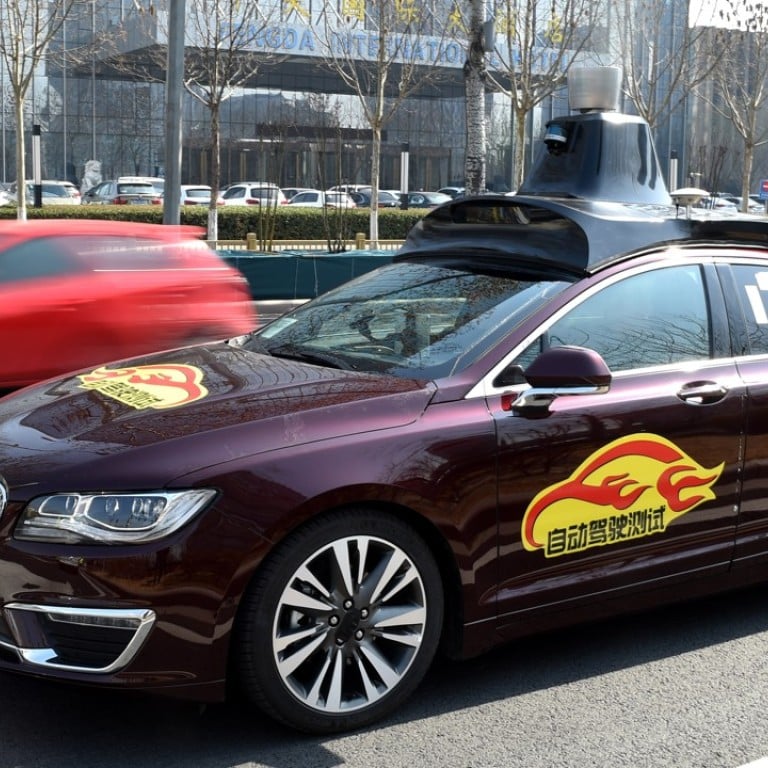
China’s Self-Driving Testing Regulations
China has emerged as a global leader in autonomous vehicle (AV) development, and its regulatory landscape for self-driving testing on public roads reflects this ambition. These regulations are designed to foster innovation while ensuring safety and public trust.
Current Regulations for Self-Driving Testing on Public Roads, China allow self driving testing public roads
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) is the primary regulatory body for AV testing. The MIIT has established a multi-layered regulatory framework, including:
- Licensing Requirements: AV developers must obtain a license from the MIIT before conducting public road testing. This license requires a thorough evaluation of the vehicle’s safety features, technical specifications, and the company’s testing capabilities.
- Testing Zones: The MIIT has designated specific testing zones in various cities across China. These zones offer controlled environments for AV developers to test their vehicles under real-world conditions.
- Safety Standards: China has implemented strict safety standards for AV testing, including requirements for redundancy in braking systems, sensor systems, and software.
- Data Collection and Privacy: Regulations also address data collection and privacy concerns, requiring AV developers to obtain user consent and implement data security measures.
Key Players and Initiatives
China’s burgeoning self-driving industry boasts a vibrant ecosystem of companies and initiatives, all vying to shape the future of mobility. From tech giants to automotive manufacturers, these key players are driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of autonomous vehicle technology.
The Chinese government’s proactive approach to self-driving technology has paved the way for significant investment and development. Several initiatives and projects are underway, fostering a thriving testing and deployment environment. These efforts aim to accelerate the adoption of self-driving vehicles, making China a leading player in the global autonomous driving landscape.
Major Companies Involved in Self-Driving Technology Development
These companies are actively developing self-driving technology, investing heavily in research, development, and testing. Their contributions are shaping the future of autonomous vehicles in China.
- Baidu: A leading internet search engine company, Baidu has established itself as a prominent player in the self-driving sector. Their Apollo platform, an open-source autonomous driving software suite, has gained significant traction within the industry, attracting partners and developers. Baidu has also been actively testing its self-driving vehicles in various cities across China.
- Tencent: Another tech giant, Tencent is investing in self-driving technology, leveraging its expertise in artificial intelligence and data analytics. They are exploring applications for autonomous vehicles, particularly in ride-hailing and logistics.
- Alibaba: Alibaba, a major e-commerce platform, is venturing into the self-driving space through its cloud computing and logistics divisions. They are developing solutions for autonomous delivery and transportation, aiming to optimize efficiency and enhance customer experiences.
- Didi Chuxing: A leading ride-hailing platform in China, Didi Chuxing is actively developing its own self-driving technology. Their focus is on developing autonomous vehicles for ride-hailing services, aiming to enhance safety and convenience for passengers.
- NIO: A rising electric vehicle manufacturer, NIO is integrating self-driving capabilities into its vehicles. Their efforts are focused on developing autonomous features for passenger vehicles, aiming to enhance safety and driving experience.
- Xpeng: Another electric vehicle manufacturer, Xpeng is making significant strides in self-driving technology. They are developing autonomous driving features for their vehicles, aiming to provide advanced driver-assistance systems and ultimately achieve full autonomy.
- Huawei: A global telecommunications giant, Huawei is leveraging its expertise in connectivity and data processing to contribute to self-driving technology. They are developing components and solutions for autonomous vehicles, focusing on areas like communication, sensing, and data analysis.
- SAIC Motor: One of China’s largest automotive manufacturers, SAIC Motor is collaborating with tech companies to develop self-driving vehicles. They are actively testing and deploying autonomous vehicles in various regions, aiming to integrate self-driving technology into their production vehicles.
- GAC Group: Another prominent automotive manufacturer, GAC Group is investing in self-driving technology, developing autonomous driving features for its vehicles. They are actively collaborating with tech companies and research institutions to advance their self-driving capabilities.
Notable Initiatives and Projects Related to Self-Driving Vehicle Testing in China
The Chinese government has established various initiatives and projects to promote the development and testing of self-driving vehicles. These programs aim to create a favorable environment for innovation and accelerate the adoption of autonomous driving technology.
- The Beijing Intelligent Connected Vehicle Pilot Zone: Launched in 2017, this pilot zone provides a dedicated space for testing and demonstrating self-driving vehicles. It offers a controlled environment for companies to evaluate their technology and gather valuable data. The pilot zone is located in the Yizhuang Economic Development Zone, south of Beijing, and features a network of roads and infrastructure specifically designed for autonomous vehicle testing.
- The Shanghai Intelligent Connected Vehicle Pilot Zone: Established in 2018, this pilot zone focuses on promoting the development and deployment of self-driving vehicles in the city of Shanghai. It provides a testing environment for autonomous vehicles, covering various scenarios, including urban roads, highways, and parking lots. The pilot zone is located in the Jiading District, a hub for automotive manufacturing in Shanghai, and offers a dedicated infrastructure for testing and demonstration.
- The Chongqing Intelligent Connected Vehicle Pilot Zone: Launched in 2019, this pilot zone aims to foster the development of self-driving technology in the city of Chongqing. It provides a testing environment for autonomous vehicles, focusing on challenging urban scenarios, such as mountainous terrain and complex road conditions. The pilot zone is located in the Liangjiang New Area, a major economic development zone in Chongqing, and offers a unique testing environment for autonomous vehicles.
Successful Deployments or Pilot Programs in Specific Regions
The development and deployment of self-driving vehicles in China have seen notable successes in specific regions. These pilot programs showcase the progress made in integrating autonomous driving technology into real-world scenarios.
- Baidu’s Apollo Go ride-hailing service: Launched in 2019, Apollo Go offers self-driving taxi services in several Chinese cities, including Beijing, Guangzhou, and Changsha. The service operates in designated areas and utilizes Baidu’s Apollo platform for autonomous driving capabilities. Passengers can hail a self-driving taxi through a mobile app and experience the convenience of autonomous transportation.
- Didi Chuxing’s self-driving ride-hailing service: Didi Chuxing has been conducting pilot programs for self-driving ride-hailing services in several cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. Their efforts are focused on integrating autonomous vehicles into their existing ride-hailing platform, aiming to provide a seamless and convenient experience for passengers.
- SAIC Motor’s self-driving buses: SAIC Motor has deployed self-driving buses in several Chinese cities, including Shanghai and Beijing. These buses operate on designated routes and provide autonomous transportation services, showcasing the potential of self-driving technology in public transportation.
Challenges and Opportunities
China’s foray into self-driving vehicle testing on public roads presents a unique blend of challenges and opportunities. While the government’s commitment to innovation and the vast potential of this technology are undeniable, navigating the complexities of infrastructure, public perception, and ethical considerations will be crucial for its successful adoption.
Infrastructure Challenges
The existing infrastructure in China, while undergoing rapid modernization, still presents challenges for self-driving vehicles.
- Road conditions: China’s vast road network, encompassing both urban and rural areas, exhibits varying levels of maintenance and quality. This inconsistency can pose difficulties for self-driving systems, requiring robust sensors and algorithms to adapt to diverse road conditions.
- Traffic density: China’s rapidly growing cities experience high traffic density, making navigation and decision-making more complex for self-driving vehicles. This requires advanced algorithms and sensors to handle dense traffic situations effectively.
- Lack of standardized infrastructure: The absence of standardized infrastructure, such as dedicated lanes for autonomous vehicles or advanced traffic management systems, poses challenges for seamless integration and operation. This necessitates collaboration between government agencies and technology companies to develop and implement standardized infrastructure.
Public Perception and Trust
Gaining public trust and acceptance is critical for the widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles.
- Safety concerns: Public perception of self-driving vehicles is often influenced by safety concerns. Concerns about accidents and the potential for system malfunctions need to be addressed through robust testing, data transparency, and clear regulations.
- Job displacement: The potential for job displacement in sectors like transportation is a significant concern. Addressing this requires proactive measures, such as retraining programs and social safety nets to ensure a smooth transition for workers affected by automation.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical dilemmas surrounding self-driving vehicles, such as decision-making in emergency situations, need to be carefully considered and addressed. This requires open dialogue and collaboration between stakeholders, including ethicists, policymakers, and technology developers.
Opportunities and Benefits
The development and adoption of self-driving technology hold immense potential for China’s transportation system and economy.
- Enhanced safety: Self-driving vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents, as they are not susceptible to human error. This could lead to a safer and more efficient transportation system.
- Improved traffic flow: Self-driving vehicles can optimize traffic flow by communicating with each other and infrastructure, reducing congestion and improving efficiency. This can lead to faster commute times and reduced fuel consumption.
- Accessibility and mobility: Self-driving vehicles can provide increased accessibility and mobility for people with disabilities, seniors, and those living in remote areas. This can promote social inclusion and economic opportunities.
- Economic growth: The development and deployment of self-driving technology can create new industries and jobs, boosting economic growth. This includes sectors like software development, sensor manufacturing, and data analysis.
Government Policies and Investments
Government policies and investments play a crucial role in fostering self-driving innovation.
- Regulatory framework: China’s government has established a comprehensive regulatory framework for self-driving vehicle testing and deployment, including clear guidelines for safety, data privacy, and ethical considerations. This provides a foundation for responsible development and deployment of the technology.
- Financial incentives: The government has introduced financial incentives and subsidies to encourage research and development in self-driving technology. This includes funding for research projects, tax breaks for companies, and investments in infrastructure development.
- Public-private partnerships: China’s government actively promotes public-private partnerships to accelerate the development and adoption of self-driving technology. This involves collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and technology companies to share resources, expertise, and knowledge.
Safety and Security Considerations: China Allow Self Driving Testing Public Roads
The deployment of self-driving vehicles on public roads in China raises critical safety and security concerns. While China is aggressively pursuing autonomous vehicle technology, it’s crucial to address these concerns to ensure public trust and safety.
Safety Protocols and Measures
China has implemented various safety protocols and measures to mitigate risks during self-driving testing on public roads. These protocols are designed to address potential hazards associated with autonomous vehicles, including:
- Strict Testing Requirements: China mandates rigorous testing procedures for self-driving vehicles before they can be deployed on public roads. These tests evaluate the vehicle’s performance under various conditions, including extreme weather, heavy traffic, and complex road scenarios.
- Human Supervision: During testing, human drivers must be present in the vehicle to take control in emergencies. This ensures a human safety net in case of unforeseen circumstances or system failures.
- Data Logging and Analysis: Self-driving vehicles collect extensive data during testing, including sensor readings, vehicle control inputs, and environmental conditions. This data is analyzed to identify potential safety issues and improve system performance.
- Safety Features: Autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced safety features, such as automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control. These features help prevent accidents and mitigate potential risks.
Cybersecurity in Autonomous Vehicles
Cybersecurity is paramount in ensuring the safe operation of self-driving vehicles. The potential for cyberattacks on autonomous vehicles is a significant concern, as malicious actors could compromise vehicle systems and cause accidents.
- Secure Software Development: China emphasizes secure software development practices to minimize vulnerabilities in autonomous vehicle systems. This includes rigorous code reviews, security testing, and the use of secure coding standards.
- Network Security: Protecting vehicle networks from unauthorized access is crucial. China is developing standards for secure communication protocols and encryption to safeguard data transmitted between vehicles and infrastructure.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Regular software updates are essential to address vulnerabilities and improve system security. China encourages manufacturers to implement secure over-the-air update mechanisms to ensure timely security patches.
- Cybersecurity Monitoring: Real-time monitoring systems are being developed to detect and respond to cyberattacks. These systems can identify suspicious activity and trigger countermeasures to protect vehicle systems.
Safety Record of Self-Driving Vehicles in China
While China has made significant progress in developing and testing self-driving vehicles, it’s too early to assess the safety record definitively. The number of autonomous vehicles deployed on public roads is still relatively small, and comprehensive data on accident rates is limited.
- Limited Data: Data on accidents involving self-driving vehicles in China is not readily available. The Chinese government is currently working to establish a comprehensive data collection system to monitor and analyze accidents involving autonomous vehicles.
- Comparison with Other Countries: China is actively learning from the experiences of other countries, such as the United States and Europe, in developing safety standards and regulations for self-driving vehicles. Data from these countries suggests that autonomous vehicles have the potential to improve road safety, but it’s important to note that these technologies are still evolving.
Public Perception and Acceptance
China’s journey towards widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles is heavily influenced by public perception. The acceptance of this technology is not solely determined by its technological prowess but also by how it resonates with societal values and addresses public concerns.
Public Attitudes towards Self-Driving Vehicles
Public attitudes towards self-driving vehicles in China are a complex mix of excitement, apprehension, and uncertainty. While many see the potential for improved safety, efficiency, and convenience, concerns about safety, job displacement, and privacy remain prevalent.
- Safety: A 2022 survey by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) revealed that 65% of respondents expressed concerns about the safety of self-driving vehicles, particularly in challenging driving conditions or during emergencies.
- Job Displacement: The potential for self-driving vehicles to automate driving tasks has led to concerns about job displacement in the transportation sector. This concern is particularly acute in China, where millions of people rely on driving-related jobs for their livelihood.
- Privacy: Concerns about data privacy are significant, as self-driving vehicles collect and process vast amounts of data about their surroundings, passengers, and driving habits. There are anxieties about how this data will be used and protected.
Future Outlook
China’s ambitious self-driving vehicle testing program has positioned the country as a global leader in this rapidly evolving field. With its vast population, expanding urban centers, and supportive government policies, China is primed to witness a significant transformation in its transportation landscape. This section delves into the potential impact of self-driving technology on China’s transportation sector, urban planning, and society as a whole, while also identifying key trends and factors that will shape the development of self-driving technology in the coming years.
Impact on Transportation Sector
The widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles is expected to revolutionize China’s transportation sector, bringing about significant changes in efficiency, safety, and accessibility.
- Increased Efficiency: Self-driving vehicles can operate 24/7, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow. They can also optimize routes and driving patterns, leading to faster and more efficient transportation. For example, the city of Shenzhen is already experimenting with self-driving buses on specific routes, showcasing the potential for improved public transportation efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Self-driving vehicles are programmed to adhere to traffic regulations and are not susceptible to human error, which is a leading cause of accidents. Studies have shown that self-driving vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce the number of accidents and fatalities on the road. For example, Waymo, a leading self-driving technology company, has reported millions of miles of safe autonomous driving in real-world conditions.
- Improved Accessibility: Self-driving vehicles can provide transportation options for individuals who are currently unable to drive, such as the elderly, disabled, and those who live in rural areas with limited public transportation. This could significantly enhance mobility and independence for a large segment of the population.
Impact on Urban Planning
The introduction of self-driving vehicles will have a profound impact on urban planning, leading to a shift towards more pedestrian-friendly and sustainable cities.
- Reduced Parking Demand: Self-driving vehicles can communicate with each other and park themselves efficiently, reducing the need for large parking lots. This will free up valuable urban space for green areas, public amenities, and other uses.
- Reimagined Cityscapes: The shift towards self-driving vehicles could lead to a redesign of urban spaces, with a greater emphasis on pedestrian walkways, bike lanes, and public transportation. This could create more vibrant and livable urban environments.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Self-driving vehicles have the potential to reduce emissions and promote sustainable transportation. By optimizing routes and reducing congestion, they can significantly minimize fuel consumption and carbon footprint.
Impact on Society
The widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles will have a far-reaching impact on society, affecting various aspects of daily life.
- Job Market Transformation: The transition to self-driving vehicles will likely displace jobs in the transportation sector, particularly for truck drivers and taxi drivers. However, it will also create new job opportunities in areas such as software development, data analysis, and vehicle maintenance.
- Increased Productivity: Self-driving vehicles can free up time for passengers, allowing them to work, relax, or socialize while traveling. This could lead to increased productivity and a more efficient use of time.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: The use of self-driving vehicles can contribute to a safer and more secure transportation system, with the potential to reduce crime rates and improve public safety.
Key Trends and Factors
The development of self-driving technology in China is influenced by several key trends and factors, including:
- Government Support: The Chinese government has actively promoted the development and deployment of self-driving vehicles through supportive policies, funding, and infrastructure development. This strong government backing is crucial for the rapid advancement of the industry.
- Technological Advancements: China’s tech giants, such as Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent, are investing heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and autonomous driving technologies. These advancements are driving innovation and accelerating the development of self-driving vehicles.
- Data Availability: China has a wealth of data on traffic patterns, road conditions, and user behavior, which is crucial for training and validating self-driving algorithms. This data advantage is helping China to develop sophisticated self-driving systems.
- Infrastructure Development: China is investing heavily in the development of smart city infrastructure, including connected roads, traffic management systems, and charging stations. This infrastructure is essential for the seamless operation of self-driving vehicles.
China allow self driving testing public roads – As China continues to refine its regulations and foster innovation, the future of self-driving technology in the country appears bright. With a blend of ambition, rigorous safety standards, and a commitment to responsible development, China is poised to become a major player in the global autonomous vehicle landscape. This journey, however, is not without its challenges. Balancing innovation with public safety, addressing ethical concerns, and navigating the complex interplay of technology, infrastructure, and social acceptance will be crucial to realizing the full potential of self-driving technology in China.
China’s recent move to allow self-driving car testing on public roads is a huge leap forward for the future of transportation. While robots take over the streets, photographers can still capture the moment with the new Canon EOS M5 officially announced. This new camera offers advanced features like 4K video recording and a high-resolution sensor, perfect for capturing the sleek lines of autonomous vehicles cruising through the city.
The future is looking pretty exciting, both on the road and behind the lens.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News