Samsung Palm Scanning Patent Overview
Samsung’s palm scanning patent, filed in 2020 and published in 2021, explores a new way to authenticate users on devices using their unique palm vein patterns. The patent details a system that utilizes near-infrared light to capture detailed images of the veins in a user’s palm, converting these images into a digital representation for secure authentication.
Palm Scanning Technology
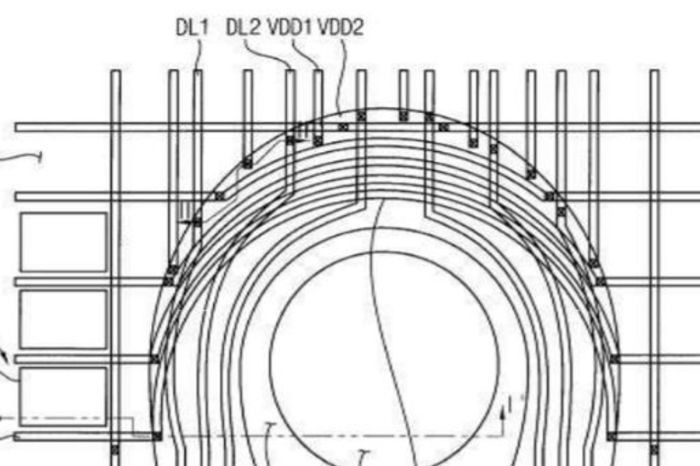
The patent Artikels a process that uses near-infrared light to illuminate the user’s palm, capturing images of the veins. This technology is based on the principle that each individual’s palm vein pattern is unique, much like fingerprints. The captured images are then processed to extract key features of the vein patterns, creating a digital signature that can be used for authentication. This digital signature is stored securely on the device and compared with the signature generated from subsequent scans, enabling secure access and authentication.
Potential Applications in Samsung Products
The patent highlights various applications for this technology across Samsung’s product lineup.
Smartphones and Tablets
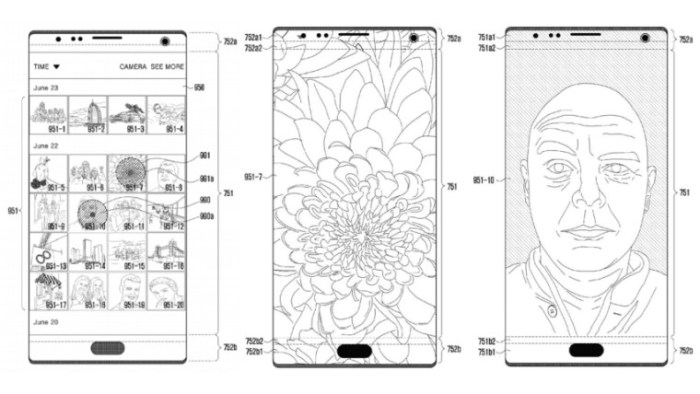
This technology could be integrated into smartphones and tablets, replacing traditional fingerprint scanners or facial recognition systems. Users could unlock their devices, authenticate payments, or access sensitive apps using their palm veins.
Wearables
Smartwatches and fitness trackers could also benefit from this technology. Users could unlock their devices, authorize payments, or track their health data using palm scanning.
Other Devices
Beyond smartphones and wearables, the technology could be implemented in other devices, such as laptops, TVs, and home appliances. This could enhance security, user experience, and convenience across a wide range of devices.
Comparison with Existing Biometric Authentication Methods
Palm scanning, as a relatively new biometric authentication method, stands alongside established technologies like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris scanning. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses compared to these existing methods is crucial for assessing its potential impact on the future of authentication.
Accuracy and Security
Palm scanning, like other biometric authentication methods, relies on unique biological features for identification. The accuracy and security of these methods are paramount, as they directly impact the reliability and trustworthiness of authentication systems.
- Fingerprint Scanning: Fingerprint scanning is a widely adopted and mature technology. Its accuracy is high, particularly for matching fingerprints captured from the same finger. However, fingerprints can be easily replicated, leading to security concerns. Additionally, fingerprints can be damaged or obscured, making authentication difficult.
- Facial Recognition: Facial recognition systems have significantly improved in recent years, achieving high accuracy in controlled environments. However, they can be easily fooled by images, videos, or masks, raising concerns about their security. Additionally, environmental factors like lighting and facial expressions can affect recognition accuracy.
- Iris Scanning: Iris scanning is considered one of the most secure biometric methods due to the unique and complex patterns in the iris. It offers high accuracy and resistance to spoofing attempts. However, the technology can be expensive and requires close proximity to the scanner, limiting its practical applications.
- Palm Scanning: Palm scanning offers a unique combination of accuracy and security. It captures multiple features, including palm geometry, vein patterns, and fingerprints, making it more difficult to spoof. Additionally, palm scanning is less sensitive to environmental factors than facial recognition and can be performed from a distance.
User Experience
The user experience of biometric authentication methods is crucial for their widespread adoption. A user-friendly and seamless authentication process is essential for user satisfaction and acceptance.
- Fingerprint Scanning: Fingerprint scanning is generally considered a convenient and user-friendly method. It is widely used in smartphones and other devices, making it familiar to users. However, some users may find the process uncomfortable or inconvenient, particularly when using fingerprint scanners on less-accessible surfaces.
- Facial Recognition: Facial recognition can be a convenient and hands-free authentication method. However, users may feel uncomfortable with the constant monitoring and potential privacy implications. Additionally, the need for clear facial images and proper lighting can limit its usability in certain situations.
- Iris Scanning: Iris scanning requires close proximity to the scanner, which can be inconvenient and uncomfortable for users. The technology is also not as widely adopted as other biometric methods, making it less familiar to users.
- Palm Scanning: Palm scanning offers a comfortable and convenient user experience. It can be performed from a distance and does not require users to touch the scanner, reducing the risk of contamination or discomfort. Additionally, the technology is less intrusive than other methods, making it more acceptable to users concerned about privacy.
Technical Aspects of Palm Scanning
The Samsung patent delves into the intricate details of a palm scanning system, outlining the components, functionalities, and algorithms that make this biometric authentication method possible. It lays out a comprehensive approach for capturing, analyzing, and verifying palm data, aiming to enhance security and user experience in various applications.
Palm Scanning System Components
The patent describes a palm scanning system consisting of several key components:
- Palm Scanner: This component captures a 3D image of the user’s palm using a depth sensor. This sensor can be a time-of-flight (ToF) camera or a structured light projector, enabling accurate measurements of the palm’s surface.
- Image Processing Unit: This unit processes the captured 3D image, removing noise and artifacts to create a clean and usable representation of the palm.
- Feature Extraction Unit: This unit extracts unique features from the processed palm image, such as the shape, size, and texture of the palm. These features are used to create a unique biometric template for each user.
- Matching Unit: This unit compares the extracted features from the captured palm image with the stored biometric templates in a database. It uses algorithms to determine the likelihood of a match, enabling authentication.
- Database: This component stores the biometric templates of registered users, enabling the matching unit to verify the identity of the user.
Palm Data Capture and Analysis, Samsung palm scanning patent
The process of capturing and analyzing palm data involves several steps:
- Palm Image Acquisition: The user places their palm on a designated area of the scanner. The scanner captures a 3D image of the palm using the depth sensor.
- Image Pre-processing: The captured image is pre-processed to remove noise, artifacts, and variations in lighting conditions. This step ensures the image is clean and suitable for feature extraction.
- Feature Extraction: The pre-processed image is analyzed to extract unique features, such as the shape, size, and texture of the palm. This involves identifying key points, lines, and patterns on the palm surface.
- Biometric Template Creation: The extracted features are used to create a unique biometric template for each user. This template represents the individual’s palm characteristics in a digital format.
- Matching and Verification: When a user attempts to authenticate, the palm scanner captures a new image, and the extracted features are compared with the stored biometric template. The matching unit uses algorithms to determine the likelihood of a match, verifying the user’s identity.
Palm Scanning Algorithms
The patent proposes various algorithms for palm scanning, including:
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA): This algorithm reduces the dimensionality of the feature space by identifying the principal components that capture the most variance in the data. It helps to reduce the computational complexity of the matching process.
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs): This algorithm learns a decision boundary that separates different classes of data, in this case, different palm templates. It is known for its robustness and accuracy in classification tasks.
- Deep Learning: This approach uses artificial neural networks to learn complex patterns and relationships in the palm data. It has shown promising results in image recognition and classification tasks, potentially improving the accuracy of palm scanning.
Challenges and Limitations of Palm Scanning
While palm scanning offers a promising biometric authentication method, it faces several challenges:
- Accuracy in Different Lighting Conditions: The accuracy of palm scanning can be affected by variations in lighting conditions. Strong light can cause glare on the palm, while low light can make it difficult to capture a clear image.
- Vulnerability to Spoofing Attacks: Palm scanning, like other biometric methods, is susceptible to spoofing attacks. A malicious actor could attempt to bypass the system by using a fake palm model or a digital image of a registered user’s palm.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of palm scanning raises privacy concerns, as it involves collecting sensitive biometric data. It is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect this data from unauthorized access and misuse.
- User Acceptance: The acceptance of palm scanning by users depends on factors such as convenience, speed, and perceived security. Some users may have concerns about the use of their biometric data, which could hinder adoption.
Potential Applications and Use Cases: Samsung Palm Scanning Patent
Palm scanning technology holds the potential to revolutionize various industries by offering a secure, convenient, and user-friendly authentication method. Its versatility allows for diverse applications, enhancing security and user experience across various sectors.
Banking
Palm scanning can significantly enhance security in the banking sector by providing a robust and tamper-proof authentication method. It can be integrated into ATMs, bank branches, and mobile banking applications, enabling users to access their accounts securely. For instance, palm scanning can be used to verify identity during account opening, transaction authorization, and cash withdrawal, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, palm scanning can be used to streamline patient identification and access control, ensuring patient privacy and data security. For example, palm scanning can be implemented in hospitals and clinics for patient registration, medication dispensing, and access to medical records. This technology can also be used for secure and efficient data sharing between healthcare providers, enabling seamless patient care.
Retail
Palm scanning can enhance the retail experience by providing a secure and contactless payment method. Customers can use their palm scans to pay for purchases, eliminating the need for physical cards or mobile devices. This technology can also be used for loyalty programs, personalized offers, and inventory management, creating a more efficient and personalized shopping experience.
Other Applications
Beyond these key industries, palm scanning technology has applications in various other sectors, including:
- Access Control: Palm scanning can be used for access control in buildings, offices, and secure areas, replacing traditional key cards or PIN codes with a more secure and user-friendly authentication method.
- Workplace Security: In workplaces, palm scanning can be implemented for employee time tracking, access control, and data security, enhancing productivity and security.
- Law Enforcement: Law enforcement agencies can use palm scanning for criminal identification and verification, aiding in investigations and crime prevention.
- Event Management: Palm scanning can be used for event ticketing, registration, and access control, ensuring a seamless and secure experience for attendees.
Market Analysis and Future Outlook
The biometric authentication market is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for secure and convenient access control solutions across various sectors. Palm scanning technology is poised to become a significant player in this market, offering a unique blend of accuracy, speed, and user-friendliness.
Market Size and Growth Prospects
The global biometric authentication market is expected to reach \$78.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 16.4% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising security concerns, increasing adoption of mobile devices, and the development of advanced biometric technologies. Palm scanning technology is expected to capture a significant share of this market, driven by its advantages over traditional methods.
Key Players in the Biometric Authentication Market
The biometric authentication market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including:
- Fingerprint Scanning: Companies like Qualcomm, Infineon Technologies, and Synaptics are major players in this segment.
- Facial Recognition: Leading players in this space include Apple, Google, and Microsoft.
- Iris Scanning: Companies like IrisGuard and Crossmatch are prominent players in the iris scanning market.
- Voice Recognition: Nuance Communications, Google, and Amazon are key players in voice recognition technology.
- Palm Scanning: Companies like Fujitsu, HID Global, and Samsung are emerging players in the palm scanning market.
Impact of Samsung’s Palm Scanning Patent
Samsung’s palm scanning patent has the potential to significantly impact the competitive landscape and the future of biometric authentication. This patent, which focuses on enhancing the accuracy and speed of palm scanning, could lead to the development of more robust and user-friendly authentication solutions.
- Increased Adoption: Samsung’s patent could encourage wider adoption of palm scanning technology, as it addresses key concerns regarding accuracy and speed.
- Enhanced Security: The patent’s focus on accuracy and speed could lead to more secure authentication solutions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Competitive Advantage: Samsung’s patent could give it a competitive edge in the biometric authentication market, enabling it to develop and deploy innovative palm scanning solutions.
Samsung palm scanning patent – Samsung’s palm scanning patent has the potential to reshape the future of biometric authentication. From unlocking your phone to verifying your identity at the bank, the applications are vast. With its increased security and user-friendliness, this technology could be the key to a more secure and convenient digital world.
Samsung’s palm scanning patent is all about convenience, aiming to make unlocking your phone as easy as a quick wave of your hand. It’s a similar concept to the unlimited ammo mod for GTA 5 PC, which lets you fire away without worrying about reloading. While one focuses on security and the other on gaming, both demonstrate the power of technology to simplify and enhance our experiences.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News