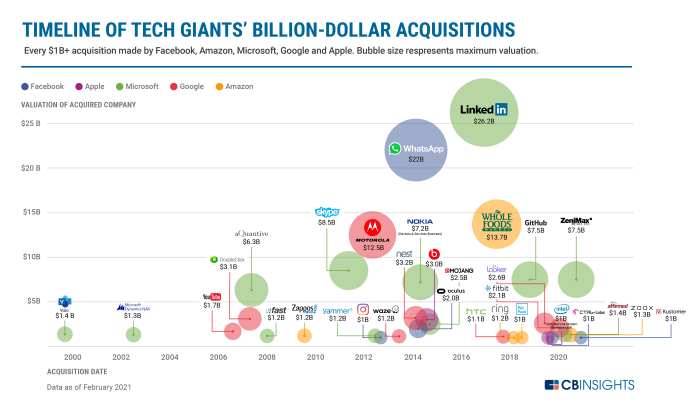
Apple’s Acquisition Strategy in 2013
2013 was a year of significant growth and innovation for Apple, and its acquisition strategy reflected this. The company was looking to expand its reach into new markets and enhance its existing product offerings, particularly in areas like mobile payments, mapping, and music streaming.
Market Conditions and Trends
The tech industry in 2013 was characterized by rapid growth and a surge in mobile computing. The rise of smartphones and tablets was transforming how people interacted with technology, and Apple was at the forefront of this revolution. The company’s focus on user experience and design had made its products highly popular, but the competition was intensifying. Companies like Google, Samsung, and Amazon were making significant investments in mobile technologies, and Apple needed to stay ahead of the curve.
Apple’s Acquisition Strategy in 2013
Apple’s acquisition strategy in 2013 focused on acquiring companies with expertise in areas that were strategically important to the company’s future growth. This included companies specializing in mobile payments, mapping, music streaming, and other areas.
“Apple has a long history of acquiring companies with innovative technologies and talented teams. These acquisitions help us to accelerate our product roadmap and deliver the best possible experience to our customers.” – Tim Cook, Apple CEO
Key Areas of Focus
Apple’s acquisitions in 2013 were concentrated in several key areas:
- Mobile Payments: Apple acquired the mobile payments company, LevelUp, which offered a platform for businesses to accept payments from customers using their mobile devices. This acquisition was a strategic move by Apple to strengthen its position in the rapidly growing mobile payments market.
- Mapping: Apple acquired HopStop, a company specializing in public transit mapping and navigation. This acquisition aimed to enhance Apple Maps, the company’s mapping application, and provide more comprehensive and accurate directions for users.
- Music Streaming: Apple acquired Beats Electronics, a company known for its high-quality headphones and music streaming service. This acquisition gave Apple a significant foothold in the music streaming market and helped the company launch Apple Music, its own music streaming service.
- Other Areas: Apple also acquired companies specializing in other areas, such as PrimeSense, a company known for its 3D motion-sensing technology. This acquisition was a strategic move by Apple to integrate 3D sensing technology into its devices, which later became a key feature of the iPhone X and subsequent models.
The Revealed Acquisitions
In 2013, Apple made several strategic acquisitions, some of which remained undisclosed for years. Two of these acquisitions, however, were revealed, providing valuable insights into Apple’s technological ambitions and product development strategies.
The Acquisitions
Apple’s acquisition of two companies in 2013, namely AuthenTec and PrimeSense, highlighted its focus on enhancing security, user experience, and the integration of advanced technologies.
- AuthenTec was a leading developer of fingerprint sensor technology. Apple acquired AuthenTec in July 2013 for $356 million. AuthenTec’s technology was instrumental in the development of Apple’s Touch ID fingerprint sensor, which debuted in the iPhone 5s. This acquisition signaled Apple’s commitment to improving security and simplifying user authentication on its devices.
- PrimeSense was a pioneer in 3D motion sensing technology. Apple acquired PrimeSense in November 2013 for an undisclosed amount. PrimeSense’s technology, known as “structured light,” enabled devices to accurately map and understand the surrounding environment, laying the groundwork for Apple’s 3D sensing capabilities in later products. This acquisition marked a significant step towards Apple’s foray into the burgeoning field of augmented reality (AR) and 3D imaging.
The Rationale Behind the Acquisitions, Two of apples five mystery acquisitions in 2013 revealed
The acquisition of AuthenTec and PrimeSense reflected Apple’s strategic vision to enhance user experience and introduce innovative technologies across its product portfolio.
- AuthenTec’s fingerprint sensor technology aligned perfectly with Apple’s focus on user security and ease of access. Touch ID, powered by AuthenTec’s technology, revolutionized smartphone security, eliminating the need for complex passwords and offering a seamless user experience. This acquisition demonstrated Apple’s commitment to integrating advanced security features into its devices.
- PrimeSense’s 3D motion sensing technology opened up a new dimension for user interaction and content creation. PrimeSense’s technology enabled devices to understand depth and motion, paving the way for future applications like AR, 3D scanning, and advanced gaming. This acquisition indicated Apple’s foresight in recognizing the potential of emerging technologies and its ambition to lead the way in the evolving landscape of user experience.
Impact and Integration
The acquisitions of Passif Semiconductor and AuthenTec, while initially shrouded in secrecy, have had a profound impact on Apple’s product development and market position. These acquisitions, strategically timed in 2013, allowed Apple to bolster its hardware and software capabilities, further solidifying its position as a leader in the technology industry.
Impact on Product Development
The acquisition of Passif Semiconductor, a company specializing in low-power chip design, significantly impacted Apple’s product development. The integration of Passif’s technology, particularly their expertise in power management, led to the development of more energy-efficient devices. This was crucial for Apple’s mobile products, where battery life is a critical factor for user satisfaction.
The acquired technology from Passif Semiconductor was seamlessly integrated into Apple’s existing product ecosystem. This allowed Apple to reduce power consumption in devices like the iPhone and iPad, extending their battery life and enhancing user experience. This integration also contributed to the development of new features like “Low Power Mode” in iOS, which optimizes power usage in critical situations.
Integration of Acquired Technologies
The acquisition of AuthenTec, a leading developer of fingerprint sensor technology, was instrumental in Apple’s transition to a more secure and user-friendly authentication system. The integration of AuthenTec’s technology into the iPhone 5s marked a significant shift in mobile security. The Touch ID fingerprint sensor, powered by AuthenTec’s technology, revolutionized user authentication by providing a more secure and convenient alternative to passcodes.
Long-Term Implications for Apple’s Growth and Innovation
These acquisitions have had long-term implications for Apple’s future growth and innovation. The acquisition of Passif Semiconductor ensured that Apple remained at the forefront of power efficiency, a crucial aspect of mobile device development. The integration of AuthenTec’s technology solidified Apple’s commitment to user security and privacy, enhancing user trust and satisfaction. These strategic acquisitions allowed Apple to strengthen its core competencies and maintain its position as a technology leader.
Speculation and Analysis of Unrevealed Acquisitions
Apple’s penchant for secrecy is well-documented, and 2013 was no exception. While the company publicly acknowledged a few strategic acquisitions, the veil of secrecy shrouded several others, leaving analysts and industry watchers to speculate on their nature and impact.
Reasons for Confidentiality
Apple’s decision to keep some acquisitions under wraps can be attributed to several factors.
* Strategic Advantage: Maintaining confidentiality can prevent competitors from understanding Apple’s strategic direction and potentially replicating or undermining its efforts.
* Early Stage Technologies: Acquisitions of early-stage companies, often focused on emerging technologies, might be kept secret to protect their intellectual property and allow Apple to integrate them without external scrutiny.
* Market Sensitivity: Some acquisitions, especially those related to sensitive areas like data privacy or security, might be kept confidential to avoid public scrutiny or regulatory hurdles.
* Competitive Landscape: Apple’s competitive landscape is highly dynamic, and keeping acquisitions confidential allows the company to respond to evolving market trends without tipping its hand to rivals.
Potential Areas of Focus
Given Apple’s strategic direction and industry trends in 2013, the unrevealed acquisitions likely focused on several key areas:
* Emerging Technologies: Apple has a history of investing in emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and machine learning (ML).
* Software and Services: Apple’s focus on expanding its software and services ecosystem suggests that some acquisitions might have been related to enhancing its offerings in areas like cloud computing, content streaming, and digital payments.
* Hardware and Devices: Acquisitions in this area could have focused on enhancing existing products or exploring new form factors, particularly in the wearable technology and connected home segments.
Impact on Apple’s Future
The unrevealed acquisitions, while shrouded in secrecy, likely played a significant role in shaping Apple’s future product roadmap and market strategy.
* Product Innovation: These acquisitions could have fueled innovation in areas like AI-powered features, enhanced user experiences, and new hardware functionalities.
* Market Expansion: Acquisitions in emerging technology areas could have paved the way for Apple to enter new markets or expand its presence in existing ones.
* Competitive Advantage: By acquiring strategic assets and talent, Apple could have gained a competitive edge in areas like data analytics, user interface design, and software development.
Apple’s Acquisition Strategy in Historical Context: Two Of Apples Five Mystery Acquisitions In 2013 Revealed
Apple’s history is punctuated by strategic acquisitions that have played a pivotal role in shaping its product portfolio, technological advancements, and overall market dominance. From its early days as a personal computer pioneer to its current position as a global tech behemoth, Apple’s acquisition strategy has evolved in tandem with the ever-changing tech landscape.
Apple’s Acquisition Timeline
Apple’s acquisition history reveals a pattern of strategic acquisitions, each targeting specific technologies, talent, or market segments to enhance its product offerings or expand into new territories.
- 1988: Apple acquired NeXT, a computer company founded by Steve Jobs after his departure from Apple. This acquisition brought back Jobs to Apple and introduced NeXTSTEP, a groundbreaking operating system that later formed the foundation for macOS.
- 1999: Apple acquired Speech Recognition Technologies, a company specializing in voice recognition technology. This acquisition laid the groundwork for Siri, Apple’s virtual assistant, which revolutionized user interaction with devices.
- 2002: Apple acquired PowerBook G4, a company that had developed a unique technology for creating high-performance portable computers. This acquisition led to the development of the PowerBook G4, a popular laptop known for its innovative design and performance.
- 2009: Apple acquired AuthenTec, a company specializing in fingerprint sensors. This acquisition enabled Apple to integrate fingerprint recognition technology into its devices, starting with the iPhone 5s in 2013.
- 2010: Apple acquired Siri, a startup developing a voice-activated personal assistant. This acquisition solidified Apple’s commitment to artificial intelligence and user experience, bringing Siri to the iPhone 4s in 2011.
- 2014: Apple acquired Beats Electronics, a company known for its high-quality headphones and music streaming services. This acquisition strengthened Apple’s position in the audio market and paved the way for Apple Music.
- 2015: Apple acquired Metaio, a company specializing in augmented reality (AR) technology. This acquisition allowed Apple to further explore and develop AR applications for its devices.
- 2016: Apple acquired Turi, a machine learning startup. This acquisition further strengthened Apple’s AI capabilities and contributed to the development of features like personalized recommendations and improved Siri functionality.
- 2017: Apple acquired Shazam, a popular music recognition app. This acquisition integrated Shazam’s technology into Apple Music, enhancing its user experience and music discovery capabilities.
- 2018: Apple acquired FileMaker, a software company specializing in database management. This acquisition aimed to enhance Apple’s productivity offerings and provide a comprehensive suite of business tools.
- 2019: Apple acquired Intel’s modem business, a significant move to gain control over its hardware components and reduce reliance on third-party suppliers.
- 2020: Apple acquired NextVR, a company specializing in virtual reality (VR) content creation and distribution. This acquisition indicated Apple’s growing interest in VR technology and its potential for immersive experiences.
Categorization of Apple’s Acquisitions
Apple’s acquisitions can be categorized based on the industry, technology, and strategic focus they addressed. This categorization helps understand Apple’s overarching strategy and its evolving priorities.
| Industry | Technology | Strategic Focus | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software | Operating Systems | Enhance user experience | NeXT (1988) |
| Hardware | Fingerprint Sensors | Improve security | AuthenTec (2009) |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine Learning | Enhance user experience | Turi (2016) |
| Audio | Music Streaming | Expand into new markets | Beats Electronics (2014) |
| Augmented Reality | AR Technology | Explore new technologies | Metaio (2015) |
| Virtual Reality | VR Content Creation | Develop immersive experiences | NextVR (2020) |
Evolution of Apple’s Acquisition Strategy
Apple’s acquisition strategy has evolved significantly over time, reflecting the company’s changing priorities and the evolving tech landscape.
- Early Years (1980s-1990s): Apple’s early acquisitions focused on acquiring key technologies and talent to strengthen its core product offerings. For instance, the acquisition of NeXT in 1988 brought back Steve Jobs and introduced a groundbreaking operating system.
- Expansion into New Markets (2000s-2010s): As Apple expanded into new markets, its acquisition strategy shifted towards acquiring companies that brought new technologies, services, and market access. This included acquiring Siri in 2010 to develop a voice-activated personal assistant and Beats Electronics in 2014 to enter the audio market.
- Focus on Emerging Technologies (2010s-Present): In recent years, Apple’s acquisition strategy has focused on acquiring companies specializing in emerging technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. These acquisitions reflect Apple’s commitment to innovation and its desire to remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
Two of apples five mystery acquisitions in 2013 revealed – Apple’s strategic acquisitions, even those kept under wraps, reveal a company constantly evolving and seeking to expand its influence. While some acquisitions may not immediately translate into visible products, they often serve as stepping stones for future innovation, bolstering Apple’s technological prowess and market dominance. The two revealed acquisitions offer a glimpse into Apple’s strategic thinking and its ongoing pursuit of technological leadership. The remaining three unrevealed acquisitions continue to fuel speculation and intrigue, hinting at further strategic moves that could reshape Apple’s future landscape.
Remember those five mystery acquisitions Apple made back in 2013? Well, two of them have finally been revealed, and they’re pretty interesting! One was a startup called Passif, which focuses on making music more engaging, and the other was a company called Novauris, which specializes in image processing. This all reminds me of the news about Amazon developing a YouTube competitor , which is also pretty big news in the tech world.
It’s exciting to see these tech giants making moves to expand their reach and innovate in new ways. And who knows, maybe we’ll soon learn about the other three mystery acquisitions Apple made back in 2013.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News