Apple’s Supply Chain: Apple Supplier Make Components Ar Devices
Apple’s supply chain is a marvel of global logistics, spanning continents and involving hundreds of suppliers. This intricate network ensures that Apple can source the components needed to manufacture its iconic products, from iPhones and Macs to AirPods and Apple Watches.
Geographical Distribution of Apple’s Key Suppliers, Apple supplier make components ar devices
Apple’s supply chain is remarkably diverse, with key suppliers located across the globe. This geographic spread is not random; it is a deliberate strategy aimed at minimizing risk, accessing specialized expertise, and optimizing costs.
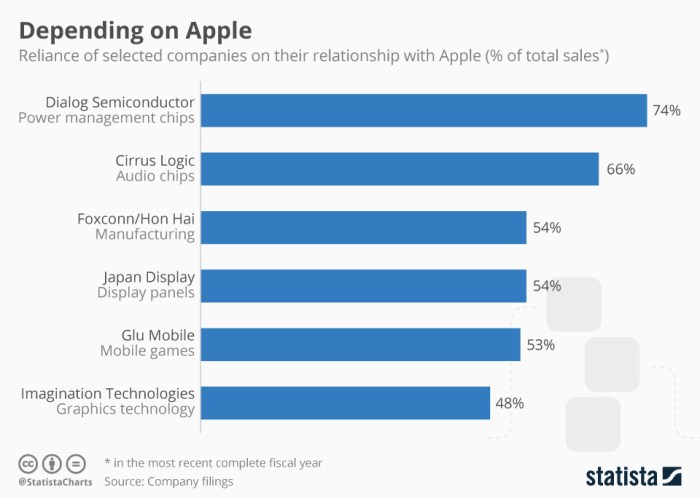
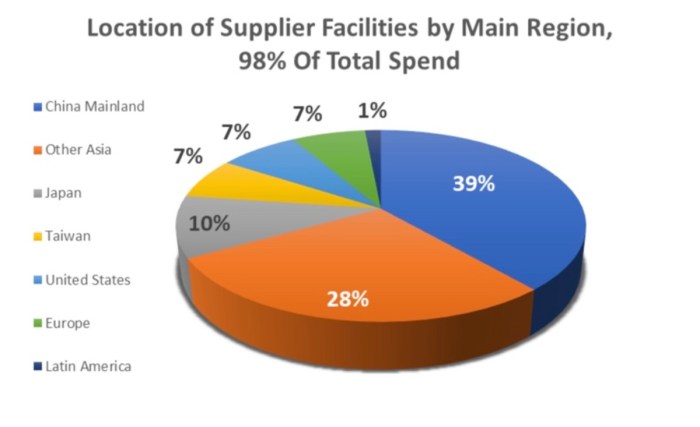
- Asia: Asia is the heart of Apple’s supply chain, with China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan being particularly important. These countries are home to many of the world’s leading electronics manufacturers, providing Apple with access to cutting-edge technology and manufacturing expertise. For example, Foxconn, a Taiwanese company, is Apple’s largest contract manufacturer, assembling a significant portion of its products in China.
- Europe: Europe plays a vital role in Apple’s supply chain, particularly for components like semiconductors and displays. Companies like ASML in the Netherlands, a leading manufacturer of lithography machines crucial for chip production, and Samsung in South Korea, a major supplier of OLED displays, are key players in this region.
- North America: While not as heavily reliant on North American suppliers as other regions, Apple still sources components like memory chips from companies like Micron Technology in the United States.
Strategic Reasons for Global Sourcing
Apple’s global sourcing strategy is not simply about finding the cheapest suppliers. It is driven by a multifaceted approach that considers factors such as:
- Access to Expertise: Apple seeks out suppliers with specialized knowledge and capabilities, ensuring that its products are built with the best possible components. For instance, TSMC in Taiwan is a leading manufacturer of advanced semiconductors, providing Apple with cutting-edge processors for its devices.
- Risk Mitigation: By diversifying its supplier base across different regions, Apple can mitigate risks associated with political instability, natural disasters, or economic fluctuations in any one country.
- Cost Optimization: Sourcing components from various locations allows Apple to take advantage of regional cost differences, potentially leading to lower manufacturing costs.
- Speed and Efficiency: Having suppliers located close to its manufacturing facilities allows Apple to streamline production processes and reduce lead times.
Major Suppliers and Their Contributions
Apple’s success is a testament to its ability to collaborate with a vast network of suppliers. Here are some examples of major suppliers and their contributions to Apple products:
| Supplier | Country | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Foxconn | Taiwan | Contract manufacturing, assembling a significant portion of Apple’s products, including iPhones and iPads. |
| TSMC | Taiwan | Semiconductor manufacturing, providing Apple with advanced processors for its devices. |
| Samsung | South Korea | OLED displays, memory chips, and other components for iPhones and other devices. |
| ASML | Netherlands | Lithography machines, crucial for the production of advanced semiconductors. |
| Micron Technology | United States | Memory chips for iPhones, Macs, and other devices. |
Components and Their Roles in Apple Devices
Apple devices, renowned for their sleek design and user-friendly interfaces, are powered by a complex interplay of sophisticated components. These components, sourced from a global network of suppliers, contribute significantly to the overall performance, functionality, and user experience of Apple products. Understanding the role of each component is crucial to appreciating the intricate engineering behind these devices.
Key Components and Their Suppliers
The following table Artikels some of the key components found in Apple devices and their respective suppliers:
| Component | Supplier(s) | Role in Production |
|---|---|---|
| Processors (A-series, M-series) | TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) | Designs and manufactures Apple’s custom-designed processors, responsible for the devices’ processing power and efficiency. |
| Memory (DRAM, NAND Flash) | Samsung, SK Hynix, Micron Technology | Provides the device’s primary memory for storing data and running applications, as well as secondary storage for data persistence. |
| Displays (OLED, LCD) | Samsung, LG Display, BOE Technology Group | Supplies the screens that provide the visual interface for users, offering features like high resolution, color accuracy, and touch responsiveness. |
| Cameras (Sensors, Lenses) | Sony, OmniVision Technologies, Largan Precision | Contributes to the image capture capabilities of Apple devices, including sensors for light detection and lenses for focusing and image quality. |
| Wireless Communication (Cellular Modems, Wi-Fi Chips) | Qualcomm, Broadcom, Intel (formerly) | Enables communication capabilities, including cellular connectivity, Wi-Fi networking, and Bluetooth pairing. |
| Batteries | CATL, LG Energy Solution, Panasonic | Provides the power source for the devices, ensuring extended usage time and efficient energy management. |
Impact of Component Quality and Innovation
Component quality and innovation are paramount to Apple’s success. The company’s commitment to using high-quality components from leading suppliers ensures reliable performance, durability, and a seamless user experience. Furthermore, Apple’s collaboration with suppliers to develop cutting-edge components drives innovation and pushes the boundaries of what is possible in mobile technology.
For instance, Apple’s partnership with TSMC for the development of custom-designed processors has resulted in significant performance improvements across generations of Apple devices. These processors, optimized for specific tasks and workloads, contribute to the devices’ speed, efficiency, and overall user experience. Similarly, the use of OLED displays in newer iPhone models has enhanced the visual experience with deeper blacks, wider color gamuts, and improved energy efficiency.
The constant pursuit of component innovation and quality is a key driver of Apple’s product differentiation and competitive advantage. By working closely with its suppliers to develop and integrate advanced components, Apple continues to deliver products that push the boundaries of technology and set the standard for the mobile industry.
The Manufacturing Process
The transformation of individual components into the sleek and sophisticated Apple devices we know and love is a marvel of engineering and logistics. This process involves a complex and meticulously orchestrated dance of sourcing, assembly, and quality control, all driven by cutting-edge technology and a relentless pursuit of perfection.
The Stages of Apple Device Manufacturing
The journey of an Apple device begins with the sourcing of individual components from a global network of suppliers. These components, ranging from processors and memory chips to displays and batteries, are carefully selected for their quality and performance. Once sourced, the components embark on a carefully choreographed journey through the manufacturing process, culminating in the final assembly of the finished product.
- Component Sourcing: Apple collaborates with a diverse range of suppliers across the globe, each specializing in specific components. This global network ensures access to the highest quality materials and cutting-edge technologies. Sourcing is a crucial stage, as it directly impacts the device’s performance, reliability, and overall quality.
- Component Testing and Validation: Before components are incorporated into devices, they undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet Apple’s stringent quality standards. This step involves subjecting components to a series of tests, simulating real-world conditions to guarantee their performance and durability.
- Assembly: The heart of the manufacturing process lies in the assembly of components into a functional device. This stage involves precision engineering and automation, with robots and specialized machinery working in harmony to assemble components with meticulous accuracy. Assembly lines are carefully designed to optimize efficiency and minimize errors.
- Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented at every stage. Devices undergo multiple rounds of inspection to ensure they meet Apple’s exacting standards. This rigorous quality control process ensures that every device leaving the factory is free from defects and delivers a flawless user experience.
- Packaging and Distribution: Once assembled and inspected, devices are packaged and prepared for distribution. This final stage involves labeling, boxing, and shipping, ensuring devices reach customers in pristine condition. Apple’s global distribution network ensures swift and efficient delivery to customers around the world.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics play a pivotal role in Apple’s manufacturing process, driving efficiency, precision, and consistency. Robots are employed for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Component Placement: Robots with advanced vision systems accurately place components onto circuit boards, ensuring precise alignment and minimizing errors.
- Soldering and Assembly: Robots perform soldering tasks with exceptional accuracy and speed, creating reliable and durable connections between components.
- Testing and Inspection: Robots equipped with sensors and cameras perform automated testing and inspection, identifying potential defects early in the manufacturing process.
- Material Handling: Robots efficiently move and handle components and finished devices, optimizing workflow and minimizing human intervention.
Apple’s Manufacturing Approach
Apple’s manufacturing approach is characterized by a focus on:
- Vertical Integration: Apple controls key aspects of the manufacturing process, from component design to final assembly, ensuring tight control over quality and consistency. This approach allows for greater innovation and customization.
- Lean Manufacturing: Apple employs lean manufacturing principles to optimize efficiency and minimize waste. This involves streamlining processes, eliminating unnecessary steps, and continuously seeking ways to improve productivity.
- Innovation and Technology: Apple invests heavily in research and development, constantly exploring new technologies and manufacturing processes to enhance product quality and efficiency. This commitment to innovation drives the company’s manufacturing prowess.
Comparison with Other Tech Companies
Compared to other tech companies, Apple’s manufacturing approach stands out for its emphasis on:
- Vertical Integration: Apple’s high level of vertical integration distinguishes it from many other tech companies that rely heavily on external suppliers for key components. This control over the manufacturing process allows for greater innovation and customization.
- Quality and Design: Apple is renowned for its meticulous attention to quality and design, evident in the premium materials and craftsmanship used in its devices. This focus on quality is reflected in the rigorous testing and quality control measures implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
- Innovation and Technology: Apple’s commitment to innovation and technology is evident in its investment in cutting-edge manufacturing processes and automation. This focus on innovation drives efficiency, precision, and continuous improvement in its manufacturing operations.
Challenges and Opportunities in Apple’s Supply Chain
Apple’s supply chain, though highly efficient and integrated, faces various challenges and opportunities that can significantly impact its future success. These factors range from geopolitical risks and trade tensions to the rise of emerging markets and the development of cutting-edge technologies.
Geopolitical Risks and Trade Tensions
Geopolitical risks and trade tensions pose significant challenges to Apple’s supply chain. The ongoing trade war between the United States and China, for instance, has disrupted global supply chains, increased tariffs on goods, and created uncertainty for businesses. Apple, with a significant portion of its manufacturing operations in China, has been directly affected by these developments. Moreover, political instability in key manufacturing regions, such as the Middle East or Southeast Asia, can disrupt production and lead to supply chain disruptions.
Environmental Concerns
Apple’s supply chain faces growing pressure to address environmental concerns, including carbon emissions, waste generation, and resource depletion. As a global leader, Apple has set ambitious environmental goals, including achieving carbon neutrality across its operations and supply chain by 2030. However, achieving these goals requires significant collaboration with suppliers, which can be challenging given the complexity of the supply chain and the need for widespread adoption of sustainable practices.
Growth of Emerging Markets
The growth of emerging markets presents a significant opportunity for Apple’s suppliers. As consumer demand for Apple products rises in these markets, suppliers can benefit from increased production volume and market share. For example, India is rapidly becoming a key market for Apple, and suppliers are investing heavily in manufacturing facilities and infrastructure to meet the growing demand.
Development of New Technologies
The development of new technologies, such as 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR), offers opportunities for Apple’s suppliers to innovate and expand their product offerings. These technologies are driving demand for advanced components and materials, creating new markets and opportunities for suppliers to develop specialized expertise.
Strategy for Mitigating Supply Chain Risks and Enhancing Resilience
To mitigate supply chain risks and enhance resilience, Apple can implement a multi-pronged strategy:
- Diversify its supply base: Reducing reliance on a single supplier or region can help mitigate the impact of disruptions. Apple can explore sourcing from multiple countries and suppliers, ensuring a more geographically diverse and resilient supply chain.
- Develop strong supplier relationships: Building close relationships with suppliers can help improve communication, collaboration, and transparency, fostering trust and mutual understanding. Apple can invest in supplier development programs and initiatives to improve their capabilities and sustainability practices.
- Invest in technology and automation: Implementing advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, can help optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enhance visibility across the supply chain. This can help Apple better anticipate and respond to disruptions.
- Foster a culture of innovation and collaboration: Apple can encourage its suppliers to invest in research and development, fostering innovation and the development of new technologies. By working closely with suppliers, Apple can create a more collaborative and agile supply chain.
The Impact of Apple’s Supply Chain on the Global Economy
Apple’s supply chain, with its intricate network of suppliers and manufacturers across the globe, exerts a significant influence on the world economy. Its vast operations generate substantial economic benefits while also presenting certain challenges.
Economic Benefits and Challenges of Apple’s Sourcing Practices
Apple’s sourcing practices, characterized by a global network of suppliers, create both economic benefits and challenges.
Economic Benefits
- Job Creation: Apple’s supply chain generates millions of jobs globally, encompassing manufacturing, assembly, logistics, and supporting services. In countries like China, Vietnam, and India, Apple’s manufacturing operations have contributed significantly to employment growth.
- Economic Growth: Apple’s substantial investments in its supply chain stimulate economic activity in various regions. This includes increased demand for raw materials, components, and services, contributing to overall economic growth.
- Technological Advancement: Apple’s stringent quality standards and demanding specifications drive innovation among its suppliers. This leads to advancements in manufacturing processes, materials, and technologies, benefiting various industries.
Economic Challenges
- Labor Practices: Concerns about labor conditions in some of Apple’s manufacturing facilities have emerged, raising ethical questions about working hours, wages, and safety.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of Apple’s supply chain, particularly in terms of resource extraction, manufacturing, and transportation, has drawn attention. The company faces pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and minimize environmental damage.
- Economic Dependence: The reliance of some countries on Apple’s supply chain can create economic vulnerabilities. If Apple shifts production or faces disruptions, these countries could experience economic setbacks.
Impact of Apple’s Supply Chain on Job Creation, Innovation, and Economic Growth in Different Countries
Apple’s supply chain significantly impacts job creation, innovation, and economic growth in various countries.
Job Creation
Apple’s manufacturing operations have contributed to significant job creation in countries like China, Vietnam, and India. For example, Foxconn, a major Apple supplier, employs hundreds of thousands of workers in China.
Innovation
Apple’s demanding specifications and quality standards have driven innovation among its suppliers. This has led to advancements in manufacturing processes, materials, and technologies, benefiting various industries.
Economic Growth
Apple’s substantial investments in its supply chain have stimulated economic activity in various regions. For instance, the growth of the electronics industry in Vietnam has been partly driven by Apple’s manufacturing operations.
Role of Apple’s Supply Chain in Shaping Global Trade Patterns and Technological Advancements
Apple’s supply chain plays a crucial role in shaping global trade patterns and technological advancements.
Global Trade Patterns
Apple’s sourcing practices have contributed to the globalization of manufacturing. The company’s vast network of suppliers has led to increased trade flows between different countries, particularly in the electronics sector.
Technological Advancements
Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation has driven technological advancements across its supply chain. The company’s demanding specifications have pushed suppliers to develop new materials, processes, and technologies, which have subsequently benefited other industries.
Apple supplier make components ar devices – Apple’s global supply chain is a testament to the power of collaboration and innovation. It’s a complex dance of engineering, manufacturing, and logistics, where each partner plays a crucial role in bringing the latest Apple devices to life. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of this intricate network will only grow, shaping the future of Apple’s products and influencing the global economy in profound ways.
Apple’s suppliers are working overtime to crank out the components that make up the iconic iPhone. These components, from the tiny chips to the sleek glass displays, are the building blocks of a device that has become a cultural phenomenon. With an estimated 54 million iPhones expected to be shipped this quarter , the pressure is on for Apple’s suppliers to keep up with the demand.
From the assembly lines in China to the factories across the globe, it’s a global effort to ensure that every iPhone is ready for its debut in the hands of eager customers.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News