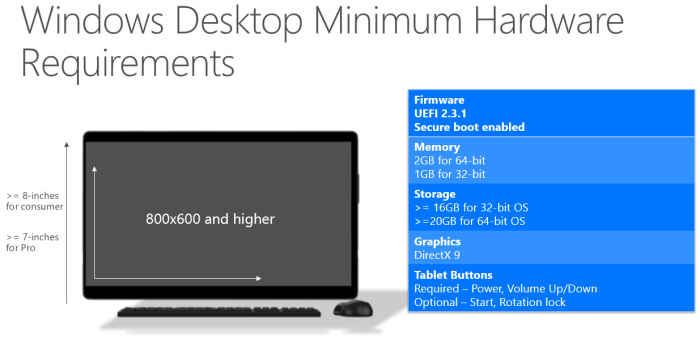
- Processor: 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster processor with 2 cores
- RAM: 1 gigabyte (GB) for 32-bit or 2 GB for 64-bit
- Hard disk space: 16 GB for 32-bit or 20 GB for 64-bit
- Graphics card: DirectX 9 or later with WDDM 1.0 driver
- Display: 800 x 600 resolution
Implications of Running Windows 10 on Minimum Requirements
While your computer might technically run Windows 10 on minimum requirements, it’s important to consider the implications. Running Windows 10 on a system that barely meets the minimum specs will likely result in a subpar user experience.
- Slow performance: The computer might struggle to keep up with basic tasks, leading to lag and sluggish responsiveness.
- Frequent crashes: Insufficient resources can lead to system crashes and instability, disrupting your workflow.
- Limited functionality: Some features and applications might not function properly or be entirely unavailable.
- Security risks: Older hardware might lack the latest security features, making your system vulnerable to threats.
Processor (CPU) Requirements: Windows 10 Minimum Hardware Requirements Revealed
Windows 10 has minimum processor requirements to ensure a smooth and functional user experience. The processor, or CPU, is the brain of your computer, responsible for handling all the calculations and tasks. While you can technically run Windows 10 on a processor that barely meets the minimum requirements, you might experience slow performance and frequent lag.
The recommended processor is designed to provide a more fluid and responsive experience, allowing you to run multiple applications and tasks without experiencing noticeable slowdowns.
Minimum Processor Requirements
The minimum processor requirement for Windows 10 is a 1 GHz processor with at least two cores. This means that the processor must be able to execute at least one billion instructions per second and have at least two separate processing units. This is sufficient for basic tasks such as browsing the web, checking emails, and using basic office applications. However, it may not be enough for more demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, or running multiple programs simultaneously.
Performance Difference Between Minimum and Recommended CPUs
Running Windows 10 on a minimum CPU will result in a noticeable performance difference compared to using a recommended CPU. The minimum CPU might struggle to handle demanding tasks, resulting in slow loading times, lagging applications, and a generally sluggish user experience.
On the other hand, a recommended CPU will be able to handle demanding tasks with ease, providing a smoother and more responsive experience. This is especially noticeable when running multiple applications simultaneously or performing tasks that require significant processing power.
Specific Processor Models That Meet the Minimum Requirements, Windows 10 minimum hardware requirements revealed
There are many different processor models that meet the minimum requirements for Windows 10. Some examples include:
- Intel Celeron processors: These are entry-level processors that offer basic performance at an affordable price. They are suitable for basic tasks like browsing the web and checking emails, but they may struggle with more demanding tasks.
- AMD Athlon processors: Similar to Intel Celeron processors, AMD Athlon processors are also entry-level processors that offer basic performance at an affordable price. They are suitable for basic tasks, but they may struggle with more demanding tasks.
- Intel Pentium processors: These processors offer slightly better performance than Celeron processors, making them suitable for tasks like light gaming and video editing. They are a good option for users who need a bit more performance than what a Celeron processor can offer.
Each of these processor models has its own advantages and disadvantages.
For example, Intel Celeron processors are known for their low power consumption, while AMD Athlon processors are known for their value for money. Intel Pentium processors offer a good balance of performance and price.
Ultimately, the best processor for you will depend on your individual needs and budget.
Memory (RAM) Requirements
Windows 10, like any operating system, requires a certain amount of RAM to function smoothly. The minimum RAM requirement ensures that the system can handle basic tasks and run essential processes. However, more RAM is generally better, as it allows you to run more applications simultaneously without performance degradation.
RAM Impact on Windows 10 Performance
Insufficient RAM can significantly impact Windows 10’s performance. When your system runs out of RAM, it starts using your hard drive as temporary storage, a process called “paging.” This is much slower than accessing RAM, leading to noticeable slowdowns and sluggishness. You might experience frequent freezes, delays in launching applications, and overall system instability.
Recommended RAM Amounts for Various Usage Scenarios
Here’s a breakdown of recommended RAM amounts based on different usage scenarios:
Basic Browsing
For basic tasks like browsing the web, checking emails, and light document editing, 4GB of RAM is usually sufficient.
Multitasking
If you plan to run multiple applications simultaneously, such as browsing the web, editing documents, and streaming videos, 8GB of RAM is recommended. This ensures that all your programs have enough memory to run smoothly without impacting each other’s performance.
Gaming
For gaming, especially modern AAA titles, at least 16GB of RAM is highly recommended. Games often demand a lot of memory to store textures, models, and other assets, and having sufficient RAM helps prevent stuttering and lag.
Storage (Hard Drive) Requirements
To install Windows 10, you need a minimum of 16GB of free storage space on your hard drive. However, this is just the bare minimum for a basic installation. For a more comfortable experience with all the features and apps you might want, you’ll likely need more storage. The amount of storage you need depends on what you plan to use your computer for, but 64GB or more is a good starting point for most users.
Types of Storage
The type of storage you have also impacts Windows 10 performance. There are two main types of storage: HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive).
- HDD: HDDs are the traditional type of storage, using spinning platters to store data. They are generally cheaper than SSDs, but they are also slower.
- SSD: SSDs use flash memory, which is much faster than spinning platters. This means that Windows 10 will load and run much faster on an SSD compared to an HDD. SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs, but the performance difference is significant.
Managing Storage Space
To avoid reaching the minimum storage requirement, you can use several methods to manage storage space on your Windows 10 system.
- Delete unnecessary files: Regularly check your Downloads folder and remove files you no longer need. You can also use the Disk Cleanup tool to remove temporary files and other unnecessary data.
- Move files to external storage: If you have large files like photos or videos, consider moving them to an external hard drive or cloud storage service. This will free up space on your internal drive.
- Uninstall unused apps: Review the apps installed on your system and uninstall any you don’t use. You can find a list of installed apps in the Settings app (Settings > Apps > Apps & features).
- Adjust system settings: Windows 10 has various settings that can help manage storage space. For example, you can change the location where new files are saved or adjust the frequency of system backups.
Graphics (GPU) Requirements
Windows 10 has a minimum graphics card requirement, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance. The graphics card, or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), plays a crucial role in visual tasks and gaming. It handles the rendering of images, videos, and animations, contributing significantly to the overall visual experience on your computer.
Graphics Card Requirements for Different Uses
The graphics card requirements for Windows 10 vary based on your intended use. For basic tasks like browsing the web, word processing, and email, a basic integrated graphics card will suffice. However, for more demanding tasks like casual gaming or video editing, a dedicated graphics card is recommended.
- Basic Tasks: An integrated graphics card, typically found on most motherboards, is sufficient for basic tasks. These cards are generally less powerful than dedicated graphics cards but are sufficient for everyday use. Examples of integrated graphics cards include Intel HD Graphics and AMD Radeon Graphics.
- Casual Gaming: For casual gaming, a dedicated graphics card with at least 1GB of video memory is recommended. This will allow you to run games at lower settings and resolutions. Examples of dedicated graphics cards for casual gaming include NVIDIA GeForce GT 710 and AMD Radeon R7 240.
- Demanding Gaming: For demanding gaming, a dedicated graphics card with at least 4GB of video memory is recommended. This will allow you to run games at higher settings and resolutions. Examples of dedicated graphics cards for demanding gaming include NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1650 and AMD Radeon RX 570.
Display Requirements
To run Windows 10 smoothly, you’ll need a display that meets the minimum requirements. These requirements ensure a clear and functional user experience.
Minimum Display Resolution and Color Depth
Windows 10 requires a minimum display resolution of 1024 x 768 pixels. This resolution allows for comfortable viewing of text and images, along with the display of essential system elements like menus and toolbars.
The minimum color depth required is 8 bits per color channel (24 bits total), which translates to 16.7 million colors. This color depth provides a wide range of colors for a visually appealing experience.
Advantages of Using a Higher Resolution Display
While the minimum requirements ensure basic functionality, using a higher resolution display offers numerous advantages:
* Sharper Images and Text: Higher resolution displays provide more pixels per inch (PPI), resulting in sharper and clearer images and text, enhancing visual clarity and readability.
* Increased Screen Real Estate: A higher resolution display allows you to fit more content on the screen, making multitasking more efficient. You can have multiple windows open simultaneously without feeling cramped.
* Enhanced User Experience: The visual fidelity of a higher resolution display enhances the overall user experience, making the interface more immersive and visually appealing.
Display Resolutions and Suitability for Different Tasks
Here’s a table showcasing various display resolutions and their suitability for different tasks:
| Resolution | Suitability |
|—|—|
| 1024 x 768 | Basic web browsing, document editing, casual gaming |
| 1366 x 768 | Improved web browsing, better multitasking, casual gaming |
| 1920 x 1080 (Full HD) | Excellent for multimedia content, demanding games, professional work |
| 2560 x 1440 (2K) | Immersive gaming, professional design work, demanding multimedia tasks |
| 3840 x 2160 (4K) | Ultra-realistic gaming, professional video editing, high-end multimedia |
Choosing a display resolution depends on your budget, the tasks you plan to perform, and your personal preferences. Higher resolutions offer a more detailed and immersive experience, but come with a higher price tag.
Other Requirements
While the CPU, RAM, storage, and graphics card are the core components for running Windows 10, several other hardware requirements are crucial for a complete and enjoyable user experience. These include sound card, network card, and Bluetooth capabilities, each playing a distinct role in enabling essential features and functionalities.
Sound Card
A sound card is a vital component that enables your computer to produce audio output. Windows 10 relies heavily on sound for various functionalities, such as playing music, watching videos, and communicating through voice calls. A dedicated sound card ensures high-quality audio output, enhancing your overall experience.
A sound card is a vital component that enables your computer to produce audio output. Windows 10 relies heavily on sound for various functionalities, such as playing music, watching videos, and communicating through voice calls.
Network Card
A network card, also known as a network interface card (NIC), facilitates your computer’s connection to the internet and other networks. It allows you to access online resources, download files, stream videos, and communicate with others. A reliable network card is essential for a seamless Windows 10 experience.
A network card, also known as a network interface card (NIC), facilitates your computer’s connection to the internet and other networks. It allows you to access online resources, download files, stream videos, and communicate with others.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology enables wireless communication between your computer and various devices, such as headphones, speakers, and smartphones. It allows you to connect to wireless peripherals, transfer files, and even use your phone as a modem for internet access. Bluetooth capabilities are increasingly essential for a modern Windows 10 experience.
Bluetooth technology enables wireless communication between your computer and various devices, such as headphones, speakers, and smartphones.
Upgrading Existing Systems
If your current computer doesn’t meet the minimum requirements for Windows 10, you might be able to upgrade it to meet the requirements. However, upgrading your system can be a complex process, and it’s essential to consider the potential costs and compatibility issues before making any decisions.
Before upgrading your system, you need to identify the specific hardware components that need to be upgraded. You can do this by checking the system specifications of your current computer and comparing them to the minimum requirements for Windows 10.
Identifying Hardware Components to Upgrade
Identifying the specific hardware components that need to be upgraded is crucial for a successful Windows 10 upgrade. This involves comparing your existing system’s specifications against the minimum requirements.
- Processor (CPU): If your current CPU is older than a few years, it might not meet the minimum requirements. You can check your CPU model and specifications using the Task Manager (press Ctrl+Shift+Esc) or a system information tool like Speccy.
- Memory (RAM): Windows 10 requires at least 4GB of RAM. If your system has less than that, upgrading your RAM is a good idea. You can check your RAM specifications in the Task Manager or System Information.
- Storage (Hard Drive): Windows 10 requires at least 32GB of storage space. If your hard drive is nearing capacity, upgrading to a larger drive might be necessary. You can check your hard drive space in File Explorer.
- Graphics (GPU): While Windows 10 doesn’t have strict GPU requirements, a more powerful GPU can improve performance, especially if you plan on playing games or using graphics-intensive applications. You can check your GPU model and specifications in the Device Manager.
- Display: Windows 10 requires a display with a resolution of at least 1024×768 pixels. If your display is older or has a lower resolution, you might need to upgrade it.
Upgrading Individual Hardware Components
Once you’ve identified the hardware components that need to be upgraded, you can start the process of upgrading them. Upgrading individual components can be a straightforward process, but it’s important to ensure compatibility.
- Processor (CPU): Upgrading your CPU is a complex process that might require replacing your motherboard. This is because different motherboards have different CPU sockets, and not all CPUs are compatible with all motherboards. You need to check your motherboard’s specifications to see which CPUs it supports.
- Memory (RAM): Upgrading your RAM is usually a straightforward process. You can add more RAM modules to your existing ones, or replace them entirely. However, it’s important to ensure that the new RAM modules are compatible with your motherboard and that they have the same speed and type (DDR3, DDR4, etc.).
- Storage (Hard Drive): Upgrading your hard drive is a relatively simple process. You can either replace your existing hard drive with a new one, or add a second hard drive for additional storage space. However, you might need to re-install Windows 10 on the new hard drive.
- Graphics (GPU): Upgrading your GPU is usually a simple process. You can replace your existing GPU with a new one, or add a second GPU for increased graphics performance. However, it’s important to ensure that the new GPU is compatible with your motherboard and power supply.
- Display: Upgrading your display is a simple process. You can simply connect a new display to your computer using the appropriate cable (HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.).
Compatibility Issues
When upgrading individual hardware components, it’s essential to be aware of potential compatibility issues. These issues can arise from differences in specifications, such as the CPU socket, RAM type, or hard drive interface.
- CPU Socket Compatibility: Different motherboards have different CPU sockets, so it’s important to ensure that the new CPU you choose is compatible with your motherboard. Checking your motherboard’s specifications and the CPU’s socket type is crucial.
- RAM Compatibility: Different motherboards support different types of RAM (DDR3, DDR4, etc.) and speeds. It’s essential to ensure that the new RAM modules you choose are compatible with your motherboard. Also, ensure the speed and type match your existing RAM.
- Storage Interface Compatibility: Hard drives come with different interfaces (SATA, NVMe, etc.). Ensure that the new hard drive you choose is compatible with your motherboard and that your motherboard has the necessary ports.
- GPU Compatibility: Different motherboards have different PCI Express (PCIe) slots, which are used to connect GPUs. Ensure that the new GPU you choose is compatible with your motherboard and that it has the appropriate PCIe slot.
Impact of Minimum Requirements on Performance
Running Windows 10 on a system that barely meets the minimum requirements can lead to a frustrating user experience. While the system might technically operate, performance will be significantly impacted, resulting in slow loading times, sluggish responsiveness, and difficulty running demanding applications.
Performance Comparison Between Minimum and Recommended Hardware
To understand the impact of using minimum hardware, it’s helpful to compare performance metrics between systems with minimum and recommended specifications.
Here’s a table illustrating the difference in performance:
| Feature | Minimum Hardware | Recommended Hardware |
|—|—|—|
| Boot Time | 3-5 minutes | 30-60 seconds |
| Application Loading | 1-2 minutes | 10-30 seconds |
| Multitasking | Significant lag, frequent crashes | Smooth, responsive experience |
Potential Limitations and Frustrations
Users experiencing the limitations of minimum hardware might encounter the following frustrations:
* Slow Boot Times: Starting your computer can take several minutes, significantly impacting productivity.
* Laggy Applications: Opening and using programs can feel sluggish, with noticeable delays and stuttering.
* Limited Multitasking: Switching between multiple applications can be a challenge, leading to slowdowns and potential crashes.
* Frequent System Crashes: The system may struggle to handle demanding tasks, resulting in frequent crashes and instability.
* Inability to Run Newer Games or Software: Minimum hardware often lacks the processing power and graphics capabilities to run the latest software or games smoothly.
Future Hardware Trends
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and the hardware requirements for operating systems like Windows 10 are no exception. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR) are driving significant changes in the computing landscape, demanding more powerful hardware to handle increasingly complex tasks. This section explores potential future trends in hardware requirements and the impact of these emerging technologies.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rise of AI and VR is transforming the way we interact with technology, pushing the boundaries of what computers can do. These technologies require significant processing power, memory, and graphics capabilities to deliver seamless experiences.
- AI: AI algorithms require massive datasets and complex computations, demanding powerful processors and ample memory. Machine learning models, used in tasks like image recognition and natural language processing, require significant computational resources to train and run effectively. For example, training a large language model like GPT-3 can require thousands of GPUs working in parallel.
- VR: VR applications require high-performance graphics processing units (GPUs) to render immersive 3D environments in real time. These applications also demand significant memory to store and process complex 3D models and textures. For example, VR games like Half-Life: Alyx require powerful hardware to deliver a smooth and immersive experience.
Evolution of Minimum Hardware Requirements
As technology advances, minimum hardware requirements for operating systems are likely to increase to accommodate the demands of emerging technologies. This trend is already evident with the increasing requirements for Windows 10 updates, which often require more powerful processors and larger amounts of memory.
- Processor (CPU): Future operating systems will likely require faster processors with more cores and threads to handle the complex computations required by AI and VR applications. The focus will shift towards higher clock speeds and more efficient multi-core architectures.
- Memory (RAM): With the increasing demands of AI and VR, operating systems will require more memory to store and process large datasets and complex graphics. We can expect minimum RAM requirements to rise significantly in the coming years.
- Storage (Hard Drive): As AI models and VR applications grow in size, larger storage capacities will be essential. SSDs will become increasingly prevalent as the standard for system storage, offering faster speeds and improved performance.
- Graphics (GPU): VR and AI applications demand powerful GPUs to deliver immersive graphics and accelerate complex computations. Minimum GPU requirements will likely increase, focusing on higher performance and dedicated graphics memory.
Windows 10 minimum hardware requirements revealed – In the world of technology, hardware plays a vital role in shaping your digital experience. Understanding the minimum hardware requirements for Windows 10 is essential for making informed decisions about your computer setup. Whether you’re building a new PC, upgrading an existing one, or simply curious about what’s needed to run the latest operating system, this guide provides the insights you need. Remember, while meeting the minimum requirements will allow you to run Windows 10, investing in hardware that exceeds these minimums will significantly enhance your overall experience.
So, you’re wondering if your old laptop can handle Windows 10? Well, while Microsoft has revealed the minimum hardware requirements, some older devices are still getting some love. Just look at the t mobile htc one m7 lollipop update released , proving that even older phones can get a taste of the latest software. But if you’re hoping to upgrade to Windows 10, make sure your computer meets the specs before diving in.
You don’t want to be stuck with a sluggish system!
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News