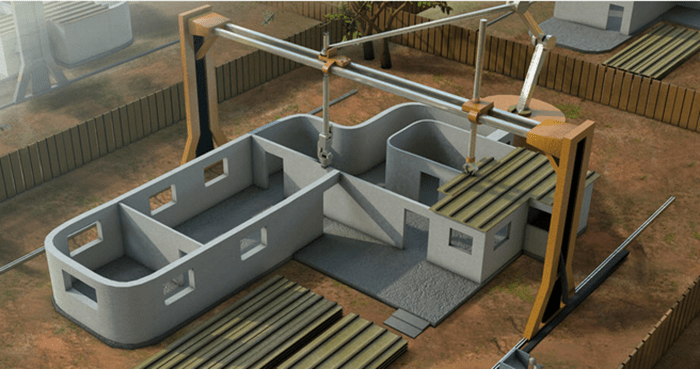
The Rise of 3D Printing in Construction
The construction industry, long known for its traditional methods, is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach, which involves building structures layer by layer using a computer-controlled machine, has the potential to revolutionize the way we design, construct, and inhabit our homes and buildings.
The History of 3D Printing in Construction
The concept of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has been around for decades. The first 3D printed house was built in 2008 by a team of researchers at the University of Southern California. This early prototype showcased the potential of the technology, but it was limited by the size and complexity of the structures that could be printed.
Over the past decade, significant advancements in 3D printing technology have enabled the construction of larger, more complex structures. In 2017, a Dutch company, called “Apis Cor,” successfully 3D printed a 400-square-foot house in just 24 hours. This milestone demonstrated the speed and efficiency of 3D printing for residential construction.
- 1980s: The development of the first 3D printers, primarily for prototyping and industrial applications.
- 2000s: The emergence of 3D printing in construction, with early prototypes and research projects demonstrating the feasibility of the technology.
- 2010s: Significant advancements in 3D printing technology, including the development of larger, more powerful machines and new materials suitable for construction.
- 2020s: The growing adoption of 3D printing in construction, with several companies and organizations working on large-scale projects and commercial applications.
Advantages of 3D Printing for Building Houses, Giant 3d printer can print a house in 24 hours
3D printing offers several advantages over traditional construction methods, making it an attractive option for building houses.
- Speed and Efficiency: 3D printing allows for the rapid construction of houses, significantly reducing the time required compared to traditional methods. This is because the process is automated, eliminating the need for manual labor and reducing the risk of delays.
- Cost-Effectiveness: 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional construction, particularly for smaller structures. This is because the technology reduces the need for labor, materials, and waste.
- Flexibility and Customization: 3D printing allows for greater flexibility in design and customization. Houses can be designed with unique shapes and features, tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the homeowner.
- Reduced Waste: 3D printing uses less material than traditional construction methods, resulting in significantly less waste. This is an important environmental benefit, as it reduces the impact of construction on landfills.
Comparison of Traditional Construction Methods and 3D Printing
While 3D printing offers several advantages, it is important to consider its limitations and compare it to traditional construction methods.
| Feature | Traditional Construction | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower, often subject to delays due to weather conditions and labor availability | Faster, automated process that is less susceptible to delays |
| Cost | Can be expensive, particularly for complex structures | Can be more cost-effective, especially for smaller structures |
| Flexibility | Limited in terms of design and customization | Offers greater flexibility in design and customization |
| Labor | Requires a large workforce, often with specialized skills | Requires fewer workers, reducing labor costs |
| Waste | Generates significant waste, impacting the environment | Generates less waste, promoting sustainability |
Giant 3D Printers
Giant 3D printers, also known as construction 3D printers, are revolutionizing the construction industry by enabling the printing of entire buildings and structures. These behemoths are capable of laying down layer upon layer of building material, creating complex and intricate designs with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
Technology and Design
Giant 3D printers are designed to handle the scale and complexity of construction projects. They typically consist of a large gantry system that moves along a set of rails, carrying a nozzle that extrudes building material. The nozzle is guided by computer-aided design (CAD) models, allowing for precise and intricate designs. The printer’s size and capacity vary depending on the specific project requirements. For example, a printer designed to build a single-family home might have a footprint of several hundred square feet, while a printer capable of building a multi-story building could be even larger.
Materials Used in 3D Printed Houses
The materials used in 3D printed houses are critical to their structural integrity and sustainability. These materials must be strong, durable, and environmentally friendly.
- Concrete: Concrete is a popular material for 3D printed houses due to its strength, affordability, and versatility. It can be reinforced with steel or fiber to improve its structural performance. Concrete can also be mixed with additives to enhance its properties, such as thermal insulation or fire resistance.
- Geopolymers: Geopolymers are a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete. They are made from industrial byproducts, such as fly ash and slag, which reduces the environmental impact of construction. Geopolymers offer similar strength and durability to concrete while being more environmentally friendly.
- Bio-based Materials: Bio-based materials, such as hempcrete and straw bale, are gaining popularity in sustainable construction. These materials are renewable, biodegradable, and have excellent thermal insulation properties. However, they may require additional structural support due to their lower compressive strength compared to concrete.
Challenges and Limitations of Scaling 3D Printing Technology
While 3D printing offers numerous advantages in construction, scaling the technology for large-scale projects presents significant challenges.
- Cost: The initial investment in a giant 3D printer and its associated infrastructure can be substantial. The cost of materials and labor for large-scale projects also needs to be carefully considered.
- Speed: Although 3D printing can significantly reduce construction time, printing large structures can still take several days or even weeks. This can be a limitation for projects with tight deadlines.
- Material Availability: The availability of suitable materials for 3D printing on a large scale can be a challenge. Ensuring consistent quality and supply of materials is crucial for successful construction projects.
- Regulations and Codes: Building regulations and codes need to be adapted to accommodate 3D printed structures. The industry is working to develop standardized testing and certification processes for 3D printed construction.
The 24-Hour House: Giant 3d Printer Can Print A House In 24 Hours
The idea of printing a complete house in just 24 hours seems like something out of a sci-fi movie. But with advancements in 3D printing technology, this futuristic vision is quickly becoming a reality. While the concept is exciting, it’s crucial to delve into the feasibility and implications of such rapid construction.
The Feasibility of Printing a House in 24 Hours
The feasibility of printing a complete house in 24 hours depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the structure, the materials used, and the efficiency of the printing process.
Currently, most 3D-printed houses are relatively small and simple in design. Printing a larger, more complex house within 24 hours would require significant advancements in printing speed and material handling. The complexity of the design, including intricate details and the integration of different materials, would also pose a challenge. Furthermore, the availability and consistency of suitable building materials, such as concrete, would be crucial for large-scale printing.
Benefits of Rapid Construction
The potential benefits of rapid construction using 3D printing are numerous.
* Faster Construction Time: A 24-hour house could significantly reduce construction time compared to traditional methods, allowing for faster completion of projects and quicker occupancy.
* Reduced Labor Costs: 3D printing requires less manual labor, potentially reducing construction costs and making housing more affordable.
* Increased Design Flexibility: 3D printing offers greater design flexibility, allowing for more intricate and customized homes.
* Sustainable Construction: 3D printing can utilize recycled materials and reduce waste, promoting sustainability in construction.
Drawbacks of Rapid Construction
While the benefits of rapid construction are compelling, there are also potential drawbacks to consider.
* Quality and Safety Concerns: The quality and safety of 3D-printed houses need to be rigorously tested and validated. Ensuring structural integrity and meeting safety standards is crucial for long-term durability and occupant safety.
* Limited Material Options: Currently, the range of materials suitable for 3D printing is limited. Expanding material options would be necessary to meet the diverse needs of different climates and building codes.
* Technological Dependence: 3D-printed houses rely heavily on advanced technology. Any technological failures or malfunctions could significantly disrupt construction and lead to delays.
* Potential Job Displacement: The automation of construction tasks through 3D printing could lead to job displacement in the traditional construction industry.
Implications for the Future of Housing and Construction
The development of 3D printing technology for construction has significant implications for the future of housing and the construction industry.
* Increased Affordability: The potential for reduced labor costs and faster construction time could make housing more affordable, addressing the growing housing crisis in many parts of the world.
* Innovative Designs: 3D printing opens up new possibilities for innovative and sustainable designs, allowing for the creation of unique and functional homes.
* Decentralized Construction: 3D printing could facilitate decentralized construction, enabling the construction of homes in remote areas or disaster-stricken regions where traditional methods are difficult or impossible.
* Transformation of the Construction Industry: The adoption of 3D printing technology could fundamentally transform the construction industry, leading to new job opportunities and requiring a skilled workforce with expertise in 3D printing and related technologies.
Applications and Impact of 3D Printed Houses
The potential of 3D printed houses extends beyond mere novelty, promising a revolution in housing solutions across various sectors. This technology can address critical challenges in affordable housing, disaster relief, and remote construction, while simultaneously shaping the future of the construction industry.
Affordable Housing
The ability of 3D printers to construct homes rapidly and efficiently makes them a promising solution for addressing the global housing shortage. The technology can reduce labor costs and material waste, resulting in more affordable housing options.
- In 2019, a non-profit organization in Mexico used a 3D printer to build a 500 square foot house in just 24 hours, demonstrating the technology’s potential for rapid and cost-effective construction.
- The use of 3D printed concrete can also reduce the need for skilled labor, potentially opening up opportunities for local communities to participate in the construction process.
Disaster Relief
3D printed houses offer a rapid and adaptable solution for disaster relief efforts. The ability to print on-site using locally sourced materials allows for quick construction of temporary shelters, reducing reliance on traditional building methods.
- In 2017, after Hurricane Maria devastated Puerto Rico, a team of engineers used a 3D printer to build a prototype house within a week, demonstrating the technology’s potential for rapid construction in disaster zones.
- The use of 3D printing in disaster relief can also reduce the environmental impact of traditional building methods, which often involve the transportation of large quantities of materials.
Remote Areas
3D printed houses can be particularly beneficial in remote areas where traditional construction methods are often difficult and expensive. The ability to print on-site reduces the need for transportation of materials and skilled labor, making construction more feasible in challenging environments.
- In 2019, a company in the Netherlands used a 3D printer to build a house in a remote location, demonstrating the technology’s potential for off-grid construction.
- The use of 3D printing in remote areas can also contribute to the development of sustainable and self-sufficient communities, as it can be used to print structures for water collection, energy generation, and other essential infrastructure.
Social and Economic Impact
The adoption of 3D printed houses has the potential to significantly impact the construction industry and its workforce.
- The technology can lead to a decrease in demand for traditional construction jobs, requiring workers to adapt to new skills and roles.
- However, 3D printing can also create new job opportunities in the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of 3D printing equipment.
Ethical Considerations
While 3D printed houses offer numerous benefits, it is crucial to consider the ethical implications of this technology.
- Accessibility and affordability are critical concerns. Ensuring that 3D printed houses are available to all income levels is essential to avoid exacerbating existing social inequalities.
- Environmental sustainability is another key consideration. The materials used in 3D printing must be environmentally friendly and sourced responsibly to minimize the technology’s impact on the planet.
Giant 3d printer can print a house in 24 hours – The ability to print a house in 24 hours opens up a world of possibilities. It could address the global housing shortage, provide affordable homes for low-income families, and even create sustainable communities in remote areas. While there are still challenges to overcome, the potential of 3D printed houses is undeniable. This technology is poised to transform the way we live and build, and it’s exciting to see what the future holds.
Imagine printing your entire house in a day! That’s the future promised by giant 3D printers, capable of building structures in a fraction of the time it takes traditional methods. While we wait for that future to arrive, there’s another exciting development in the tech world: the Meizu MX4G rumored to come in two variants. Perhaps soon, we’ll be able to print our own phones too! But until then, let’s just marvel at the potential of these groundbreaking technologies.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News