Apple’s Supplier Ecosystem for Face ID in 2018 iPhones
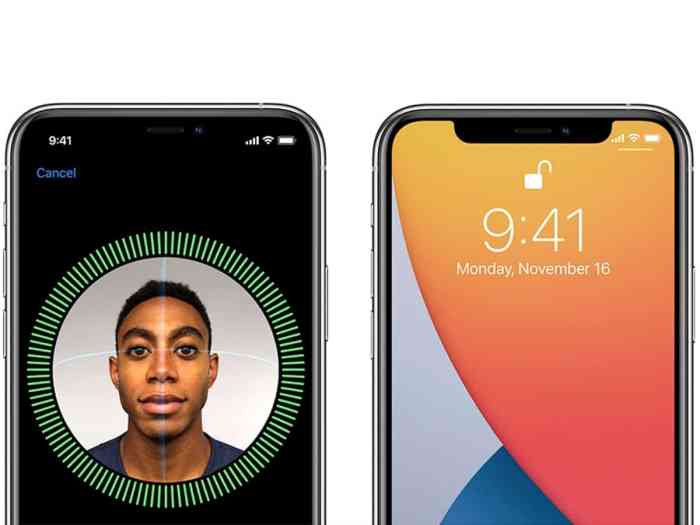
The Face ID feature, introduced in the iPhone X in 2017, revolutionized smartphone security. Apple’s 2018 iPhone models, including the iPhone XS, XS Max, and XR, continued to leverage Face ID, leading to a complex and geographically diverse supplier ecosystem. Understanding this network of suppliers is crucial to appreciating the intricacies of Apple’s product development and manufacturing processes.
Key Suppliers Involved in the Production of Face ID Components
The development and production of Face ID components involve a diverse range of suppliers, each playing a critical role in the supply chain. These suppliers are responsible for providing key components, such as the dot projector, infrared camera, and flood illuminator, which work together to enable Face ID’s facial recognition capabilities.
- Sony: Sony is a prominent supplier of the dot projector, a critical component that projects an array of infrared dots onto the user’s face. This data is then used by the infrared camera to create a 3D map of the face, enabling accurate facial recognition. Sony’s expertise in image sensors and semiconductor technology makes it a key player in the Face ID supply chain.
- Finisar: Finisar, a US-based company, was the initial supplier of the vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) array for the flood illuminator. The flood illuminator provides infrared light to illuminate the user’s face, ensuring accurate data capture in various lighting conditions. Finisar’s VCSEL technology played a crucial role in the development of Face ID.
- Lumentum: Lumentum, another US-based company, subsequently joined the supply chain as an alternative supplier of VCSELs for the flood illuminator. This diversification in the supply chain helps Apple mitigate risks and ensure a steady supply of components.
- AMS: AMS, an Austrian company, supplies the infrared camera used in Face ID. This camera captures the infrared dot pattern projected by the dot projector, providing the necessary data for facial recognition. AMS’s expertise in sensor technology and image processing makes it a valuable partner for Apple.
- Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC): TSMC, a Taiwanese company, is a leading semiconductor foundry. TSMC manufactures the A-series processors used in iPhones, including the processors that power the Face ID algorithms. TSMC’s advanced manufacturing capabilities ensure the high performance and efficiency of the Face ID system.
Geographic Locations of Suppliers and Manufacturing Facilities
The Face ID supply chain spans multiple countries, showcasing the global nature of Apple’s product development and manufacturing.
- Sony: Sony’s manufacturing facilities for the dot projector are located in Japan, where the company has a long history of innovation in electronics and semiconductor technology.
- Finisar: Finisar’s manufacturing facilities for VCSELs were primarily located in the United States, specifically in Texas. However, following its acquisition by II-VI Incorporated in 2019, Finisar’s operations have been integrated into II-VI’s broader manufacturing network.
- Lumentum: Lumentum’s manufacturing facilities for VCSELs are located in the United States, with a significant presence in California.
- AMS: AMS’s manufacturing facilities for the infrared camera are located in Austria, where the company has a strong reputation for precision engineering and sensor technology.
- TSMC: TSMC’s primary manufacturing facilities are located in Taiwan, where the company has established itself as a global leader in semiconductor fabrication.
Technological Advancements in Face ID for 2018 iPhones
The 2018 iPhone models, including the iPhone X, iPhone XS, iPhone XS Max, and iPhone XR, marked a significant leap in Face ID technology. These advancements built upon the foundation laid by the original iPhone X, introducing new features and refinements that enhanced both security and user experience.
Improved Hardware and Algorithms
The 2018 iPhone models incorporated a new generation of hardware and algorithms for Face ID, resulting in a more accurate and secure facial recognition system. The TrueDepth camera system, responsible for capturing depth information, was enhanced with a more sophisticated infrared sensor and a faster A12 Bionic chip. These improvements enabled Face ID to perform more efficiently, even in challenging lighting conditions.
The A12 Bionic chip’s Neural Engine, specifically designed for machine learning, allowed for faster and more accurate facial recognition processing.
This improved hardware and algorithms resulted in a faster and more reliable Face ID experience. The system could now recognize faces more quickly and accurately, even in challenging environments.
Enhanced Security Features
The 2018 iPhone models also introduced several security enhancements to Face ID, further solidifying its position as a robust biometric authentication method. These enhancements included:
- Improved Anti-Spoofing Capabilities: The new TrueDepth camera system was designed to be more resistant to spoofing attempts, such as using photographs or masks. The enhanced infrared sensor and advanced algorithms allowed Face ID to better detect and reject these attempts.
- Secure Enclave Integration: Face ID data was stored securely in the iPhone’s Secure Enclave, a dedicated hardware component that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Attention Detection: Face ID gained the ability to detect whether the user was actually looking at the phone. This feature added an extra layer of security by preventing unauthorized access when the user was not actively looking at the device.
Enhanced User Experience
The technological advancements in Face ID for 2018 iPhones not only improved security but also enhanced the user experience.
- Faster Recognition: The improved hardware and algorithms resulted in faster facial recognition, making unlocking the phone and authenticating payments a seamless process.
- Wider Angle of Recognition: Face ID now recognized faces from a wider angle, making it more convenient to unlock the phone in various situations.
- Improved Accuracy in Challenging Lighting: Face ID could now accurately recognize faces even in challenging lighting conditions, such as dim lighting or direct sunlight.
Challenges Faced by Apple Suppliers for Face ID Production
The implementation of Face ID in the 2018 iPhones presented a formidable challenge for Apple’s suppliers. These suppliers had to navigate a complex web of technical hurdles and logistical complexities to deliver the components that powered this groundbreaking feature.
Manufacturing and Assembling Face ID Components
The intricate nature of Face ID components, including the dot projector, infrared camera, and flood illuminator, required specialized manufacturing processes and assembly techniques. Suppliers faced significant challenges in achieving the precision and accuracy demanded by Apple’s strict quality standards.
- Precision Manufacturing: The dot projector, a key component of Face ID, utilizes thousands of tiny infrared dots to create a 3D map of a user’s face. Producing these dots with the required precision and uniformity posed a major challenge for suppliers. The dot projector’s complex design also demanded specialized manufacturing equipment and highly skilled technicians.
- Component Alignment: Accurate alignment of the various Face ID components, including the dot projector, infrared camera, and flood illuminator, was crucial for the system’s functionality. Suppliers had to develop sophisticated assembly processes to ensure that these components were perfectly aligned, requiring specialized tools and equipment. Any misalignment could lead to inaccurate face recognition or even system failure.
- Miniaturization: The demand for compact and sleek iPhones necessitated miniaturizing Face ID components. Suppliers had to overcome the technical challenges of reducing the size of these components while maintaining their performance and functionality. This involved innovative design techniques and advanced manufacturing processes.
Technical Difficulties and Logistical Hurdles, Apple supplier face id 2018 iphone
Beyond the manufacturing complexities, suppliers encountered numerous technical difficulties and logistical hurdles. These challenges required innovative solutions and close collaboration with Apple to ensure the timely and successful production of Face ID components.
- Yield Rates: The intricate nature of Face ID components resulted in lower-than-expected yield rates during production. Suppliers had to optimize their manufacturing processes and invest in quality control measures to improve yield rates and meet Apple’s stringent production targets.
- Supply Chain Management: Managing the global supply chain for Face ID components was a logistical challenge. Suppliers had to coordinate with numerous vendors across different countries, ensuring timely delivery of raw materials and components. The complexity of the supply chain required sophisticated logistics systems and effective communication to avoid delays and disruptions.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing and validation were essential to ensure the reliability and accuracy of Face ID. Suppliers had to develop comprehensive testing protocols and establish dedicated testing facilities to meet Apple’s stringent quality standards. This involved simulating real-world usage scenarios and conducting extensive performance evaluations.
Impact of Face ID on the iPhone Supply Chain
The introduction of Face ID in 2018 iPhones significantly impacted Apple’s supply chain, necessitating adjustments in production, logistics, and distribution. This advanced facial recognition technology required new components and manufacturing processes, influencing the entire iPhone supply chain.
Production Process Changes
The implementation of Face ID introduced several changes in the production process for iPhone models.
- Integration of New Components: Face ID relies on a complex system of components, including the TrueDepth camera system, the A11 Bionic chip, and specialized software. The integration of these components required Apple to collaborate with a wider range of suppliers, including those specializing in 3D sensing technology and advanced image processing.
- Enhanced Manufacturing Capabilities: The production of Face ID components demanded a higher level of precision and accuracy than previous iPhone components. This necessitated upgrades in manufacturing facilities and the acquisition of specialized equipment. Suppliers had to invest in research and development to meet the stringent quality standards required for Face ID.
- Increased Complexity: The integration of Face ID increased the overall complexity of iPhone assembly. This required more sophisticated manufacturing processes and tighter quality control measures to ensure the seamless functioning of the Face ID system. This complexity added challenges to the production process and increased the demand for skilled labor.
Changes in Supply Chain Dynamics
The introduction of Face ID significantly altered the dynamics of Apple’s supply chain.
- Expansion of Supplier Network: Apple needed to expand its supplier network to include companies specializing in 3D sensing technology, advanced image processing, and specialized components for Face ID. This resulted in a more geographically diverse supply chain, with new suppliers from countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany joining the network.
- Increased Collaboration: The complexity of Face ID technology demanded greater collaboration between Apple and its suppliers. This included shared research and development, joint testing, and the establishment of dedicated teams to ensure the smooth integration of Face ID components.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Apple had to optimize its supply chain to manage the increased complexity and demand for Face ID components. This involved streamlining logistics, improving inventory management, and implementing new quality control measures to ensure timely delivery of components.
Overall Impact on Efficiency and Effectiveness
The introduction of Face ID had a significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of the iPhone supply chain.
- Increased Efficiency: The integration of Face ID led to a more streamlined and efficient production process, resulting in faster production times and reduced costs. This was achieved through improved manufacturing processes, better coordination between suppliers, and the adoption of advanced automation technologies.
- Enhanced Quality: The high-quality standards required for Face ID components led to an overall improvement in the quality of iPhones. This was achieved through rigorous testing, advanced quality control measures, and the use of high-precision manufacturing equipment.
- Enhanced Security: Face ID provided a more secure and user-friendly authentication method compared to traditional methods like passcodes. This enhanced the overall security of iPhones and reduced the risk of unauthorized access.
Future Trends in Face ID Technology and Supply: Apple Supplier Face Id 2018 Iphone
The rapid evolution of facial recognition technology and its increasing adoption in smartphones suggest a future where Face ID will become even more sophisticated and integrated into our lives. This evolution will be driven by advancements in hardware, software, and the ever-growing need for enhanced security and user convenience.
Timeline of Expected Advancements in Face ID Technology
The development of Face ID technology is expected to follow a trajectory of continuous improvement, with new features and capabilities emerging over time. Here’s a glimpse into the potential future of Face ID:
- 2024-2026: Improved depth sensing and infrared imaging will allow Face ID to function in challenging environments, like direct sunlight or low-light conditions, with greater accuracy and reliability.
- 2027-2029: Integration of advanced machine learning algorithms will enable Face ID to recognize faces from multiple angles and even in disguise, making it more secure and adaptable.
- 2030 and beyond: The convergence of Face ID with other technologies like augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) could lead to innovative applications, such as personalized user interfaces and interactive experiences.
Potential Future Trends in Face ID Component Production and Supply
The production and supply of Face ID components will likely undergo significant changes as the technology evolves. Here are some key trends:
- Miniaturization: Component sizes will continue to shrink, allowing for thinner and more aesthetically pleasing smartphone designs. For example, Apple’s TrueDepth camera system, which houses the Face ID sensors, has already become increasingly compact with each new iPhone generation.
- Increased Integration: More components will be integrated onto a single chip, simplifying the manufacturing process and reducing costs. This trend is already evident in the development of System-on-a-Chip (SoC) solutions that combine multiple functionalities on a single chip.
- Advanced Materials: The use of advanced materials, such as sapphire glass and ceramic, will enhance the durability and performance of Face ID components. These materials are resistant to scratches and offer better optical clarity, ensuring optimal sensor performance.
Impact of These Trends on the iPhone Supply Chain and the Overall Smartphone Industry
The evolution of Face ID technology and its associated supply chain will have a profound impact on the iPhone supply chain and the broader smartphone industry. Here are some key implications:
- Increased Competition: The increasing adoption of Face ID and similar technologies will intensify competition among smartphone manufacturers. Companies will need to invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead of the curve and offer the most advanced and secure facial recognition solutions.
- Shift in Power Dynamics: The demand for specialized components, such as depth sensors and infrared emitters, will create new opportunities for niche suppliers. This could lead to a shift in power dynamics within the smartphone supply chain, as these suppliers gain more leverage.
- New Opportunities for Innovation: The advancements in Face ID technology will create new opportunities for innovation in areas such as AR, AI, and cybersecurity. This could lead to the development of new products and services that enhance the user experience and address emerging security challenges.
The journey into the world of Apple Supplier Face ID 2018 iPhone offers a compelling glimpse into the intricate web of innovation, collaboration, and challenges that define the world of smartphone technology. From the technological advancements that revolutionized facial recognition to the complexities of manufacturing and assembling these intricate components, this exploration unveils the remarkable journey of Face ID from conception to implementation. The impact of Face ID extends beyond the realm of security, influencing the dynamics of the iPhone supply chain and shaping the future of the smartphone industry. This story is a testament to the constant evolution of technology and the crucial role of collaboration in driving innovation forward.
Remember those rumors about Apple suppliers struggling to keep up with the demand for Face ID in 2018 iPhones? Well, it seems like the tech world is full of unexpected twists and turns. While those suppliers were probably sweating bullets, the world of gaming was busy celebrating the release of the Nioh Complete Edition for PC. Talk about a change of pace! So, maybe those Face ID components weren’t so hard to produce after all, or maybe everyone was just too busy slaying demons in feudal Japan.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News