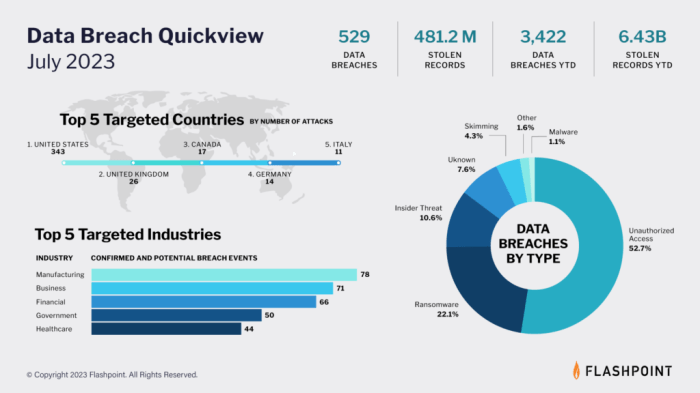
Badly handled data breaches 2023 takes center stage, highlighting a critical issue that impacts businesses and individuals alike. The consequences of these breaches can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and a decline in consumer trust. In a world increasingly reliant on digital information, the need for robust data security practices is paramount. This article delves into the impact of data breaches, common causes, best practices, and emerging trends in data security.
From stolen credit card details to leaked personal information, the consequences of data breaches are far-reaching. Businesses can suffer significant financial losses, while individuals face identity theft, fraud, and emotional distress. The repercussions extend beyond immediate consequences, impacting consumer trust and brand loyalty in the long run. Understanding the root causes of these breaches is crucial to mitigating risks and implementing effective security measures.
Impact of Data Breaches
In the digital age, data breaches are an unfortunate reality, with potentially devastating consequences for both businesses and individuals. Poorly handled data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and a decline in consumer trust.
Financial Consequences
Data breaches can result in substantial financial losses for businesses. The cost of a data breach can include:
- Legal and regulatory fines: Organizations that fail to protect sensitive data adequately can face hefty fines from regulatory bodies, such as the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California.
- Notification costs: Companies are often required to notify affected individuals about a data breach, which can involve significant costs for communication, credit monitoring, and identity theft protection services.
- Loss of revenue: A data breach can damage a company’s reputation and lead to a decline in sales, as customers may lose trust and choose to do business elsewhere.
- Business interruption: The process of investigating and responding to a data breach can disrupt business operations, leading to lost productivity and potential delays in product or service delivery.
- Insurance premiums: After a data breach, insurance premiums may increase, as insurers perceive the organization as a higher risk.
Reputational Damage
A data breach can severely damage a company’s reputation, eroding public trust and impacting brand loyalty.
- Negative media coverage: Data breaches often receive widespread media attention, which can be damaging to a company’s image and reputation.
- Loss of customer trust: Customers may lose trust in a company that has experienced a data breach, especially if they feel their personal information was not adequately protected.
- Decreased brand loyalty: Customers who have been affected by a data breach may be less likely to do business with the company in the future, leading to a decline in brand loyalty.
- Impact on employee morale: Data breaches can also impact employee morale, as employees may feel their privacy has been compromised or that the company is not doing enough to protect their data.
Examples of Impact
Several high-profile data breaches in recent years have demonstrated the devastating consequences of poorly handled data security. For example, the 2017 Equifax breach affected over 147 million individuals, leading to significant financial losses for the company and reputational damage that continues to this day. The 2018 Marriott breach exposed the personal information of over 500 million guests, highlighting the importance of strong data security measures. These examples illustrate the importance of taking data security seriously, as the consequences of a breach can be far-reaching and long-lasting.
Common Causes of Data Breaches
Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, and the consequences can be devastating for individuals and organizations alike. Understanding the common causes of these breaches is crucial for preventing them.
Vulnerabilities Exploited in Data Breaches
Cybercriminals exploit various vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data. Some of the most common vulnerabilities targeted in 2023 include:
- Outdated Software: Many organizations still use outdated software that contains known security flaws. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain access to systems and steal data.
- Weak Passwords: Many individuals and organizations use weak passwords that are easy to guess or crack. This makes it easy for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts and systems.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details. These attacks are often carried out through emails or websites that appear legitimate but are actually designed to steal data.
- SQL Injection: SQL injection attacks target databases by injecting malicious code into data inputs. This allows attackers to bypass security measures and gain access to sensitive data.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easy for attackers to intercept data transmitted over the network.
- Misconfigured Cloud Services: Cloud services can be vulnerable to attacks if they are not properly configured. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to data stored in the cloud.
Human Error and Negligence
Human error and negligence play a significant role in many data breach incidents.
- Clicking on Malicious Links: Employees may inadvertently click on malicious links in emails or websites, which can lead to malware infections and data breaches.
- Sharing Sensitive Information: Employees may share sensitive information with unauthorized individuals, either intentionally or unintentionally. This can expose data to attackers.
- Failing to Implement Security Measures: Employees may fail to implement or follow security measures, such as password policies or data encryption. This can leave data vulnerable to attacks.
- Lack of Security Awareness Training: Employees who are not adequately trained on security best practices may be more likely to make mistakes that expose data to risk.
Outdated Technology and Lack of Security Measures
Outdated technology and a lack of security measures are also major contributors to data breaches.
- Outdated Software: Organizations that fail to update their software regularly are vulnerable to attacks that exploit known security flaws.
- Insufficient Security Controls: Organizations may have inadequate security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption. This can leave data exposed to attackers.
- Lack of Data Backup and Recovery Plans: Organizations that lack data backup and recovery plans may be unable to restore data after a breach, resulting in significant financial losses.
- Lack of Security Monitoring: Organizations that fail to monitor their systems for suspicious activity may be unaware of breaches until it is too late.
Best Practices for Data Security
Data security is no longer an option; it’s a necessity. In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, businesses need to take proactive measures to protect their valuable data. Implementing robust data security practices can help mitigate the risk of data breaches, safeguard customer trust, and ensure business continuity.
Essential Data Security Measures
Here’s a breakdown of the essential data security measures that businesses should implement:
| Measure | Description | Benefits | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Using strong passwords with a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and enabling MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification. | Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data by making it difficult for attackers to guess or hack passwords. | Using a password like “P@$$wOrd123” instead of “password” and requiring a code sent to a mobile device in addition to a password. |
| Data Encryption | Converting data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. | Protects sensitive data, such as customer information and financial records, from unauthorized access and theft. | Encrypting customer credit card details stored in a database. |
| Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments | Periodically assessing the security posture of systems and applications to identify and address vulnerabilities. | Identifies weaknesses in security controls and allows for timely remediation, reducing the risk of successful attacks. | Hiring a third-party security firm to conduct an annual penetration test of the company’s network. |
| Employee Training and Awareness | Educating employees on best practices for data security, such as phishing awareness, password management, and data handling. | Reduces the likelihood of human error and increases awareness of potential threats, minimizing the risk of accidental data breaches. | Providing employees with regular training on how to identify and report phishing emails. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions | Implementing software that monitors and controls data movement, preventing sensitive information from leaving the organization’s network. | Protects sensitive data from unauthorized copying, sharing, or transfer, reducing the risk of data leaks. | Using DLP software to prevent employees from sending confidential documents to personal email accounts. |
| Regular Software Updates and Patches | Keeping software and operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities. | Fixes known security flaws and vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploitation by attackers. | Installing the latest security updates for the company’s operating system and applications. |
| Access Control and Least Privilege Principle | Granting employees access only to the information they need to perform their jobs, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. | Reduces the risk of data breaches by limiting the number of people who have access to sensitive information. | Restricting access to the company’s financial database to only authorized finance personnel. |
| Data Backup and Recovery | Regularly backing up data and ensuring that it can be restored in case of a disaster or data loss. | Provides a safety net in case of a data breach or other unforeseen event, minimizing business disruption and data loss. | Maintaining regular backups of all critical data on a separate server or cloud storage. |
The Importance of Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are crucial for maintaining a strong data security posture. These assessments help identify weaknesses in security controls, such as outdated software, misconfigured systems, and weak passwords. By identifying these vulnerabilities early, businesses can take steps to remediate them before they can be exploited by attackers.
“Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are like a checkup for your digital health. They help you identify potential problems before they become major issues.”
Creating a Comprehensive Data Breach Response Plan
A comprehensive data breach response plan is essential for minimizing the damage and impact of a data breach. It Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including:
- Incident Detection and Reporting: Establish clear procedures for detecting and reporting suspected data breaches. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for incident response teams.
- Containment and Mitigation: Implement steps to contain the breach and prevent further data loss. This may involve isolating affected systems, shutting down services, or changing passwords.
- Data Recovery and Restoration: Develop a plan for recovering and restoring data that has been compromised. This may involve using backups or data recovery tools.
- Notification and Communication: Determine the notification process for affected individuals, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders. This includes providing clear and concise information about the breach and its impact.
- Forensics and Investigation: Conduct a thorough investigation to determine the cause of the breach, the extent of the data loss, and the actions taken by the attackers.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with relevant data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
- Post-Breach Remediation: Implement corrective measures to address the vulnerabilities that led to the breach and strengthen security controls to prevent future incidents.
Data Breach Response Strategies
In 2023, the landscape of data breaches has evolved, demanding organizations to adapt their response strategies to effectively mitigate damage and restore trust. Organizations are increasingly adopting a proactive approach, prioritizing swift and efficient incident response plans. This shift is driven by the growing awareness of the potential consequences of delayed or inadequate responses, including reputational damage, financial losses, and regulatory penalties.
Effectiveness of Incident Response Strategies
The effectiveness of incident response strategies is often evaluated based on the speed and efficiency of containment, the extent of data recovery, the effectiveness of communication with affected individuals, and the ability to restore trust.
- Incident Response Plans: Well-defined incident response plans are crucial for guiding organizations through a data breach. They Artikel specific steps for detection, containment, investigation, and recovery, ensuring a coordinated and timely response. Organizations that have implemented robust incident response plans, including regular testing and training, tend to be more effective in handling breaches.
- Threat Intelligence: Proactive threat intelligence gathering helps organizations anticipate potential threats and vulnerabilities. By monitoring emerging attack trends and identifying potential targets, organizations can strengthen their defenses and refine their incident response strategies. Organizations that actively utilize threat intelligence are better equipped to detect and respond to breaches promptly.
- Automated Tools: Leveraging automated tools for threat detection, incident response, and remediation can significantly enhance the effectiveness of breach response. These tools can automate tasks like vulnerability scanning, log analysis, and incident notification, enabling organizations to respond quickly and efficiently.
Notifying Affected Individuals and Regulatory Bodies
Prompt and transparent communication is essential in mitigating the impact of a data breach. Organizations must notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies of the breach, providing clear and concise information about the nature of the breach, the data compromised, and the steps taken to mitigate the impact.
- Affected Individuals: Organizations must notify affected individuals promptly, ideally within 72 hours of discovering the breach. The notification should include details about the type of data compromised, the potential risks to individuals, and steps they can take to protect themselves.
- Regulatory Bodies: Organizations are required to report data breaches to relevant regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States or the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the United Kingdom. The reporting requirements vary depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the breach.
Minimizing Damage and Restoring Trust
After a data breach, organizations must focus on minimizing damage and restoring trust with stakeholders. This involves taking proactive steps to mitigate the impact of the breach, address concerns of affected individuals, and demonstrate a commitment to data security.
- Data Recovery and Remediation: Organizations must prioritize data recovery and remediation efforts to minimize the impact of the breach. This may involve restoring lost data, patching vulnerabilities, and implementing additional security measures to prevent future breaches.
- Communication and Transparency: Open and transparent communication with affected individuals, the public, and regulatory bodies is crucial for restoring trust. Organizations should provide regular updates about the investigation, remediation efforts, and steps taken to prevent future breaches.
- Compensation and Support: Organizations may offer compensation to affected individuals for the inconvenience caused by the breach. They may also provide support services, such as credit monitoring or identity theft protection.
- Reputation Management: Organizations must proactively manage their reputation following a data breach. This may involve engaging in public relations efforts, addressing concerns in the media, and demonstrating a commitment to data security.
Emerging Trends in Data Security: Badly Handled Data Breaches 2023
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so are the threats to data security. 2023 has seen a surge in sophisticated cyberattacks, fueled by advancements in technology and the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for organizations to stay ahead of the curve and protect their valuable data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Data Breach Prevention
AI and ML are playing a transformative role in data security. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activity. This proactive approach helps in preventing data breaches before they occur.
- Threat Detection and Response: AI-powered systems can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and other data sources to detect suspicious activities in real-time. This allows for faster and more effective response to potential threats.
- Vulnerability Assessment: AI can be used to identify vulnerabilities in software and systems, helping organizations prioritize patching and security updates. This proactive approach reduces the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI can analyze user behavior patterns to detect deviations that might indicate compromised accounts or insider threats. This helps in identifying and mitigating potential risks before they escalate.
Data Privacy Regulations and Their Influence on Data Security Practices, Badly handled data breaches 2023
The growing awareness of data privacy has led to the implementation of stringent regulations like GDPR and CCPA. These regulations are driving organizations to adopt more robust data security practices to ensure compliance and protect user data.
- Data Minimization: Organizations are now required to collect only the necessary data for their operations, reducing the amount of sensitive information they need to protect.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is becoming a standard practice to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data Retention Policies: Organizations are implementing clear policies for data retention, ensuring that they only store data for as long as necessary. This reduces the risk of data breaches and helps with compliance.
- Data Subject Rights: Regulations empower individuals to access, correct, and delete their personal data. Organizations need to implement processes to handle these requests efficiently and securely.
In the wake of a data breach, a swift and effective response is essential. Organizations must prioritize transparency, informing affected individuals and regulatory bodies promptly. Restoring trust requires a comprehensive approach that includes addressing vulnerabilities, implementing robust security protocols, and demonstrating a commitment to data protection. As the cyber landscape evolves, staying ahead of emerging threats is crucial. By embracing best practices, leveraging advanced technologies, and adhering to data privacy regulations, organizations can safeguard their data and mitigate the risks associated with badly handled data breaches.
2023 has been a wild ride for data security, with high-profile breaches making headlines almost daily. But amidst the chaos, it’s worth noting that even companies at the forefront of innovation aren’t immune to tough decisions. Motional, a self-driving car company backed by Hyundai and Aptiv, recently cut about 550 employees, around 40% of its workforce , in a bid to streamline operations.
This move, while unfortunate for those affected, highlights the delicate balance between technological advancement and financial stability, especially in the face of data security concerns. Ultimately, these events underscore the importance of robust security measures, even as companies navigate the ever-evolving landscape of data privacy and protection.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News