Bitcoin Mining Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining is a crucial process that secures the Bitcoin network and enables transactions. It involves powerful computers solving complex mathematical problems to verify and add new transactions to the blockchain. However, this process requires significant energy consumption, leading to concerns about its environmental impact.
Bitcoin Mining Process and Energy Consumption
Bitcoin mining is a computationally intensive process that involves solving complex mathematical problems known as “proof-of-work” puzzles. Miners compete to solve these puzzles first, and the winner receives a reward in Bitcoin. This process ensures the security and integrity of the Bitcoin network. The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining arises from the vast computing power required to solve these puzzles. Miners use specialized hardware called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) designed for high-speed calculations. The more powerful the hardware, the higher the chances of solving a puzzle and receiving a reward.
Bitcoin Mining Electricity Consumption
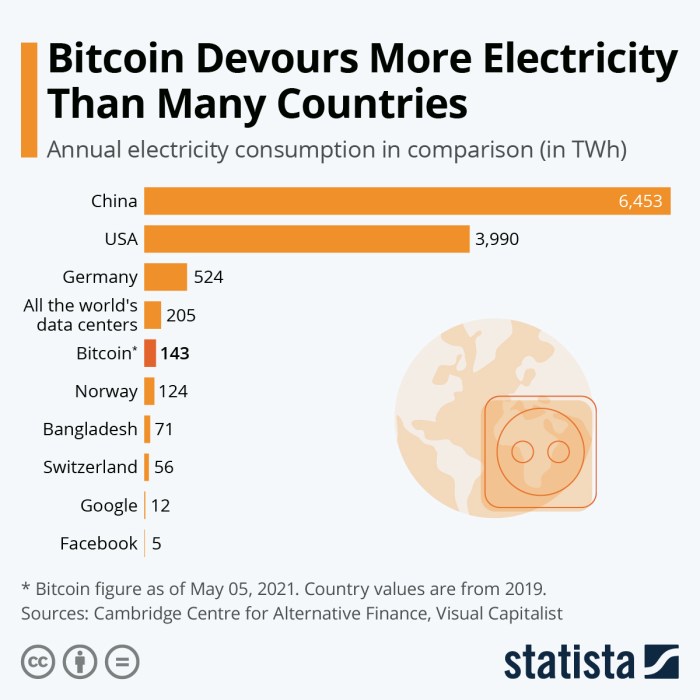
The electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining varies depending on factors such as the difficulty of the puzzles, the efficiency of the mining hardware, and the price of Bitcoin. As of 2023, the estimated annual electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining is around 130 terawatt-hours (TWh), which is comparable to the energy consumption of countries like the Netherlands or Argentina.
The average energy consumption per Bitcoin transaction is estimated to be around 700 kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Factors Contributing to High Energy Consumption
Several factors contribute to the high energy consumption of Bitcoin mining, including:
- Proof-of-Work Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin uses a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, which requires miners to expend significant computational power to secure the network. This mechanism ensures the integrity and security of the blockchain, but it comes at the cost of high energy consumption.
- Mining Difficulty: The difficulty of mining Bitcoin puzzles adjusts automatically to maintain a consistent block creation rate. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, requiring more computing power and energy to solve the puzzles.
- Hardware Competition: Miners are constantly competing to acquire the most powerful hardware to increase their chances of solving puzzles. This competition drives innovation in hardware development, but it also leads to increased energy consumption.
Comparison with Other Industries
The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is significant when compared to other industries. For example, the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is estimated to be comparable to the energy consumption of the entire country of Argentina.
- Data Centers: Data centers consume significant amounts of energy, but their consumption is spread across a wide range of services, including cloud computing, data storage, and online services. Bitcoin mining, on the other hand, is a single, energy-intensive application.
- Transportation: The transportation sector is a major consumer of energy, particularly from fossil fuels. However, the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is comparable to the energy consumption of a small country.
Energy Consumption Comparison to European Countries
Bitcoin mining has become increasingly energy-intensive, consuming vast amounts of electricity. In fact, the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is estimated to be higher than the electricity consumption of some European countries. This comparison highlights the significant energy demands associated with Bitcoin mining and raises concerns about its environmental impact.
Estimated Electricity Consumption of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is a computationally intensive process that requires significant energy to solve complex mathematical problems. This energy consumption has been estimated to be comparable to the annual electricity consumption of several European countries.
Comparison of Bitcoin Mining Energy Consumption to 20 European Countries
The following table lists the estimated annual electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining compared to the annual electricity consumption of 20 European countries:
| Country | Estimated Annual Electricity Consumption (TWh) | Bitcoin Mining Annual Electricity Consumption (TWh) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 69 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 1.7 times more electricity than Austria. |
| Belgium | 88 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 1.4 times more electricity than Belgium. |
| Bulgaria | 28 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 4.3 times more electricity than Bulgaria. |
| Croatia | 17 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 7.1 times more electricity than Croatia. |
| Cyprus | 5 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 24 times more electricity than Cyprus. |
| Czech Republic | 71 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 1.7 times more electricity than the Czech Republic. |
| Denmark | 33 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 3.6 times more electricity than Denmark. |
| Estonia | 10 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 12 times more electricity than Estonia. |
| Finland | 66 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 1.8 times more electricity than Finland. |
| Greece | 52 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 2.3 times more electricity than Greece. |
| Hungary | 38 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 3.2 times more electricity than Hungary. |
| Iceland | 18 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 6.7 times more electricity than Iceland. |
| Ireland | 33 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 3.6 times more electricity than Ireland. |
| Latvia | 8 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 15 times more electricity than Latvia. |
| Lithuania | 13 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 9.2 times more electricity than Lithuania. |
| Luxembourg | 7 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 17 times more electricity than Luxembourg. |
| Netherlands | 118 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 1.0 times more electricity than the Netherlands. |
| Norway | 133 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 0.9 times more electricity than Norway. |
| Portugal | 50 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 2.4 times more electricity than Portugal. |
| Slovakia | 25 | 120 | Bitcoin mining consumes 4.8 times more electricity than Slovakia. |
Note: The estimated annual electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining is based on data from the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index (CBECI). The electricity consumption of European countries is based on data from Eurostat.
Environmental Impact of Bitcoin Mining: Bitcoin Mining Requires More Electricity Than 20 European Countries
Bitcoin mining, the process of verifying and adding transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain, has a significant environmental impact due to its energy-intensive nature.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The energy used for Bitcoin mining comes primarily from fossil fuels, leading to the release of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide. These emissions contribute to climate change, a global environmental issue with far-reaching consequences. The amount of electricity consumed by Bitcoin mining is estimated to be comparable to the electricity consumption of entire countries.
Climate Change Impact
The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining is a major concern, as it exacerbates the already existing problem of climate change. The large-scale energy consumption associated with Bitcoin mining can lead to increased reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to the release of greenhouse gases and accelerating the rate of global warming.
Natural Resource Depletion
Bitcoin mining also has an impact on natural resources. The mining process requires vast amounts of electricity, which is often generated from non-renewable sources like coal and natural gas. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to the depletion of these resources, ultimately leading to environmental damage and resource scarcity.
Comparison to Other Industries
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining is often compared to the impact of other industries. While some argue that Bitcoin mining is comparable to industries like aviation, others claim that its impact is relatively small compared to industries like agriculture or manufacturing.
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining is a complex issue with various perspectives and considerations.
Solutions to Reduce Energy Consumption
The high energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is a significant concern, prompting exploration of solutions to mitigate its environmental impact. These solutions aim to reduce the energy intensity of the process, enhance energy efficiency, and promote the use of renewable energy sources.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Implementing energy efficiency improvements is crucial for reducing the energy footprint of Bitcoin mining. This involves optimizing mining hardware, software, and infrastructure to minimize energy consumption while maintaining or even increasing mining efficiency.
- Hardware Optimization: Advancements in semiconductor technology have led to the development of more energy-efficient ASIC chips, which are specifically designed for Bitcoin mining. These chips offer higher hash rates while consuming less power, contributing to reduced energy consumption per unit of mining output. Examples include the Antminer S19 series and the Whatsminer M30 series, which boast significant energy efficiency improvements compared to previous generations.
- Software Optimization: Mining software can be optimized to reduce energy consumption by improving resource allocation, minimizing idle time, and optimizing communication protocols. Efficient mining pools, which aggregate the computing power of multiple miners, can also contribute to energy efficiency by reducing the energy overhead associated with individual miners operating independently.
- Infrastructure Optimization: Optimizing the infrastructure used for Bitcoin mining can significantly reduce energy consumption. This includes optimizing cooling systems, using energy-efficient lighting and ventilation, and adopting data center designs that minimize energy waste.
Renewable Energy Sources
Leveraging renewable energy sources is essential for making Bitcoin mining more sustainable. By shifting to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power, Bitcoin mining can significantly reduce its carbon footprint.
- Solar Power: Solar panels can be installed on mining facilities or in nearby locations to generate clean electricity for mining operations. This approach is particularly suitable in regions with high solar irradiance, such as Arizona and Nevada in the United States.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines can be deployed in areas with strong wind resources to provide a sustainable source of energy for Bitcoin mining. This approach is well-suited for locations with consistent wind patterns, such as the Great Plains in the United States.
- Hydro Power: Hydroelectric dams can generate clean electricity from the flow of water, providing a reliable and sustainable energy source for Bitcoin mining. This approach is particularly suitable in regions with abundant water resources, such as the Pacific Northwest in the United States.
Mining Pool Optimization
Mining pools play a crucial role in Bitcoin mining by aggregating the computing power of multiple miners, thereby increasing the chances of finding a block and earning rewards. However, the energy consumption of mining pools can be optimized to reduce their environmental impact.
- Efficient Block Finding: Mining pools can optimize their block-finding algorithms to minimize the energy spent on unsuccessful mining attempts. This can be achieved by using sophisticated algorithms that prioritize profitable blocks and reduce the number of wasted computations.
- Energy-Efficient Communication: Mining pools can reduce energy consumption by optimizing communication protocols between miners and the pool server. This involves minimizing data transmission, using efficient communication protocols, and optimizing the network infrastructure.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Mining pools can encourage their members to use renewable energy sources by providing incentives or preferential treatment to miners who utilize clean energy. This can promote the adoption of renewable energy in the Bitcoin mining industry.
Regulation and Incentives, Bitcoin mining requires more electricity than 20 european countries
Government regulations and incentives can play a significant role in promoting the adoption of energy-efficient and sustainable Bitcoin mining practices.
- Carbon Tax: Implementing a carbon tax on Bitcoin mining could incentivize miners to reduce their energy consumption and transition to cleaner energy sources. This would create a financial incentive for miners to adopt sustainable practices.
- Renewable Energy Subsidies: Providing subsidies or tax breaks for miners who utilize renewable energy sources can encourage the adoption of clean energy in the Bitcoin mining industry. This would make renewable energy more affordable and accessible for miners.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Establishing energy efficiency standards for Bitcoin mining hardware and infrastructure can incentivize manufacturers to develop more energy-efficient products and encourage miners to adopt these technologies.
Alternative Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin’s energy consumption has sparked debate about its environmental impact. This has led to the exploration of alternative cryptocurrencies that consume less energy during their mining process.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Understanding the energy consumption of alternative cryptocurrencies requires a comparison with Bitcoin. Bitcoin’s energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism relies on miners solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. This process requires significant computational power, resulting in high energy consumption.
- Ethereum, before its transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), was also a PoW cryptocurrency, consuming considerable energy. However, its energy consumption was significantly lower than Bitcoin’s, estimated to be around 20% of Bitcoin’s energy consumption.
- Litecoin, another PoW cryptocurrency, uses a similar algorithm to Bitcoin but with a faster block time. Its energy consumption is estimated to be around 10% of Bitcoin’s.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative Cryptocurrencies
Alternative cryptocurrencies, especially those employing PoS consensus mechanisms, offer advantages in terms of energy consumption:
- Lower energy consumption: PoS algorithms eliminate the need for miners to solve complex mathematical problems. Instead, they rely on validators who stake their cryptocurrency holdings to secure the network. This significantly reduces energy consumption.
- Increased scalability: PoS systems can handle a higher number of transactions per second compared to PoW systems, making them more scalable.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- Potential for centralization: PoS systems can be susceptible to centralization if a few large stakeholders control a significant portion of the staked coins.
- Security concerns: PoS systems rely on the integrity of validators, and any malicious activity by a validator can compromise the network.
Potential for Replacement
The future of alternative cryptocurrencies in replacing Bitcoin is a complex issue. While PoS cryptocurrencies offer advantages in energy consumption and scalability, they also present challenges in terms of security and potential for centralization.
- Ethereum’s transition to PoS: Ethereum’s successful transition to PoS in 2022 has demonstrated the feasibility of reducing energy consumption while maintaining network security. This transition has significantly lowered Ethereum’s energy consumption, setting a precedent for other PoW cryptocurrencies.
- Market adoption: The adoption of alternative cryptocurrencies depends on factors like user experience, developer community support, and regulatory landscape.
- Technological advancements: Continued research and development in blockchain technology could lead to more efficient and energy-friendly consensus mechanisms.
Bitcoin mining requires more electricity than 20 european countries – While Bitcoin’s energy consumption is a major concern, it’s not all doom and gloom. The cryptocurrency community is actively exploring solutions to reduce energy consumption, including shifting to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. The future of Bitcoin and its environmental impact will depend on the success of these efforts and the willingness of the community to prioritize sustainability. Ultimately, the question remains: can we have a decentralized digital currency without sacrificing the health of our planet?
You know how Bitcoin mining uses more electricity than 20 European countries? Well, imagine that energy powering the rumored 5.5-inch screen on the Samsung Galaxy S6 Active, which is said to be coming out soon. It’s a little mind-boggling to think about, but it just goes to show how much power these technologies require.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News