Apple patent button less touch id – Apple Patent: Buttonless Touch ID takes center stage, ushering in a new era of fingerprint security. Gone are the days of clunky buttons; instead, Apple has ingeniously integrated Touch ID directly into the display, seamlessly blending security with modern design. This revolutionary technology, a testament to Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation, promises to redefine how we interact with our devices.
The concept is simple: imagine unlocking your iPhone or authorizing a payment with just a touch of your finger, directly on the screen. But the magic lies in the intricate technology behind it. Apple’s patent details a sophisticated sensor embedded beneath the display, capable of accurately detecting and verifying your fingerprint even through the glass. This technology not only enhances security but also streamlines user experience, eliminating the need for physical buttons and offering a more intuitive and elegant interaction.
Apple’s Buttonless Touch ID Technology
Apple’s Touch ID technology, a fingerprint-based authentication system, has revolutionized the way we interact with our devices. Since its introduction in 2013, Touch ID has become an integral part of the Apple ecosystem, providing a secure and convenient way to unlock our iPhones, iPads, and Macs.
Evolution of Touch ID
Touch ID has undergone significant advancements since its debut. Initially, it was implemented using a physical button embedded in the home button of iPhones and iPads. This button housed a fingerprint sensor that scanned and verified a user’s fingerprint. However, the reliance on a physical button posed certain limitations and presented challenges.
Challenges of Traditional Touch ID
The physical button implementation of Touch ID had its drawbacks.
- The button was susceptible to wear and tear, potentially leading to malfunction or failure over time.
- The button’s presence added bulk to the device and limited the overall design flexibility.
- The button could be a point of failure, disrupting the user experience if it became damaged or unresponsive.
Apple’s Buttonless Touch ID Technology
Apple’s buttonless Touch ID technology, introduced with the iPhone X, addressed these limitations by integrating the fingerprint sensor directly into the display. This innovative approach eliminated the need for a physical button, resulting in a more streamlined and aesthetically pleasing design.
Technical Innovations
The implementation of buttonless Touch ID involved several key technical innovations.
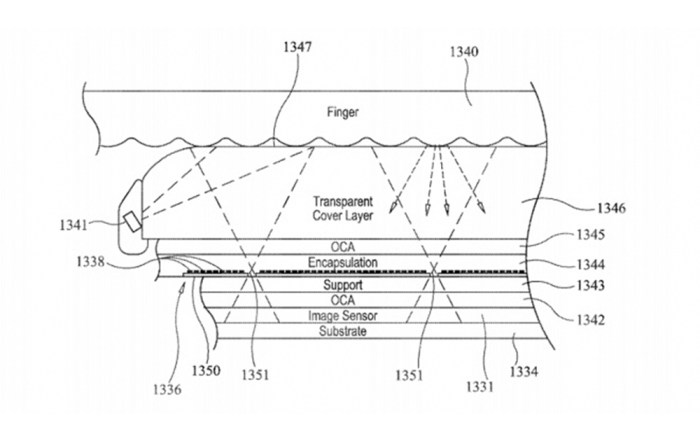
- Optical Fingerprint Sensing: Instead of using a capacitive sensor like previous implementations, buttonless Touch ID utilizes an optical sensor. This sensor emits light that penetrates the display and interacts with the fingerprint ridges, capturing a high-resolution image of the fingerprint.
- Integrated Sensor and Display: The optical sensor is seamlessly integrated into the display, allowing for a flush and uninterrupted surface. This integration requires sophisticated engineering and manufacturing processes to ensure precise alignment and optimal performance.
- Advanced Image Processing: The captured fingerprint image is processed by advanced algorithms that analyze and verify the fingerprint against the stored data. These algorithms are designed to be highly secure and resistant to spoofing attempts.
Technical Aspects of Buttonless Touch ID
Apple’s buttonless Touch ID technology represents a significant leap in biometric authentication, integrating the fingerprint sensor seamlessly beneath the display. This innovation eliminates the need for a physical home button, enhancing the aesthetics and user experience of Apple devices.
Sensor Technology
The buttonless Touch ID sensor relies on a sophisticated capacitive sensing technology. This technology utilizes an array of tiny capacitors beneath the display, capable of detecting subtle changes in capacitance caused by the ridges and valleys of a fingerprint.
Working Principle
When a user places their finger on the display, the sensor’s capacitors measure the capacitance variations between the finger and the sensor. These variations form a unique fingerprint pattern, which is then converted into a digital representation. This digital fingerprint image is compared to the user’s enrolled fingerprints stored in the device’s secure enclave.
Algorithms and Software
The fingerprint recognition and authentication process involves complex algorithms and software. The algorithms analyze the digital fingerprint image, comparing it to the enrolled fingerprints. They use advanced pattern recognition techniques to identify matching points and assess the degree of similarity. This process is highly secure, utilizing sophisticated encryption and authentication protocols to protect user data.
Impact and Applications of Buttonless Touch ID
The elimination of the physical home button has had a profound impact on the design and functionality of Apple devices, paving the way for a more streamlined and immersive user experience. Buttonless Touch ID technology has revolutionized the way users interact with their devices, enhancing security, convenience, and overall usability.
Impact on Design and Functionality
The absence of a physical home button has enabled Apple to create devices with larger displays and slimmer profiles, maximizing screen real estate and enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal. The removal of the button has also allowed for a more seamless and intuitive user interface, with gestures replacing physical button presses for navigation and interaction. This design change has fundamentally altered the way users interact with their Apple devices, leading to a more fluid and responsive experience.
Enhancing User Experience in Various Applications
Buttonless Touch ID has significantly enhanced the user experience across various applications, making interactions more secure, convenient, and intuitive.
Unlocking Devices
Buttonless Touch ID allows users to unlock their devices quickly and securely with a simple touch. This eliminates the need for cumbersome passcodes or complex unlocking procedures, providing a seamless and secure way to access their devices.
Mobile Payments
Buttonless Touch ID has revolutionized mobile payments by enabling secure and convenient transactions with a single touch. Users can authorize payments with Apple Pay using their fingerprint, eliminating the need for physical cards or PINs, and ensuring secure and private transactions.
Secure App Access
Buttonless Touch ID provides an added layer of security for sensitive applications by allowing users to authenticate their identity with a fingerprint scan. This feature protects users’ personal information and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data, enhancing the overall security of their devices.
Potential Future Applications and Advancements
Buttonless Touch ID technology is constantly evolving, with potential future applications and advancements that could further enhance the user experience.
Enhanced Security Features
Future advancements in buttonless Touch ID could incorporate advanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication, to further enhance the security of Apple devices. These features could utilize biometrics like facial recognition or iris scanning in conjunction with fingerprint authentication to create a more robust and secure authentication system.
Improved User Experience
Future iterations of buttonless Touch ID could focus on improving the user experience by enhancing the speed and accuracy of fingerprint recognition. This could involve the development of new sensor technologies or algorithms that can more accurately and quickly identify fingerprints, leading to a smoother and more seamless user experience.
Expanded Applications
Buttonless Touch ID could be expanded to support a wider range of applications beyond device unlocking, mobile payments, and app authentication. For example, it could be integrated with other devices and services, such as smart home systems, wearable technology, and automotive systems, to provide a secure and convenient way to interact with these technologies.
Patents and Intellectual Property: Apple Patent Button Less Touch Id
Apple has been actively securing its buttonless Touch ID technology through a series of patents, demonstrating its commitment to protecting its innovative approach to biometric authentication. These patents cover various aspects of the technology, from the underlying sensor design to the integration with the display and user interface.
The key patents filed by Apple related to buttonless Touch ID technology offer a comprehensive protection strategy for this innovative approach to biometric authentication. These patents cover various aspects of the technology, including the sensor design, display integration, and user interface.
Apple’s patent strategy for buttonless Touch ID can be analyzed by examining the claims and scope of these patents. These patents encompass a wide range of aspects, including:
- Sensor design: Apple has secured patents covering the design and functionality of the capacitive sensor used for fingerprint detection. These patents describe innovative approaches to sensor placement, integration with the display, and the use of advanced algorithms for fingerprint analysis.
- Display integration: Apple has also filed patents relating to the seamless integration of the Touch ID sensor with the display. These patents cover the design of the display itself, ensuring that it allows for accurate fingerprint detection while maintaining a visually appealing and functional user interface.
- User interface: Apple’s patent portfolio also includes patents related to the user interface for buttonless Touch ID. These patents describe how the technology is integrated into the overall user experience, including the methods for prompting users to authenticate, displaying feedback, and handling errors.
These patents play a crucial role in protecting Apple’s intellectual property and safeguarding its investment in buttonless Touch ID technology. By securing these patents, Apple aims to prevent other companies from replicating its innovations and ensure that it retains a competitive edge in the market.
Impact on Industry
Apple’s patent strategy for buttonless Touch ID has significant implications for the development of similar technologies by other companies.
- Competition: The existence of these patents could deter other companies from developing similar technologies, as they may face legal challenges from Apple. This could potentially limit the pace of innovation in the biometric authentication space.
- Licensing: Alternatively, Apple might choose to license its buttonless Touch ID technology to other companies, allowing them to incorporate it into their devices. This could potentially accelerate the adoption of buttonless biometric authentication, but Apple would need to carefully manage licensing terms to ensure that its intellectual property is protected.
The impact of Apple’s patents on the development of similar technologies by other companies will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific claims of the patents, the legal landscape, and the competitive dynamics within the industry.
Apple’s Buttonless Touch ID patent signifies a paradigm shift in the world of biometric authentication. It’s not just about removing buttons; it’s about pushing the boundaries of user experience and security. This technology, with its potential to revolutionize how we interact with devices, could be a game-changer for Apple and the entire tech industry. It’s a glimpse into a future where seamless, secure interactions become the norm, paving the way for a new era of technological advancements.
Apple’s patent for a buttonless Touch ID is a bold move, showcasing their commitment to sleek design and user-friendly technology. While Apple is busy innovating with physical interfaces, it seems like Google is struggling to keep their AI in check, as evidenced by their recent admission of losing control of their image-generating AI. Embarrassing and wrong, Google admits it lost control of image generating AI.
Maybe Apple’s focus on the physical realm is a safer bet, especially if AI is prone to unpredictable behavior.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News