Cisa government sisense reset credentials cyberattack – Imagine a scenario where a government agency’s data analytics platform, Sisense, becomes the target of a sophisticated cyberattack. This isn’t a far-fetched thriller; it’s a real-world threat, and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) is on the frontlines of safeguarding government systems from such attacks. CISA, Sisense, and the reset credentials cyberattack are intertwined in a complex web of cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and understanding the nuances of this threat is crucial for protecting government data and operations.
Government agencies rely heavily on data analytics tools like Sisense to make informed decisions, but these platforms can also become entry points for cybercriminals. The potential for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in Sisense to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data, or even disrupt critical government functions is a serious concern. This is where CISA steps in, providing guidance, resources, and support to government agencies to bolster their cybersecurity posture and mitigate these risks.
CISA Government Cybersecurity
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) plays a critical role in safeguarding government systems and networks from cyber threats. It serves as a vital resource for federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial governments, providing guidance, tools, and support to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
CISA’s Role in Protecting Government Systems
CISA’s primary mission is to protect the nation’s critical infrastructure from cyberattacks. This includes providing guidance and resources to government agencies to improve their cybersecurity practices and respond to incidents. CISA’s efforts encompass various activities, including:
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: CISA collects and analyzes threat intelligence to identify emerging cyber threats and vulnerabilities. It shares this information with government agencies, enabling them to proactively defend against attacks.
- Vulnerability Management: CISA identifies and assesses vulnerabilities in government systems and networks. It provides guidance and resources to help agencies patch vulnerabilities and mitigate risks.
- Incident Response: CISA assists government agencies in responding to cyber incidents. It provides technical support, guidance, and coordination to help agencies contain and recover from attacks.
- Cybersecurity Awareness and Training: CISA conducts cybersecurity awareness and training programs for government employees. These programs aim to educate employees about cybersecurity threats, best practices, and how to identify and report suspicious activity.
Importance of CISA’s Guidance and Resources
CISA’s guidance and resources are essential for government agencies to effectively manage cybersecurity risks. These resources provide agencies with the knowledge, tools, and support they need to:
- Develop and implement robust cybersecurity policies and procedures.
- Identify and assess cybersecurity risks.
- Protect sensitive data and systems from cyberattacks.
- Respond effectively to cyber incidents.
CISA’s Initiatives to Improve Cybersecurity Posture
CISA has implemented several initiatives to enhance the cybersecurity posture of government agencies. Some notable examples include:
- The Continuous Diagnostics and Mitigation (CDM) Program: This program provides agencies with tools and resources to continuously monitor and assess their cybersecurity posture. It helps agencies identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.
- The National Cybersecurity Protection System (NCPS): This system provides a framework for sharing information and coordinating cybersecurity efforts across government agencies. It helps agencies to collaborate and learn from each other’s experiences.
- The Cybersecurity Capacity Program (CCP): This program provides funding and technical assistance to state, local, tribal, and territorial governments to improve their cybersecurity capabilities.
Sisense and Government Data Security: Cisa Government Sisense Reset Credentials Cyberattack
Sisense is a powerful business intelligence (BI) platform that helps organizations analyze and visualize data to make informed decisions. It’s widely used in government agencies for various purposes, including financial reporting, performance management, and citizen engagement. This popularity stems from Sisense’s ability to handle large datasets, its intuitive user interface, and its flexibility in creating dashboards and reports.
Data Analytics and Reporting in Government, Cisa government sisense reset credentials cyberattack
Government agencies face a unique set of challenges when it comes to data analytics and reporting. They need to be able to access and analyze data from multiple sources, often with complex data structures. They also need to ensure that their data is accurate, secure, and compliant with regulations. Sisense can help government agencies address these challenges by providing a centralized platform for data analysis and reporting.
- Financial Reporting: Sisense can be used to create financial reports that track spending, revenue, and budget performance. This information is crucial for ensuring fiscal responsibility and transparency.
- Performance Management: Sisense can be used to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the effectiveness of government programs. This data can help agencies identify areas for improvement and optimize their operations.
- Citizen Engagement: Sisense can be used to create dashboards and reports that provide citizens with access to information about government services. This can help improve transparency and accountability, and foster trust in government.
Security Risks Associated with Sisense
While Sisense offers significant benefits to government agencies, it’s essential to be aware of the potential security risks associated with its use.
- Data Breaches: If Sisense is not properly secured, sensitive government data could be exposed to unauthorized access. This could lead to data breaches, identity theft, and other serious consequences.
- Data Manipulation: Unauthorized users could potentially manipulate data within Sisense, leading to inaccurate reports and compromised decision-making.
- System Downtime: A cyberattack or system failure could disrupt Sisense’s operations, leading to downtime and impacting critical government services.
Securing Sisense Deployments in Government
To mitigate these risks, government agencies need to implement robust security measures when deploying Sisense. Here are some key recommendations:
- Access Control: Implement strong access control measures to limit access to Sisense to authorized users. This includes using multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all data stored and transmitted within Sisense, both at rest and in transit. This helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access even if the system is compromised.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security controls are effective.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide security awareness training to all users of Sisense to educate them about potential threats and best practices for protecting data.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate Sisense systems from other critical government networks to prevent lateral movement of attackers.
- Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management program to ensure that Sisense systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration from Sisense systems.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security incidents effectively.
Resetting Credentials in Government Systems
Government systems are the backbone of our nation’s infrastructure, handling sensitive data and critical operations. Securing these systems is paramount, and a crucial element of this security is maintaining strong and secure credentials.
Importance of Strong Password Policies
Strong password policies are essential for safeguarding government systems from unauthorized access. These policies dictate the complexity and frequency of password changes, ensuring that credentials are robust and difficult to guess.
- Minimum Length and Complexity: Passwords should meet minimum length requirements (e.g., 12 characters) and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to use brute-force methods to crack passwords.
- Regular Password Rotation: Government employees should be required to change their passwords regularly, typically every 90 days. This helps mitigate the risk of compromised credentials being used for extended periods.
- Password History: Systems should prevent users from reusing passwords from a recent history, ensuring that even if a password is compromised, it cannot be immediately reused.
- Password Complexity Enforcement: Password policies should enforce complexity requirements, such as prohibiting common words or easily guessable patterns. This adds another layer of security by making it harder for attackers to guess passwords.
Risks Associated with Weak or Compromised Credentials
Weak or compromised credentials pose a significant threat to government systems, potentially leading to data breaches, system disruptions, and financial losses.
- Data Breaches: Attackers can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, and national security secrets. This can have devastating consequences for individuals, organizations, and the nation as a whole.
- System Disruptions: Compromised credentials can be used to disrupt critical government services, leading to service outages, data loss, and financial losses. This can have a significant impact on the economy and national security.
- Financial Losses: Attackers can use compromised credentials to steal funds, commit fraud, or manipulate financial systems. This can result in significant financial losses for the government and taxpayers.
- Reputation Damage: Data breaches and system disruptions can damage the reputation of government agencies, eroding public trust and confidence.
Best Practices for Resetting Credentials
Resetting credentials is a critical process that must be handled securely and efficiently to minimize risks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all government systems. This requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device, making it much harder for attackers to gain access.
- Secure Password Reset Mechanisms: Use secure password reset mechanisms, such as email or SMS-based verification, to ensure that only authorized users can reset their passwords.
- Password Complexity Enforcement: During password reset, enforce strong password policies to ensure that users create new passwords that meet the minimum complexity requirements.
- Account Lockout: Implement account lockout policies to prevent brute-force attacks. After a certain number of failed login attempts, an account should be temporarily locked to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities related to credential management. This includes reviewing password policies, identifying weak passwords, and assessing the effectiveness of security controls.
Cyberattacks Targeting Government Agencies
Government agencies are increasingly becoming targets of cyberattacks, posing significant threats to national security, economic stability, and public trust. These attacks can disrupt critical services, compromise sensitive information, and undermine the government’s ability to function effectively.
Motivations Behind Cyberattacks
The motivations behind cyberattacks targeting government agencies are diverse and complex, ranging from financial gain to political influence and espionage.
- Financial Gain: Cybercriminals often target government agencies for financial gain, seeking to steal sensitive data, such as financial records or personal information, which can be sold on the black market or used for identity theft.
- Political Influence: Nation-state actors and politically motivated groups may launch cyberattacks to disrupt government operations, influence elections, or spread propaganda.
- Espionage: Intelligence agencies may target government agencies to gather information on national security, military capabilities, or foreign policy decisions.
- Ideological Motivations: Hacktivist groups may target government agencies to protest government policies or promote their own ideologies.
- Extortion: Cybercriminals may demand ransom payments from government agencies to prevent the release of stolen data or to restore access to compromised systems.
Examples of Recent Cyberattacks
Recent years have witnessed a surge in cyberattacks targeting government agencies worldwide. Some notable examples include:
- The SolarWinds Hack (2020): Russian government-backed hackers compromised the software supply chain of SolarWinds, a software company used by numerous government agencies and private organizations. The attack allowed attackers to gain access to sensitive data and systems, including those of the U.S. Treasury and Commerce Departments.
- The Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021): A ransomware attack on Colonial Pipeline, a major fuel pipeline in the United States, caused widespread disruptions to fuel supply chains and highlighted the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyberattacks.
- The NotPetya Attack (2017): A ransomware attack attributed to Russia, NotPetya, targeted organizations worldwide, including several government agencies. The attack caused billions of dollars in damages and disrupted government operations in several countries.
Potential Impact of Successful Cyberattacks
Successful cyberattacks against government agencies can have far-reaching consequences, including:
- Disruption of Critical Services: Cyberattacks can disrupt essential government services, such as healthcare, transportation, and law enforcement, leading to significant public inconvenience and potential harm.
- Compromise of Sensitive Information: Hackers can steal sensitive information, such as classified documents, financial records, and personal data, compromising national security, privacy, and public trust.
- Economic Damage: Cyberattacks can cause significant economic damage, disrupting government operations, hindering economic growth, and increasing costs for taxpayers.
- Loss of Public Trust: Cyberattacks can erode public trust in government institutions, particularly if they result in the loss of sensitive information or the disruption of essential services.
- Escalation of Conflicts: Cyberattacks can escalate tensions between nations, particularly if they are attributed to state actors, leading to international disputes and potential military confrontations.
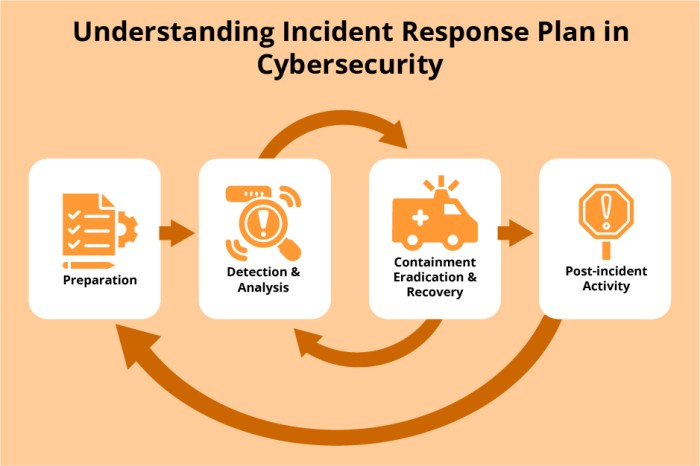
Incident Response and Recovery
In the face of evolving cyber threats, a robust incident response plan is crucial for government agencies to mitigate damage, ensure business continuity, and maintain public trust. A well-defined plan enables swift and effective responses to cyberattacks, minimizing disruption and maximizing recovery efforts.
Responding to a Cyberattack
Responding to a cyberattack involves a systematic and coordinated approach, encompassing several key steps.
- Detection and Analysis: Promptly detecting suspicious activity is critical. This involves implementing security monitoring tools, intrusion detection systems, and continuous threat intelligence gathering. Upon detection, the agency must analyze the nature and scope of the attack, identifying the compromised systems, data affected, and potential impact.
- Containment: Once the attack is identified, immediate action is necessary to contain its spread. This might involve isolating infected systems, disconnecting from the network, or implementing security controls to restrict access. The goal is to prevent further damage and data exfiltration.
- Eradication: The next step involves eradicating the threat by removing malicious software, restoring compromised systems to a clean state, and patching vulnerabilities. This process may require specialized tools, forensic analysis, and collaboration with security experts.
- Recovery: After the threat is eradicated, the agency must focus on restoring normal operations. This involves recovering lost data, restoring systems, and ensuring business continuity. The recovery process may involve data backups, system recovery procedures, and potentially reconfiguring network infrastructure.
- Post-Incident Review: A thorough post-incident review is essential to learn from the experience and improve future defenses. This involves analyzing the attack, identifying weaknesses in security controls, and implementing corrective actions to enhance resilience.
Recovering from a Cyberattack
Recovering from a cyberattack involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing several key recommendations.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly backing up critical data and systems is paramount. This ensures data can be restored in the event of a cyberattack or other disaster. Implementing a comprehensive backup strategy, including off-site backups, is essential.
- Business Continuity Planning: Having a robust business continuity plan is crucial for maintaining critical operations during and after a cyberattack. This plan should Artikel alternative operational processes, communication protocols, and resource allocation strategies to minimize disruption.
- Vulnerability Management: Proactively identifying and patching vulnerabilities in systems and software is vital. This involves regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, applying security updates, and implementing strong password policies.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices is crucial. This includes training on phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and proper password management.
- Incident Response Team: Establishing a dedicated incident response team with expertise in cybersecurity is essential. This team should be responsible for coordinating response efforts, communicating with stakeholders, and managing the recovery process.
The intersection of CISA, Sisense, and reset credentials cyberattacks highlights the ever-evolving landscape of government cybersecurity. As technology advances and cybercriminals become more sophisticated, it’s essential for government agencies to stay vigilant and proactively address vulnerabilities. Implementing strong password policies, securing Sisense deployments, and having robust incident response plans are critical components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By working together, CISA and government agencies can build a more resilient and secure digital environment.
The CISA government’s recent Sisense reset credentials cyberattack highlights the importance of strong cybersecurity measures, especially in government agencies. While we’re all grappling with the fallout from this attack, it’s hard not to wonder if we’ll ever get to play the long-awaited Mortal Kombat X on our PS3s and Xbox 360s, or if has Mortal Kombat X for PS3Xbox 360 been delayed again.
Regardless of the gaming world’s woes, the CISA government’s Sisense reset credentials cyberattack serves as a stark reminder of the constant threat posed by cybercriminals, and the need for vigilance in protecting our data.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News