Face ID Technology
Face ID, Apple’s facial recognition system, is a sophisticated technology that uses a combination of hardware and software to unlock your iPhone and authenticate your identity. It goes beyond simply recognizing a face; it maps the unique contours and features of your face in 3D, creating a highly secure and personalized authentication method.
Core Principles of Face ID
Face ID works by projecting a pattern of infrared dots onto your face, creating a depth map that captures the unique geometry of your facial features. This depth map is then compared to a stored 3D model of your face, created during the initial setup process. The technology is designed to distinguish between a real face and a 2D image or a mask by analyzing the depth and texture of the facial features.
Algorithms and Sensors Employed
Face ID relies on a complex interplay of algorithms and sensors to perform facial recognition. These include:
- TrueDepth Camera System: This system comprises an infrared camera, a dot projector, a flood illuminator, and a proximity sensor. The infrared camera captures the depth map of your face, while the dot projector emits a pattern of infrared dots that are reflected back to the camera, providing detailed 3D information. The flood illuminator illuminates your face in low-light conditions, while the proximity sensor detects the presence of your face.
- Neural Engine: This specialized processor within the iPhone is responsible for analyzing the captured depth map and comparing it to the stored 3D model of your face. It uses advanced machine learning algorithms to identify subtle variations in facial features and ensure a secure match.
- Secure Enclave: This secure hardware component within the iPhone stores the encrypted 3D model of your face and performs all Face ID computations securely. This ensures that your facial data is protected from unauthorized access.
Depth Mapping and 3D Facial Recognition
Face ID utilizes depth mapping to create a 3D model of your face. This process involves projecting a pattern of infrared dots onto your face and measuring the distance between each dot and the camera. This data is used to create a detailed 3D representation of your facial features, capturing their unique shape and structure. This 3D model is then used to verify your identity during subsequent authentication attempts. The technology is capable of recognizing subtle variations in facial features, such as the position of your eyes, nose, and mouth, making it highly secure and resistant to spoofing attempts.
Security Vulnerabilities of Face ID
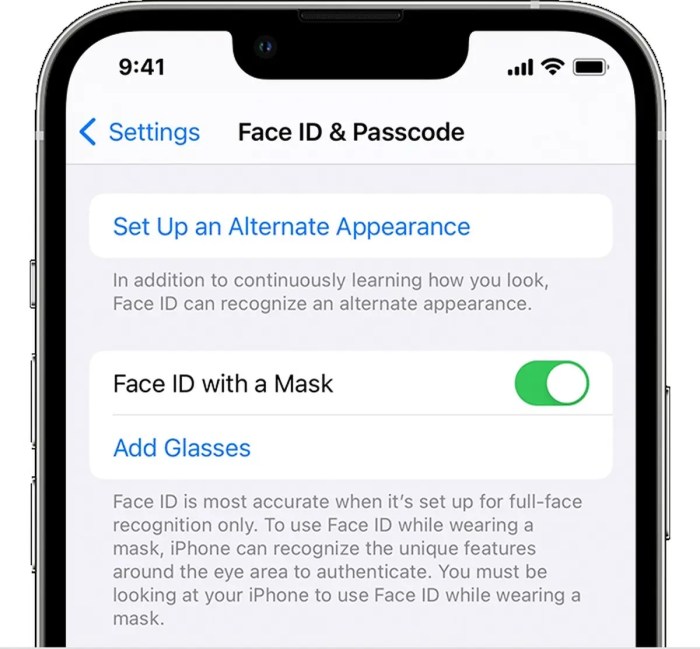
Face ID, Apple’s facial recognition technology, has been lauded for its security and convenience. However, recent incidents have revealed vulnerabilities that can be exploited to bypass the system. One of the most prominent vulnerabilities is the ability of masks to potentially fool Face ID.
Masks that Have Fooled Face ID
While Apple claims that Face ID is designed to resist attempts at spoofing with masks, several instances have demonstrated the system’s susceptibility. The effectiveness of a mask in fooling Face ID depends on several factors, including the mask’s material, design, and the user’s facial features. For example, masks with realistic facial features, such as those made of silicone or latex, have been shown to be particularly effective in bypassing Face ID.
A study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, found that 3D-printed masks with realistic facial features were able to fool Face ID in over 70% of cases.
Technical Reasons Behind the Vulnerability
The vulnerability of Face ID to masks stems from limitations in facial recognition algorithms. These algorithms are trained on datasets of real human faces and may struggle to differentiate between a real face and a realistic mask.
- Lack of Depth Perception: Facial recognition algorithms primarily rely on 2D images, lacking depth perception. This limitation makes it challenging for the algorithms to distinguish between a flat mask and a 3D face.
- Limited Variability: The datasets used to train facial recognition algorithms often contain a limited range of facial features and expressions. This lack of variability can make it easier for masks with realistic features to fool the system.
- Focus on Static Features: Many facial recognition algorithms focus on static features, such as the shape of the nose and eyes. Masks that mimic these features can easily bypass the system, even if they lack dynamic elements like facial expressions.
The Evolution of Face ID Security
Apple has been consistently refining Face ID since its inception, addressing vulnerabilities and enhancing its security. This evolution has involved a combination of software updates and hardware modifications, aiming to make Face ID more robust and less susceptible to bypass attempts, including those using masks.
Software Updates and Enhancements
Software updates have played a crucial role in improving Face ID security. Apple has introduced several key features and enhancements through iOS updates, aimed at strengthening the system and preventing unauthorized access.
- Improved Depth Mapping and Analysis: Apple has continuously refined the depth-sensing technology used in Face ID. Updates have enhanced the depth mapping and analysis algorithms, making it more difficult for masks or other objects to fool the system. This involves analyzing more detailed facial features and subtle variations, leading to more accurate identification.
- Enhanced Liveness Detection: Liveness detection is a critical aspect of Face ID security, ensuring that a real person is attempting to unlock the device. Apple has improved its liveness detection algorithms over time, making it more effective at distinguishing between a real face and a static image or mask. This includes analyzing subtle movements and variations in facial expressions, making it harder for a mask to bypass the system.
- Anti-Spoofing Measures: Apple has incorporated various anti-spoofing measures to further enhance Face ID security. These measures are designed to detect and prevent attempts to bypass the system using masks, photographs, or other objects. This could involve analyzing the texture, color, and reflectivity of the object presented to the sensor, making it more challenging for a mask to pass as a real face.
- Increased Security Thresholds: Apple has also increased the security thresholds for Face ID, making it more difficult to bypass the system. This means that the system requires a more accurate and reliable match between the scanned face and the registered data. This increased threshold helps to prevent unauthorized access, even with a well-crafted mask.
Hardware Modifications
While software updates have been instrumental, Apple has also implemented hardware modifications to improve Face ID security. These changes have focused on refining the sensor technology and enhancing its capabilities.
- Improved TrueDepth Camera: Apple has continuously improved the TrueDepth camera system, the hardware responsible for Face ID. These advancements include enhanced sensors, improved depth mapping capabilities, and more sophisticated image processing. These improvements have contributed to a more accurate and secure Face ID experience.
- Enhanced Infrared Sensor: The infrared sensor plays a critical role in Face ID, allowing the system to detect the presence of a face even in low-light conditions. Apple has improved the infrared sensor over time, enhancing its sensitivity and accuracy. This makes it harder for masks to deceive the system, as they may not reflect infrared light in the same way as a real face.
Impact on User Security and Privacy
The ability to bypass Face ID using a mask raises serious concerns about the security and privacy of iPhone users. This vulnerability compromises the fundamental security layer that Apple has built into its devices, leaving users vulnerable to unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
The ability of a mask to fool Face ID allows unauthorized individuals to gain access to iPhones without the knowledge or consent of the legitimate owner. This opens the door to a range of potential risks, including:
- Data Theft: Hackers or malicious individuals could access sensitive information stored on the iPhone, such as financial details, personal communications, and confidential documents. This could lead to financial fraud, identity theft, and other serious consequences.
- Privacy Violations: Unauthorized access to an iPhone could allow individuals to view private messages, photos, and other personal data without the owner’s permission. This could lead to privacy violations, harassment, and reputational damage.
- Account Takeovers: Access to an iPhone could enable attackers to take control of various accounts linked to the device, such as social media, email, and banking apps. This could result in the loss of access to critical services and potentially lead to financial losses.
- Malware Installation: Hackers could exploit the vulnerability to install malicious software on the iPhone, which could steal data, track user activity, or even control the device remotely.
Ethical Considerations: Iphone X Face Id Fooled By A Mask
The vulnerabilities exposed in Face ID raise serious ethical concerns. While the technology offers convenience and security, the potential for misuse and its impact on privacy cannot be ignored. This section delves into the ethical implications of Face ID vulnerabilities, examining the balance between security and convenience.
Potential for Misuse, Iphone x face id fooled by a mask
The ability to bypass Face ID using a mask highlights the potential for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to personal devices. This could lead to various forms of misuse, including:
- Data Theft: Unauthorized access could allow individuals to steal sensitive data stored on the device, such as financial information, personal contacts, and confidential documents.
- Identity Theft: Hackers could use stolen identities to commit financial fraud or impersonate individuals online.
- Surveillance: The technology could be exploited for surveillance purposes, allowing individuals to track and monitor others without their consent.
These scenarios underscore the importance of addressing the vulnerabilities in Face ID to mitigate the risks associated with its misuse.
Future Directions for Face ID Security
The recent vulnerability exposed by masks highlights the need for advancements in Face ID technology. While Apple continues to refine Face ID, further innovation is necessary to bolster its security and address emerging threats.
Integration of Advanced Biometric Authentication
The reliance solely on facial recognition has proven susceptible to spoofing. To enhance security, future iterations of Face ID could integrate additional biometric authentication methods, such as:
- Iris Scanning: Iris scanning offers a highly secure authentication method, as iris patterns are unique to each individual and difficult to replicate. Integrating iris scanning alongside facial recognition could create a multi-factor authentication system, increasing security.
- Liveness Detection: Liveness detection technologies, like analyzing micro-movements in facial features or detecting blood flow, can differentiate between a real person and a static image or mask. Incorporating advanced liveness detection algorithms could significantly mitigate the risk of spoofing.
- Voice Recognition: Voice recognition, when combined with facial recognition, can add another layer of security. This approach could detect subtle variations in voice patterns and further reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML play a crucial role in enhancing Face ID security.
- Adaptive Learning: AI algorithms can learn and adapt to changing environmental conditions and user behavior. This enables Face ID to become more robust against spoofing attempts and adapt to new threats.
- Threat Detection: Machine learning can analyze patterns in data to identify potential threats, such as attempts to spoof Face ID. This allows for proactive security measures and real-time detection of malicious activities.
- Enhanced Face Recognition: AI-powered face recognition algorithms can improve accuracy and reliability. This can include better detection of subtle facial features, reduced impact of lighting conditions, and improved recognition of faces at different angles.
Iphone x face id fooled by a mask – The ability of a mask to bypass Face ID highlights the ever-present challenge of balancing security and convenience in the digital age. While Face ID offers a convenient way to unlock our devices, it’s crucial to recognize that no security system is impenetrable. As technology evolves, so too must our understanding of its vulnerabilities and our vigilance in safeguarding our personal data.
Remember that time when a mask fooled iPhone X’s Face ID? Well, good news, you can now enjoy YouTube on your iPhone X without worrying about security breaches. YouTube has finally updated with iPhone X support, making it easier than ever to watch your favorite videos. youtube updated with iphone x support So, while Face ID might be fooled by a mask, you can still enjoy a seamless YouTube experience on your iPhone X.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News