Android m could be debuted at google io 2015 – Android M: Unveiled at Google I/O 2015, Google’s annual developer conference, marked a significant milestone in the evolution of the Android operating system. The anticipation for Android M’s release was palpable, as developers and tech enthusiasts eagerly awaited the latest features and innovations. Google I/O had become a tradition for unveiling new Android versions, with previous releases like Android Ice Cream Sandwich and Jelly Bean making their debut at the event. This year, the spotlight was on Android M, promising a suite of improvements and enhancements designed to elevate the user experience.
Android M arrived with a plethora of exciting features, including a revamped app permissions system, enhanced battery life, and a refined user interface. The new app permissions system gave users greater control over how apps accessed personal data, addressing privacy concerns. Improved battery life extended device usage, while the redesigned user interface offered a cleaner and more intuitive experience. These advancements showcased Google’s commitment to delivering a more secure, efficient, and user-friendly Android experience.
Google I/O 2015
Google I/O, the annual developer conference hosted by Google, is a major event in the tech world. It’s where Google unveils its latest innovations, including new versions of Android, its mobile operating system. The anticipation surrounding Android M at Google I/O 2015 was palpable. Developers and tech enthusiasts eagerly awaited the announcement of the latest iteration of the world’s most popular mobile operating system.
History of Android Releases at Google I/O
Google I/O has historically been the stage for unveiling major Android releases. Here’s a glimpse at some of the notable announcements from past conferences:
- Android 1.0 (2008): The first version of Android was announced at Google I/O 2008. It was a groundbreaking moment, ushering in a new era of mobile computing.
- Android 2.0 (2009): Google I/O 2009 saw the release of Android 2.0, which introduced significant improvements, including a new user interface and enhanced multimedia capabilities.
- Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich (2011): Google I/O 2011 witnessed the unveiling of Android 4.0, a major overhaul that brought a unified user experience across different screen sizes.
- Android 5.0 Lollipop (2014): Google I/O 2014 was the platform for the launch of Android 5.0 Lollipop, which introduced a redesigned user interface, Material Design, and performance enhancements.
Android M
Android M, the successor to Android Lollipop, was unveiled at Google I/O 2015, promising a smoother, more secure, and more efficient mobile experience. While Android Lollipop introduced Material Design and significant performance improvements, Android M built upon these foundations, focusing on enhancing user privacy, improving battery life, and streamlining app permissions.
Key Features and Innovations
Android M introduced several key features and innovations that significantly impacted the user experience. These improvements addressed user pain points, enhanced security, and streamlined app management.
App Permissions
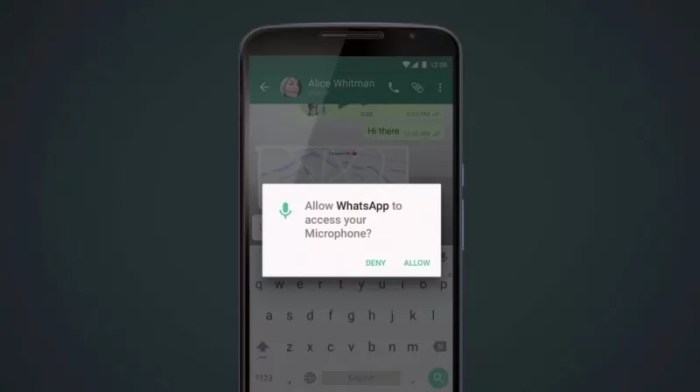
Android M significantly changed the way apps request and manage permissions. Previously, apps could request all permissions upfront, often without clear explanation. Android M introduced a more granular approach, allowing users to grant or deny specific permissions for individual apps.
- Runtime Permissions: Users now grant or deny permissions while the app is running, giving them more control over what data apps can access. This approach provides users with greater transparency and control over their privacy.
- Permission Rationale: Apps are required to provide clear explanations for why they need specific permissions. This ensures users understand the implications of granting access and makes informed decisions.
- Permission Revocation: Users can revoke permissions previously granted to apps, providing ongoing control over their data.
App Standby
Android M introduced App Standby, a feature designed to optimize battery life by managing how apps consume power when they’re not actively being used. This feature significantly reduced background activity, saving battery life and improving device performance.
- Power Management: App Standby categorizes apps based on their usage patterns and limits their background activity when they are not in use. This reduces power consumption and extends battery life.
- User Control: Users can customize the App Standby settings, allowing them to prioritize certain apps and control their power consumption.
- Performance Optimization: By reducing background activity, App Standby improves overall device performance and responsiveness.
Fingerprint Authentication
Android M introduced support for fingerprint authentication, enhancing device security and providing a more convenient way to unlock devices and authorize transactions.
- Improved Security: Fingerprint authentication provides a more secure way to unlock devices compared to traditional PIN or password methods, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Convenience: Fingerprint authentication is a more convenient and user-friendly way to unlock devices, eliminating the need to remember and enter complex passwords.
- Enhanced Privacy: Fingerprint authentication can be used to secure sensitive data, providing an additional layer of privacy protection.
Doze Mode
Android M introduced Doze Mode, a feature that further enhanced battery life by minimizing power consumption when the device is idle. This feature is particularly effective when the device is not in use for extended periods, such as overnight or when it’s in a bag or pocket.
- Power Optimization: Doze Mode significantly reduces power consumption by limiting background activity and network access when the device is idle. This extends battery life and improves device performance.
- Automatic Activation: Doze Mode automatically activates when the device is idle for a certain period, ensuring that power consumption is minimized even when the user is not actively using the device.
- User Control: Users can customize Doze Mode settings to adjust its sensitivity and ensure that essential apps continue to function properly.
Android Pay
Android M introduced Android Pay, a mobile payment platform that allows users to make secure and convenient contactless payments using their Android devices.
- Seamless Payments: Android Pay simplifies the payment process, allowing users to make payments quickly and easily using their Android devices.
- Security and Privacy: Android Pay uses tokenization technology to protect sensitive payment information, ensuring secure transactions.
- Wide Acceptance: Android Pay is accepted at millions of locations worldwide, making it a convenient and widely available payment option.
Other Notable Features
In addition to the core features discussed above, Android M introduced several other improvements and enhancements:
- Direct Share: This feature simplifies sharing content with specific contacts or apps, streamlining the sharing process.
- USB Type-C Support: Android M introduced support for USB Type-C, a new standard for charging and data transfer, offering faster charging speeds and improved connectivity.
- Enhanced Security: Android M included several security enhancements, including improved malware detection and protection against unauthorized access.
Comparison with Android Lollipop
Android M built upon the foundations laid by Android Lollipop, introducing several key improvements and enhancements. While Android Lollipop focused on Material Design and performance enhancements, Android M prioritized user privacy, battery life, and app permissions.
| Feature | Android Lollipop | Android M |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Introduced Material Design, a new visual language for Android | Refined Material Design, enhancing its visual appeal and user experience |
| Performance | Significant performance improvements, including faster app launches and smoother animations | Further optimized performance, with improvements in battery life and background app management |
| Permissions | Apps could request all permissions upfront | Introduced runtime permissions, allowing users to grant or deny permissions while the app is running |
| Battery Life | Improved battery life, but still faced challenges with background app activity | Introduced App Standby and Doze Mode, significantly enhancing battery life and reducing background activity |
| Security | Enhanced security features, but vulnerabilities remained | Introduced fingerprint authentication and other security enhancements, improving device security and user privacy |
| Mobile Payments | Did not include a native mobile payment platform | Introduced Android Pay, a secure and convenient mobile payment platform |
Impact and Reception of Android M
Android M, later known as Android Marshmallow, marked a significant step forward for Google’s mobile operating system. It introduced several notable features and improvements, garnering a mixed reception from users and developers alike. While some lauded its enhancements, others raised concerns about its impact on performance and user experience.
Initial Reception and User Feedback
The initial reception of Android M was largely positive, with many users and tech reviewers praising its new features and design. The introduction of features like Doze mode, App permissions, and Google Now on Tap were particularly well-received. Doze mode, for instance, significantly improved battery life by optimizing power consumption when the device was idle. App permissions offered users greater control over how applications accessed sensitive data, enhancing privacy and security. Google Now on Tap, with its ability to provide contextually relevant information directly from the user’s screen, proved to be a popular and innovative feature.
However, some users reported experiencing performance issues and bugs with the initial release of Android M. The update was known to cause slowdowns and battery drain on certain devices, particularly older models. These issues led to negative feedback from some users, who found the update to be more of a burden than an improvement.
Impact on the Mobile Landscape
Android M had a significant impact on the mobile landscape. The introduction of features like Doze mode and App permissions set a new standard for battery optimization and user privacy. These features were quickly adopted by other mobile operating systems, demonstrating the influence of Android M on the industry. The update also helped to solidify Google’s position as a leader in mobile innovation, pushing the boundaries of what was possible with a mobile operating system.
Influence on Subsequent Android Versions
The features and improvements introduced in Android M laid the groundwork for subsequent Android versions. Doze mode, for example, evolved into more sophisticated power-saving mechanisms in later versions, like Android Nougat’s “Adaptive Battery” feature. Similarly, the granular app permission system introduced in Android M became a cornerstone of Android security, with further refinements in later versions to enhance user control and privacy.
Legacy and Evolution of Android M: Android M Could Be Debuted At Google Io 2015
Android M, officially released as Android 6.0 Marshmallow, was a pivotal release in the Android ecosystem. It introduced several key features and improvements that have shaped the platform’s trajectory for years to come. This section delves into the long-term impact of Android M and explores how its innovations have evolved over time.
Impact on the Android Ecosystem, Android m could be debuted at google io 2015
Android M’s influence on the Android ecosystem is undeniable. It brought about significant changes in areas such as app permissions, power management, and user interface design. These changes have had a lasting impact on how Android users interact with their devices and how developers build apps for the platform.
- App Permissions: Android M introduced granular app permissions, allowing users to control which permissions apps could access. This shift empowered users and enhanced privacy, becoming a cornerstone of modern Android security practices.
- Doze Mode: This feature, introduced in Android M, significantly improved battery life by intelligently managing power consumption when the device is idle. Doze mode has become a vital component of power optimization in later Android versions, extending battery life and improving user experience.
- Android Pay: Android M introduced Android Pay, Google’s mobile payment platform. This feature facilitated contactless payments and spurred the adoption of mobile payments across the Android ecosystem.
Evolution of Android M Features
Android M’s innovations have continued to evolve and expand in subsequent Android releases. The core principles of user control, security, and performance introduced in Android M have been further refined and built upon.
- App Permissions: The granular app permissions introduced in Android M have evolved to provide users with even more control. Later Android versions introduced features like “one-time permissions” and “auto-reset permissions” that enhance user privacy and security.
- Doze Mode: Doze mode has been continuously refined in later Android versions. Features like “App Standby” and “Adaptive Battery” have been added to further optimize power consumption and extend battery life.
- Android Pay: Android Pay has evolved into Google Pay, a comprehensive mobile payment platform that supports various payment methods and features.
Timeline of Android M and its Successors
Android M’s release marked a significant turning point in the Android ecosystem. Here is a timeline illustrating the development and evolution of Android M and its successors:
| Date | Android Version | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| October 2015 | Android 6.0 Marshmallow | App permissions, Doze mode, Android Pay, Now on Tap, fingerprint sensor support |
| August 2016 | Android 7.0 Nougat | Multi-window support, bundled notifications, improved data saver mode |
| August 2017 | Android 8.0 Oreo | Picture-in-picture mode, notification channels, improved performance |
| August 2018 | Android 9.0 Pie | Gesture navigation, adaptive battery, digital wellbeing features |
| September 2019 | Android 10 | Dark mode, gesture navigation, privacy enhancements |
Android M’s debut at Google I/O 2015 marked a pivotal moment in the Android ecosystem. The introduction of key features and innovations addressed user needs and industry trends, shaping the future of mobile operating systems. Its impact extended beyond the immediate release, influencing the development of subsequent Android versions and solidifying its place as a cornerstone of the mobile landscape. Android M’s legacy continues to resonate today, serving as a testament to Google’s dedication to innovation and user-centric design.
While Google gears up to unveil Android M at their annual I/O conference, the world of tech is also buzzing with another groundbreaking development: the world’s first self-driving semi truck hitting the road. It’s a clear sign that the future of technology is moving fast, and we can’t wait to see what Google has in store for us with Android M.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News