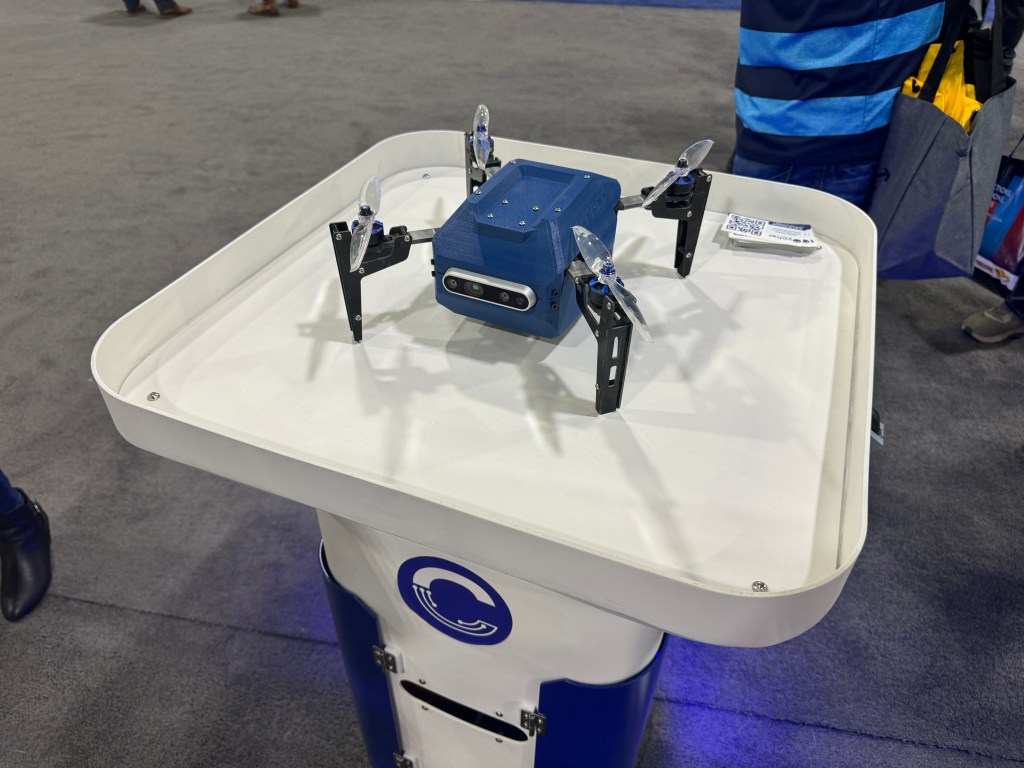
Cyphers inventory drone launches from an autonomous mobile robot base – Imagine a future where warehouses and factories are patrolled by autonomous robots, each carrying a swarm of drones. These drones, known as “cyber inventory drones,” are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, allowing them to scan and track every item within a facility, from raw materials to finished products. These drones are launched and retrieved by mobile robot bases, which act as their home base and command center. This cutting-edge technology has the potential to revolutionize inventory management, offering unprecedented levels of accuracy, efficiency, and real-time visibility.
This system works by integrating drones with a network of mobile robot bases. These bases are equipped with sophisticated navigation systems and communication networks, enabling them to move around facilities autonomously and coordinate drone operations. The drones themselves are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, including inventory tracking, asset monitoring, and data collection. They can even identify and report any discrepancies or anomalies in stock levels, ensuring that businesses always have a clear picture of their inventory status.
Cyber Inventory Drone Technology
Cyber inventory drones represent a cutting-edge approach to inventory management, leveraging the power of autonomous flight and advanced sensing capabilities to revolutionize how businesses track and manage their assets.
Operational Principles of Cyber Inventory Drones
Cyber inventory drones are typically equipped with sophisticated software and hardware that enable them to navigate autonomously within designated areas. They rely on a combination of technologies, including:
- GPS and GNSS: For precise positioning and navigation.
- LiDAR or 3D cameras: To create detailed maps of the environment and identify objects.
- Computer vision algorithms: To analyze images and videos, recognizing specific objects and their locations.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): To optimize flight paths, manage data collection, and perform advanced analysis.
These drones are often integrated with a central control system that manages their operations, data collection, and analysis.
Types of Sensors and Payloads
The sensors and payloads carried by cyber inventory drones are tailored to the specific tasks they are designed to perform.
- Barcode and RFID readers: For identifying and tracking individual items with unique labels.
- Thermal cameras: To detect temperature anomalies, potentially indicating issues with equipment or storage conditions.
- Multispectral cameras: To capture images in different wavelengths, allowing for analysis of materials and conditions that may not be visible to the human eye.
- Gas sensors: To detect the presence of specific gases, such as leaks or hazardous substances.
- Environmental sensors: To measure parameters like temperature, humidity, and light levels.
Specific Tasks Cyber Inventory Drones Can Perform
Cyber inventory drones can perform a wide range of tasks, making them valuable tools for businesses across various industries.
- Inventory tracking: Drones can scan warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities to quickly and accurately track inventory levels, identify missing or misplaced items, and optimize stock management.
- Asset monitoring: Drones can be used to inspect critical infrastructure, such as pipelines, power lines, and solar farms, identifying potential issues and preventing costly downtime.
- Data collection: Drones can collect data on environmental conditions, such as air quality, soil moisture, and vegetation health, aiding in environmental monitoring and resource management.
- Security and surveillance: Drones can be deployed for perimeter security, detecting unauthorized entry or suspicious activity, and providing real-time situational awareness.
Autonomous Mobile Robot Base: Cyphers Inventory Drone Launches From An Autonomous Mobile Robot Base
The autonomous mobile robot base serves as a central hub for the Cyber Inventory Drone fleet, providing a platform for launching, landing, and managing the drones. It is a crucial component of the system, ensuring efficient and reliable drone operations.
Design and Functionality
The autonomous mobile robot base is designed to be a robust and adaptable platform. It typically consists of a chassis equipped with wheels or tracks for mobility, a payload bay for storing and deploying drones, a power source, communication systems, and sensors for navigation and environmental awareness. The base can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as payload capacity, range, and operating environment.
The base utilizes advanced navigation systems, such as GPS, inertial navigation systems (INS), and LiDAR, to accurately determine its position and navigate autonomously. It can also use map-based navigation and path planning algorithms to plan optimal routes and avoid obstacles. Communication systems, including radio frequency (RF) and cellular networks, enable the base to communicate with the drones and the central control station, providing real-time data and control.
Power Sources and Energy Management
The autonomous mobile robot base is powered by a combination of battery packs and solar panels, depending on the specific application. The base’s energy management system optimizes power consumption and ensures sufficient energy for both the base and the drones. The drones are typically equipped with their own batteries, which can be recharged at the base. The base may also incorporate energy harvesting technologies, such as wind turbines or piezoelectric sensors, to supplement its power sources.
Drone Launch and Retrieval Mechanisms
The design of a drone launch and retrieval system for a mobile robot base is crucial for ensuring efficient and safe operation. This system needs to be reliable, robust, and adaptable to various environmental conditions.
The launch and retrieval mechanism should be integrated with the robot base’s autonomous navigation system, allowing for seamless drone deployment and retrieval. This integration ensures that the drones can be launched and retrieved at the optimal location and time, maximizing their operational efficiency.
Safety Considerations and Procedures
Safety is paramount in the design and operation of any drone system. The following considerations are essential for ensuring safe drone launch and landing:
* Drone Launch:
* Clear Launch Area: The launch area must be free of obstacles and hazards, ensuring a clear path for the drone to ascend.
* Wind Conditions: The wind speed and direction should be within the drone’s operating limits to prevent instability during takeoff.
* Emergency Stop Mechanisms: The drone should have an emergency stop mechanism that allows for immediate termination of flight in case of unexpected events.
* Drone Landing:
* Designated Landing Zone: A designated landing zone must be established, ensuring a safe and controlled landing.
* Landing Guidance System: The drone should be equipped with a landing guidance system to assist in precision landing, especially in challenging environments.
* Obstacle Detection: The drone should have obstacle detection capabilities to avoid collisions during landing.
The integration of the launch and retrieval mechanism with the robot base’s autonomous navigation system is essential for achieving efficient and coordinated operations.
* Location Tracking: The robot base’s navigation system must accurately track the location of the drones during launch and retrieval.
* Path Planning: The navigation system should plan the optimal path for the robot base to reach the designated launch and landing zones.
* Synchronization: The launch and retrieval mechanism should be synchronized with the robot base’s movements to ensure smooth and timely drone deployment and retrieval.
Integration and Coordination
The seamless operation of the Cypher Inventory Drone system relies on a robust and intelligent integration of the drones, the autonomous mobile robot base, and the overarching control system. This integration encompasses communication protocols, data exchange mechanisms, software architecture, and the application of artificial intelligence to optimize drone missions.
Communication Protocols and Data Exchange
Effective communication between the drones and the robot base is crucial for coordinating drone operations and ensuring data accuracy. The system employs a combination of wireless communication protocols, including:
- Wi-Fi: For short-range communication between drones and the robot base when they are within close proximity.
- Cellular Networks: For long-range communication, enabling the drones to remain connected to the base even when they are operating beyond the immediate vicinity of the robot.
- Satellite Communication: For communication in remote or challenging environments where cellular coverage is limited.
Data exchange between the drones and the robot base is handled through a secure and efficient data transfer protocol, ensuring the reliable transmission of inventory data, flight parameters, and mission updates.
Software Architecture and Coordination Algorithms
The software architecture of the Cypher Inventory Drone system is designed to manage and coordinate drone operations effectively. It employs a centralized control system, where the robot base serves as the central hub for coordinating all drone activities. The software architecture encompasses the following components:
- Mission Planning: The system utilizes advanced algorithms to plan drone missions, taking into account factors such as inventory targets, geographical constraints, and optimal flight paths.
- Drone Control: The software provides real-time control over the drones, enabling adjustments to flight paths, altitude, and speed based on environmental conditions and mission requirements.
- Data Processing: The system gathers and processes data collected by the drones, including inventory information, sensor readings, and flight logs, for analysis and reporting.
- Autonomous Navigation: The software enables the drones to navigate autonomously using GPS, sensor data, and pre-programmed flight plans, reducing reliance on human intervention.
The coordination algorithms employed by the system ensure efficient and synchronized drone operations, enabling the drones to work together to complete inventory tasks effectively.
Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of the Cypher Inventory Drone system. The AI algorithms are responsible for:
- Mission Optimization: AI algorithms analyze inventory data, environmental conditions, and historical data to optimize drone missions, minimizing flight time, maximizing efficiency, and reducing operational costs.
- Real-time Decision Making: AI algorithms enable the drones to make real-time decisions based on changing environmental conditions, such as adjusting flight paths to avoid obstacles or adapting to unexpected weather patterns.
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms analyze inventory data and sensor readings to detect anomalies or inconsistencies, flagging potential issues for human review.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze drone performance data to predict potential maintenance needs, reducing downtime and ensuring optimal system performance.
The integration of artificial intelligence significantly improves the accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability of the Cypher Inventory Drone system, enabling it to operate more effectively and reliably in diverse environments.
Security and Privacy
The integration of autonomous drones into inventory management presents unique security and privacy challenges. These challenges demand robust security measures and careful consideration of ethical implications to ensure responsible and secure operations.
Security Vulnerabilities and Threats
Cyber inventory drone operations face a range of security vulnerabilities and threats that could compromise data integrity, disrupt operations, or even cause physical harm.
- Drone Hijacking: Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in drone communication protocols or software to gain unauthorized control, potentially diverting drones for unauthorized purposes or causing physical damage.
- Data Breaches: Sensitive inventory data, including product details, stock levels, and location information, could be vulnerable to theft or manipulation through unauthorized access to drone communication channels or data storage systems.
- Denial of Service Attacks: Disrupting drone communication or navigation systems through denial-of-service attacks could hinder inventory operations, causing delays and disruptions in supply chains.
- Malware Infections: Drones could be infected with malware that compromises their functionality, steals data, or even transforms them into weapons capable of causing harm.
Securing Drone Communication Channels and Data Transmission
Robust security measures are essential to protect drone communication channels and data transmission from unauthorized access and manipulation.
- Encryption: Implementing strong encryption protocols for all drone communication and data transmission ensures that even if intercepted, data remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties.
- Authentication and Authorization: Secure authentication and authorization mechanisms verify the identity of drones and users, preventing unauthorized access to drone systems and data.
- Secure Communication Protocols: Employing secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL ensures secure data exchange between drones, the mobile robot base, and other systems.
- Network Segmentation: Isolating drone communication networks from other systems minimizes the risk of spreading malware or unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in drone systems and communication channels, allowing for timely remediation.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Implications
The use of autonomous drones for inventory management raises ethical considerations and privacy implications that require careful attention.
- Data Privacy: Drones collect data about inventory, including product information, location details, and potentially sensitive information like employee movements. Implementing robust data privacy policies and adhering to data protection regulations are crucial to safeguard this information.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in drone operations and data collection practices is essential to build trust and ensure accountability. Clearly communicating the purpose and scope of data collection, and providing mechanisms for individuals to access and control their data, are crucial.
- Bias and Discrimination: Autonomous drones rely on algorithms and data that could potentially reflect biases present in training data. It’s essential to address potential biases in algorithms and ensure that drone operations do not perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities.
- Job Displacement: The use of autonomous drones for inventory management could potentially lead to job displacement for human workers. Addressing this concern requires careful planning and consideration of retraining and reskilling programs for affected employees.
Applications and Use Cases
Cyber inventory drones, with their ability to navigate complex environments and gather data autonomously, offer a wide range of potential applications across various industries. These drones can revolutionize inventory management, logistics, and manufacturing processes, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
Warehousing
Warehousing operations can benefit greatly from cyber inventory drones. These drones can be deployed to scan and track inventory levels, identify misplaced items, and even assist with picking and packing orders. The data collected by the drones can be used to optimize warehouse layouts, streamline workflows, and reduce the risk of stockouts.
“Cyber inventory drones can help reduce the time and resources required for manual inventory checks, leading to significant cost savings.”
Manufacturing
In manufacturing settings, cyber inventory drones can be used to monitor production lines, identify bottlenecks, and ensure quality control. They can also be used to inspect equipment, identify potential maintenance issues, and even deliver parts to different workstations.
“These drones can help manufacturers optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency.”
Logistics, Cyphers inventory drone launches from an autonomous mobile robot base
The logistics industry can leverage cyber inventory drones to optimize delivery routes, track shipments in real-time, and ensure timely delivery. These drones can also be used to inspect cargo, identify potential damage, and even deliver packages to remote locations.
“Cyber inventory drones can help logistics companies improve delivery efficiency, reduce transportation costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.”
| Industry | Potential Applications | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warehousing | Inventory tracking, item identification, picking and packing assistance | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, improved accuracy, minimized stockouts | Integration with existing warehouse systems, security and privacy concerns, potential for drone malfunction |
| Manufacturing | Production line monitoring, quality control, equipment inspection, parts delivery | Optimized production processes, reduced downtime, improved quality, enhanced safety | Integration with existing manufacturing systems, data security, potential for drone interference with production processes |
| Logistics | Shipment tracking, delivery route optimization, cargo inspection, package delivery | Improved delivery efficiency, reduced transportation costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, expanded delivery capabilities | Integration with existing logistics systems, regulatory compliance, potential for drone accidents, weather conditions |
Future Developments
The world of autonomous inventory drone operations is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in drone technology, artificial intelligence, and robotics. These advancements are poised to transform the way we manage inventory, streamline logistics, and optimize operational efficiency across various industries.
Enhanced Drone Autonomy
The future of cyber inventory drone operations hinges on increasing drone autonomy. This involves developing drones capable of navigating complex environments, making intelligent decisions, and executing tasks with minimal human intervention.
- Advanced Navigation Systems: Drones will leverage advanced navigation systems like LiDAR, computer vision, and artificial intelligence to navigate complex and dynamic environments with greater precision and accuracy. This will enable them to operate in challenging conditions, such as warehouses with narrow aisles, outdoor environments with obstacles, and even in hazardous areas.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Drones will be equipped with powerful onboard processing units to analyze real-time data from sensors and cameras. This allows them to adapt to changing conditions, identify potential hazards, and make informed decisions without relying on constant human input. For example, a drone could detect a blocked aisle in a warehouse and reroute itself to complete its inventory scan.
- Self-Learning Algorithms: Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms will empower drones to learn from experience and improve their performance over time. This will enable them to optimize their routes, adapt to changing inventory patterns, and even predict potential stockouts based on historical data.
The integration of cyber inventory drones with autonomous mobile robot bases is a game-changer for industries like warehousing, manufacturing, and logistics. By automating inventory management and data collection, this technology streamlines operations, reduces errors, and unlocks valuable insights. As drone technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated applications emerge, further transforming the way businesses manage their assets and optimize their supply chains.
Imagine a future where cypher’s inventory drones launch from an autonomous mobile robot base, navigating complex warehouse landscapes with pinpoint accuracy. This kind of logistical efficiency could be a reality sooner than you think, especially in light of the recent OpenAI fiasco. As we see the limitations of centralized AI development, the need for a more decentralized approach becomes clear, a point highlighted in how the openai fiasco could bolster meta and the open ai movement.
This shift towards decentralized AI could accelerate the development of innovative solutions like autonomous robot bases, paving the way for a future where cypher’s drones seamlessly integrate with our world.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News