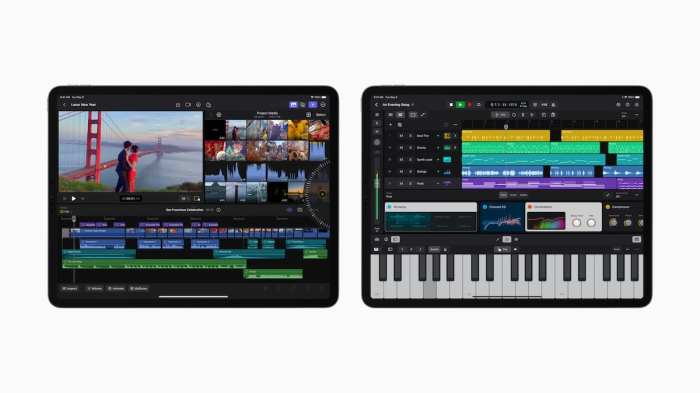
Apple final cut camera – Apple Final Cut Pro, a powerhouse video editing software, has long been a favorite among professionals and enthusiasts alike. But how does it handle camera footage? From importing and managing to editing and exporting, Final Cut Pro offers a comprehensive suite of tools for working with camera footage from a variety of sources.
This guide will explore the intricacies of using Final Cut Pro for camera footage, delving into its compatibility with different camera models and formats, as well as its advanced editing capabilities. We’ll cover everything from importing and organizing your footage to applying professional-grade effects and exporting your final masterpiece.
Apple Final Cut Pro and Camera Compatibility
Final Cut Pro, Apple’s professional video editing software, has a long history of evolving alongside the ever-changing landscape of video technology. Its compatibility with cameras has been a key factor in its success, as filmmakers and editors rely on its ability to seamlessly handle footage from various sources.
History of Camera Support
Final Cut Pro’s journey with camera support has been marked by significant milestones and updates. Early versions primarily supported Apple’s own video formats, but as the video industry evolved, Final Cut Pro expanded its support to include a wider range of codecs and camera models.
- Early Versions (Final Cut Pro 1-3): Primarily focused on Apple’s own video formats like QuickTime and DV, with limited support for third-party cameras.
- Final Cut Pro 4 (2004): Introduced support for the popular H.264 codec, which became widely used in consumer and professional cameras.
- Final Cut Pro 7 (2006): Expanded camera support to include more professional cameras and formats, including RED and Arri cameras.
- Final Cut Pro X (2011): Marked a significant shift, with a focus on a streamlined workflow and support for a wider range of cameras and formats, including ProRes, DNxHD, and more.
- Final Cut Pro (2019): Introduced significant improvements in camera support, including better handling of high-resolution footage and advanced color grading tools.
Current State of Camera Compatibility
Final Cut Pro currently offers excellent compatibility with a vast range of cameras, including DSLRs, mirrorless cameras, and professional cinema cameras.
- DSLRs and Mirrorless Cameras: Final Cut Pro supports popular models from Canon, Nikon, Sony, Panasonic, and more, including those that record in popular codecs like H.264 and H.265.
- Professional Cinema Cameras: Final Cut Pro supports a wide range of professional cinema cameras, including those from RED, Arri, Sony, Blackmagic Design, and others, which record in high-quality formats like ProRes, REDCODE, and ARRIRAW.
Limitations of Camera Support, Apple final cut camera
While Final Cut Pro excels in camera compatibility, it’s essential to be aware of some limitations:
- Codec Limitations: Final Cut Pro may not support every codec available, particularly those that are less common or proprietary to specific camera manufacturers.
- Camera Feature Support: While Final Cut Pro supports a wide range of camera features, some specific features, like advanced metadata or custom color spaces, might not be fully supported or require additional plugins.
- Workflow Considerations: Working with high-resolution footage from certain cameras may require powerful hardware for smooth editing and playback.
Importing and Managing Camera Footage in Final Cut Pro
Importing and managing camera footage in Final Cut Pro is a crucial step in the post-production workflow. It involves bringing your video clips into the Final Cut Pro library, organizing them for easy access, and optimizing them for editing. This process ensures that your footage is readily available for editing, allowing you to efficiently create your final video project.
Importing Camera Footage
Importing footage into Final Cut Pro can be done using various methods, each offering flexibility and convenience based on your needs.
- Dragging and Dropping: This method is simple and intuitive. You can drag and drop your camera footage directly from your computer’s file explorer into the Final Cut Pro library. This allows for quick importing of individual files or entire folders.
- Using the Import Dialog: This method provides more control and options for importing. Access the Import dialog by selecting File > Import from the menu bar. Here, you can choose specific files, select multiple files, and customize import settings.
- Using the Media Browser: The Media Browser is a powerful tool for managing and importing footage. It provides a central location to access all your media, including footage, audio, and images. You can import files directly from the Media Browser by dragging and dropping them into your library.
Organizing and Managing Camera Footage
Final Cut Pro offers robust tools for organizing and managing your camera footage, ensuring efficient workflow and easy access to your assets.
- Creating Libraries: Libraries are the foundation of your Final Cut Pro workflow. They act as containers for your projects, events, and media. You can create multiple libraries to separate projects, organize footage by shoot date, or group related projects together.
- Creating Events: Events are subfolders within libraries that help further organize your footage. You can create events for each shooting day, location, or project phase. This allows you to easily navigate and find specific footage within a library.
- Creating Projects: Projects are the final destination for your edited footage. They contain all the elements of your video, including clips, transitions, effects, and audio. You can create multiple projects within a library to manage different versions of your video or work on multiple projects simultaneously.
Optimizing Imported Camera Footage
Optimizing imported camera footage for editing is crucial for smooth workflow and efficient performance in Final Cut Pro. This process involves transcoding, creating proxies, and managing file sizes.
- Transcoding: Transcoding converts your camera footage into a format that Final Cut Pro can easily process. This can be especially important for footage with high resolution or complex codecs. Transcoding allows for smoother playback and editing, reducing lag and improving overall performance.
- Creating Proxies: Proxies are smaller, lower-resolution versions of your original footage. They are created for efficient editing, especially when working with high-resolution footage or on computers with limited processing power. Proxies allow for faster playback and editing, while still maintaining the quality of your original footage.
- Managing File Sizes: Managing file sizes is essential for maintaining a smooth editing workflow and preventing storage issues. You can manage file sizes by transcoding, creating proxies, or using Final Cut Pro’s built-in optimization features.
Editing Camera Footage in Final Cut Pro
Final Cut Pro is a powerful video editing software that offers a comprehensive set of tools for editing camera footage. Whether you’re a professional videographer or a beginner, Final Cut Pro provides the features and flexibility to create high-quality videos.
Understanding the Editing Tools
Final Cut Pro’s editing tools are designed to make the process intuitive and efficient. The Magnetic Timeline is a key feature that allows you to easily arrange and edit clips without worrying about gaps or overlaps. You can use the trimming tools to adjust the length of clips, and transitions to smoothly connect different scenes. Final Cut Pro also offers a wide range of effects, including color correction, filters, and motion graphics, to enhance your footage and create a unique look.
Trimming and Transitions
Trimming clips is a fundamental editing task, and Final Cut Pro provides various tools to make it precise. You can use the blade tool to split clips, the trim tool to adjust their start and end points, and the ripple tool to move clips without creating gaps. Transitions are used to connect different clips seamlessly. Final Cut Pro offers a variety of transitions, including cross dissolves, fades, and wipes. You can customize the duration and style of transitions to achieve the desired effect.
Effects and Color Correction
Effects can be used to enhance your footage in various ways. Final Cut Pro offers a vast library of effects, including filters, distortions, and motion effects. You can use these effects to add creative flourishes, correct imperfections, or simply enhance the overall look of your video. Color correction is another important aspect of editing. Final Cut Pro provides tools for adjusting the color balance, contrast, and saturation of your footage. You can use these tools to correct color issues, create a specific mood, or enhance the overall visual appeal of your video.
Practical Tips for Effective Editing
Using the Magnetic Timeline
The Magnetic Timeline is a powerful feature that makes editing easier and more efficient. It automatically adjusts the positions of clips as you move them, ensuring that there are no gaps or overlaps. This eliminates the need for manual adjustments, allowing you to focus on the creative aspects of editing.
Working with Clips
Understanding how to work with clips effectively is crucial for efficient editing. Final Cut Pro allows you to create multiple versions of a clip, apply different effects, and even edit within a clip. This flexibility allows you to experiment with different editing styles and find the best way to tell your story.
Applying Different Editing Styles
Final Cut Pro provides a wide range of editing styles to choose from. You can use these styles to create different moods and atmospheres in your video. For example, you can use a fast-paced editing style for action sequences or a slower, more contemplative style for emotional scenes.
Leveraging Final Cut Pro’s Built-in Tools
Stabilizing Shaky Footage
Shaky footage can be distracting and unprofessional. Final Cut Pro’s built-in stabilization tools can help to smooth out shaky footage and create a more polished look. You can adjust the level of stabilization to suit the needs of your footage.
Correcting Color
Color correction is an essential aspect of video editing. Final Cut Pro provides a variety of tools for correcting color issues, including white balance, color balance, and color grading. You can use these tools to ensure that your footage has accurate colors and a consistent look.
Adding Visual Effects
Final Cut Pro offers a wide range of visual effects that can be used to enhance your footage. These effects include filters, distortions, and motion graphics. You can use these effects to add creative flourishes, correct imperfections, or simply enhance the overall look of your video.
Working with Camera Metadata in Final Cut Pro
Camera metadata is a treasure trove of information embedded within your video files, providing valuable insights into how your footage was captured. This data can be a powerful tool for enhancing your editing workflow in Final Cut Pro, offering a wealth of information about your footage and helping you make informed decisions throughout the editing process.
Accessing and Viewing Camera Metadata
Camera metadata is readily accessible within Final Cut Pro, offering a detailed look into the technical aspects of your footage. To access this information, simply select a clip in your timeline and navigate to the Inspector window. The Info tab within the Inspector will display a wealth of metadata, including:
* Camera Model: The specific model of the camera used to capture the footage.
* Lens Used: The lens attached to the camera during recording.
* Exposure Settings: Aperture, shutter speed, and ISO values used to capture the image.
* White Balance: The white balance setting applied during recording.
* Date and Time: The date and time the footage was captured.
* Location: The GPS coordinates of the recording location, if available.
Using Camera Metadata for Editing Tasks
Camera metadata can be leveraged to streamline your editing workflow and enhance the quality of your final product. Here are some examples of how this information can be used:
* Organizing Footage: Metadata can be used to organize your footage effectively. You can use s or filters based on camera model, lens used, or even the date and time of recording to quickly locate specific clips. This makes it easier to manage large libraries of footage and find what you need quickly.
* Creating Color Grades: The exposure settings captured in the metadata can provide valuable insights for creating accurate color grades. By understanding the aperture, shutter speed, and ISO values used, you can recreate the original look of the footage or adjust it to match the desired aesthetic.
* Applying Specific Effects: Metadata can also be used to apply specific effects based on the technical aspects of the footage. For instance, if you know that a particular clip was shot with a specific lens, you can apply a lens correction effect to address any distortion or vignetting.
Exporting and Sharing Camera Footage from Final Cut Pro: Apple Final Cut Camera
Final Cut Pro offers a comprehensive set of export options that enable you to tailor your camera footage for various platforms and purposes. Whether you’re sharing your work online, broadcasting it on television, or archiving it for future use, understanding the different export settings is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Export Options in Final Cut Pro
The export settings in Final Cut Pro allow you to control various aspects of your video output, including the format, resolution, and codec. This flexibility ensures that you can create files suitable for diverse platforms and intended uses.
Video Formats
- QuickTime Movie: A versatile format compatible with various platforms, offering different codecs and resolutions.
- H.264: A widely supported format ideal for online video sharing, including platforms like YouTube and Vimeo.
- ProRes: A high-quality codec commonly used for professional video editing and post-production.
- Apple ProRes RAW: A raw video format preserving the original camera data for maximum flexibility in post-production.
- MPEG-4: A compressed format suitable for DVD authoring and some online platforms.
Resolutions
- Standard Definition (SD): 720 x 480 pixels, suitable for older televisions and some online platforms.
- High Definition (HD): 1280 x 720 pixels (720p) or 1920 x 1080 pixels (1080p), commonly used for television broadcasting and online video sharing.
- Ultra High Definition (UHD): 3840 x 2160 pixels (4K) or higher, offering exceptional detail and clarity for large screens and high-resolution displays.
Codecs
- H.264: A widely supported codec known for its efficient compression and compatibility with various platforms.
- ProRes: A high-quality codec offering excellent image quality and minimal compression artifacts.
- Apple ProRes RAW: A raw video format that preserves the original camera data, providing maximum flexibility in post-production.
Considerations for Choosing Export Settings
When selecting export settings, it’s essential to consider the intended use of your footage. Different platforms and applications have specific requirements for video formats, resolutions, and codecs.
Online Sharing
For online sharing, the most common format is H.264, as it offers a good balance between quality and file size. YouTube and Vimeo recommend using a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels (1080p) for optimal playback.
Broadcast
Television broadcasting typically requires specific formats, resolutions, and codecs. Consult with your broadcaster for their specific requirements.
Archival
When archiving footage for future use, consider using a high-quality codec like ProRes or Apple ProRes RAW to preserve the original camera data.
Exporting Camera Footage from Final Cut Pro
Final Cut Pro provides a user-friendly interface for exporting your edited footage. Follow these steps to export your video for various platforms:
Exporting for Social Media
1. Select “Share” from the menu bar.
2. Choose “Master File” from the “Share” menu.
3. In the “Format” drop-down menu, select “H.264.”
4. Choose the desired resolution (1080p is recommended).
5. Select the appropriate frame rate (24, 25, or 30 frames per second).
6. Click “Next” to proceed to the export settings.
7. Adjust the “Quality” slider to balance file size and quality.
8. Choose a destination folder for your exported file.
9. Click “Export” to start the export process.
Exporting for YouTube
1. Select “Share” from the menu bar.
2. Choose “YouTube” from the “Share” menu.
3. Log in to your YouTube account.
4. Enter the title, description, and tags for your video.
5. Select the desired resolution and frame rate.
6. Click “Next” to proceed to the export settings.
7. Adjust the “Quality” slider to balance file size and quality.
8. Choose a destination folder for your exported file.
9. Click “Export” to start the export process.
Exporting for Professional Productions
1. Select “Share” from the menu bar.
2. Choose “Master File” from the “Share” menu.
3. In the “Format” drop-down menu, select “ProRes” or “Apple ProRes RAW.”
4. Choose the desired resolution and frame rate.
5. Select the appropriate codec for your intended use.
6. Click “Next” to proceed to the export settings.
7. Adjust the “Quality” slider to balance file size and quality.
8. Choose a destination folder for your exported file.
9. Click “Export” to start the export process.
Whether you’re a seasoned filmmaker or just starting out, mastering the art of editing camera footage in Final Cut Pro can elevate your video projects to new heights. With its intuitive interface, powerful features, and seamless workflow, Final Cut Pro empowers you to unleash your creative vision and craft stunning visual stories. So, dive into the world of Final Cut Pro and unlock the potential of your camera footage!
Apple Final Cut Pro has always been a powerhouse for video editing, but with the rise of the Apple Vision Pro, it’s interesting to see how the two technologies will converge. The possibilities for editing and creating immersive content are endless, and the techcrunch minute where the apple vision pro stands now the launch day hype has dropped off provides a glimpse into the future.
Imagine seamlessly editing footage in a virtual environment, or using your hands to manipulate video elements, all within the Vision Pro. The future of video editing is truly exciting, and Apple Final Cut Pro is sure to play a key role in shaping it.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News