E2ee police chiefs lawful access – E2EE, police chiefs, and lawful access – a trio that’s sparked a heated debate. While end-to-end encryption promises digital fortresses, law enforcement agencies argue it hinders their ability to combat crime. Imagine a world where encrypted messages are unbreakable, leaving criminals free to operate in the shadows. This is the reality many police chiefs fear, leading to a complex dance between privacy and security.
The battleground is the digital realm, where encrypted communication apps like WhatsApp and Signal have become the norm. These platforms use sophisticated encryption algorithms to ensure only the sender and recipient can read messages, leaving law enforcement agencies outside the loop. But is this impenetrable shield a haven for criminals, or a necessary safeguard for individual privacy? This question has become a central focus of the ongoing debate about lawful access.
E2EE
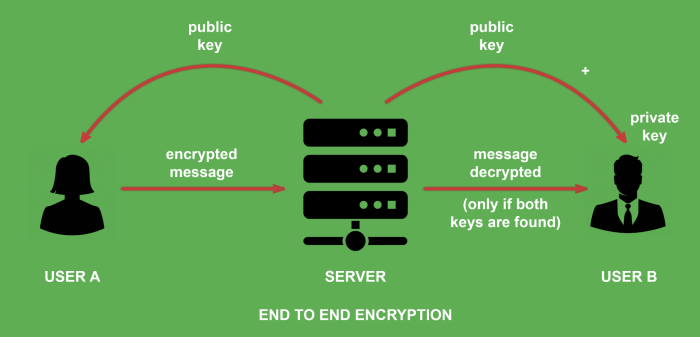
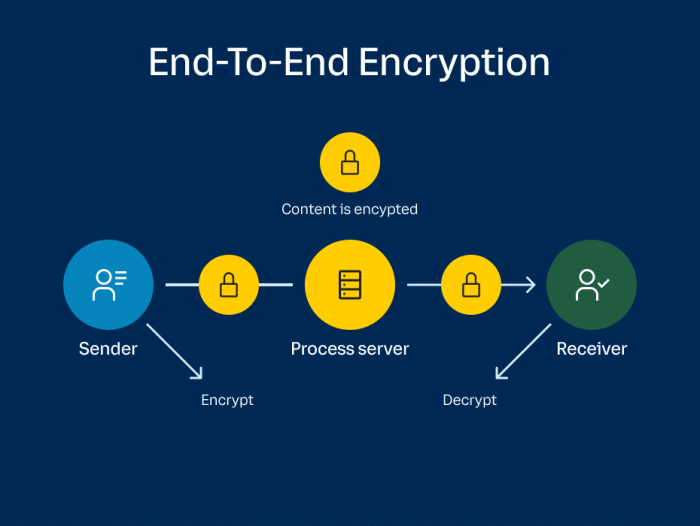
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a crucial security measure that safeguards digital communication by ensuring only the sender and intended recipient can access the message content. This technology has revolutionized online privacy, offering a shield against unauthorized access and surveillance.
E2EE: Core Principles and Impact on Data Privacy
E2EE works by encrypting messages at the source device, so only the intended recipient’s device can decrypt them. This means that even if a message is intercepted, the content remains hidden, effectively protecting sensitive information from prying eyes. The core principles of E2EE include:
* Encryption at the Source: Data is encrypted before it leaves the sender’s device, ensuring it’s secure from the outset.
* Decryption at the Destination: Only the intended recipient’s device, using the appropriate decryption key, can unlock and read the message.
* Key Management: Secure key management protocols are crucial to prevent unauthorized decryption. Keys are typically generated and exchanged between devices, ensuring that only the sender and recipient possess the necessary information to decrypt messages.
E2EE significantly enhances data privacy by preventing third parties, including service providers, governments, or hackers, from accessing the content of communications. It empowers individuals to control their data and protect their privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
E2EE: Encryption Algorithms
E2EE systems rely on various encryption algorithms to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of messages. These algorithms use complex mathematical functions to scramble data, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. Some common algorithms used in E2EE include:
* Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A widely adopted symmetric encryption algorithm known for its robust security. AES uses a secret key to encrypt and decrypt data, making it a popular choice for secure messaging applications.
* RSA: A widely used asymmetric encryption algorithm that relies on public and private keys. RSA is often used for key exchange and digital signatures, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of communications.
* Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): A modern encryption method that uses elliptic curves to generate keys. ECC offers high security levels with smaller key sizes, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices.
E2EE: Strengths and Weaknesses
E2EE offers significant advantages in securing communication, but it’s essential to understand its limitations:
Strengths
- Enhanced Privacy: E2EE effectively protects sensitive data from unauthorized access, even by service providers or governments.
- Strong Security: Robust encryption algorithms make it extremely difficult for attackers to intercept and decrypt messages.
- User Control: E2EE empowers users to control their data and privacy, reducing reliance on third-party services.
Weaknesses
- Potential for Abuse: E2EE can be used to conceal criminal activity, making it challenging for law enforcement to investigate crimes.
- Key Management Challenges: Secure key management is crucial for E2EE’s effectiveness. Weak key management practices can compromise security.
- Limited Metadata: While E2EE protects message content, metadata such as timestamps, sender, and recipient information may still be accessible.
E2EE Messaging Apps: A Comparison
The following table compares popular E2EE messaging apps and their encryption implementations:
| App | Encryption Algorithm | Key Management | Additional Security Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal | AES-256, Salsa20 | Double Ratchet Algorithm | Forward Secrecy, End-to-End File Encryption |
| AES-256, Signal Protocol | Signal Protocol | Two-Factor Authentication, Disappearing Messages | |
| Telegram | AES-256, RSA, ECC | Client-Server Encryption (not E2EE for all messages) | Cloud Storage, Secret Chats (E2EE) |
| iMessage | AES-256 | Apple’s iMessage protocol | End-to-End File Encryption, iMessage Continuity |
Lawful Access Debates
The debate surrounding lawful access to encrypted communications is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant implications for both individual privacy and public safety. At the heart of this debate lies the tension between the government’s need to investigate criminal activity and protect national security, and individuals’ right to privacy and freedom of expression.
Arguments for Government Access
Arguments in favor of government access to encrypted communications often emphasize the importance of law enforcement’s ability to investigate criminal activity and protect national security. Proponents argue that encrypted communications provide a haven for criminals and terrorists, allowing them to operate with impunity. They contend that granting law enforcement access to encrypted platforms is essential to preventing crimes, disrupting terrorist plots, and ensuring public safety. Furthermore, they argue that encryption technologies are often used to facilitate child exploitation, drug trafficking, and other serious crimes.
Arguments Against Government Access
Opponents of government access to encrypted communications argue that such access would undermine individual privacy and freedom of expression. They contend that granting law enforcement access to encrypted platforms would create a chilling effect on free speech, as individuals would be hesitant to communicate freely for fear of government surveillance. Moreover, they argue that such access could be abused by governments to target political dissidents, journalists, and other individuals who exercise their right to free speech. Furthermore, they emphasize the potential for unintended consequences, such as the creation of backdoors that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Legal Frameworks and Precedents
The legal frameworks and precedents related to lawful access to encrypted communications vary significantly across different jurisdictions. In some countries, governments have enacted laws that require technology companies to provide backdoors to encrypted communications, while others have adopted a more privacy-centric approach, emphasizing the importance of strong encryption and limiting government access. The United States, for example, has a long history of legal precedent regarding government access to communications, with the landmark case of *Katz v. United States* (1967) establishing the Fourth Amendment’s protection against unreasonable searches and seizures. However, the rapid development of encryption technologies has presented new challenges to traditional legal frameworks, leading to ongoing debates about the balance between security and privacy.
Potential Consequences of Granting Law Enforcement Access
Granting law enforcement access to encrypted platforms could have a number of significant consequences. One potential consequence is the erosion of trust in technology companies and the internet as a whole. If individuals believe that their communications are being monitored by the government, they may be less likely to use online services, potentially leading to a decline in innovation and economic growth. Another potential consequence is the creation of a “chilling effect” on free speech, as individuals may be hesitant to express themselves freely for fear of government surveillance. This could have a detrimental impact on democratic societies, where free speech is essential to political discourse and the exchange of ideas. Additionally, granting law enforcement access to encrypted platforms could create new vulnerabilities for individuals and businesses, as backdoors could be exploited by malicious actors.
Real-World Cases
There have been a number of real-world cases where encrypted communications have hindered criminal investigations. For example, in the 2015 San Bernardino shooting, the FBI was unable to access data on the shooter’s iPhone, which was protected by strong encryption. This case highlighted the challenges that law enforcement agencies face in investigating crimes involving encrypted communications. However, it is important to note that the inability to access encrypted data does not necessarily mean that criminals are operating with impunity. Law enforcement agencies have a variety of other tools and techniques at their disposal, such as traditional investigative methods and cooperation with foreign governments.
Police Chiefs’ Perspectives
Police chiefs, as leaders responsible for maintaining law and order, are at the forefront of the ongoing debate surrounding end-to-end encryption (E2EE) and its implications for law enforcement. Their perspectives on E2EE and lawful access are shaped by the challenges they face in investigating crimes involving encrypted communications, and their commitment to protecting public safety.
Challenges in Investigating Crimes Involving Encrypted Communications
The widespread adoption of E2EE has presented significant challenges for police chiefs in their efforts to investigate crimes. The encryption technology, designed to protect user privacy, effectively shields communication content from unauthorized access, including law enforcement. This presents a hurdle for investigators seeking to gather evidence, identify suspects, and prosecute criminals.
- Difficulty in Obtaining Evidence: E2EE prevents law enforcement from accessing the content of encrypted communications, hindering the ability to gather crucial evidence in criminal investigations. This can make it challenging to establish the intent, motive, or involvement of suspects in criminal activities.
- Limited Access to Metadata: While E2EE protects the content of communications, metadata, such as timestamps, sender and receiver information, and location data, can still be valuable in investigations. However, accessing this metadata can be restricted by privacy laws and regulations, further limiting law enforcement’s investigative capabilities.
- Increased Difficulty in Tracking Criminal Activity: Encrypted communications make it harder for law enforcement to monitor and track criminal activity, particularly in cases involving organized crime, terrorism, or human trafficking. The anonymity provided by E2EE can allow criminals to operate with greater impunity.
Strategies and Tools Employed to Overcome E2EE Obstacles
Recognizing the challenges posed by E2EE, police chiefs have been exploring strategies and tools to overcome these obstacles while balancing public safety concerns with individual privacy rights. These efforts aim to find a middle ground that allows law enforcement to effectively investigate crimes without compromising the security and privacy of law-abiding citizens.
- Collaboration with Technology Companies: Police chiefs have advocated for increased collaboration with technology companies to facilitate lawful access to encrypted communications. This collaboration could involve developing technical solutions that enable law enforcement to access encrypted data in specific circumstances, such as with a warrant or court order.
- Leveraging Metadata and Other Investigative Techniques: While direct access to encrypted content remains challenging, police chiefs emphasize the importance of leveraging available metadata and other investigative techniques to gather evidence. This includes utilizing digital forensics, network analysis, and intelligence gathering to build cases and identify suspects.
- Enhancing Law Enforcement Training and Expertise: Police chiefs are investing in training and development programs to equip officers with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively investigate crimes involving encrypted communications. This includes training on digital forensics, cybercrime investigation, and the use of specialized software and tools.
Different Stances on E2EE and Lawful Access
The perspectives of police chiefs on E2EE and lawful access are diverse, reflecting the complexities of the issue and the need to balance public safety with individual privacy.
| Stance | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Advocate for Lawful Access | Police chiefs who strongly advocate for lawful access argue that E2EE hinders law enforcement’s ability to investigate crimes and protect public safety. They believe that technology companies should provide backdoors or other mechanisms to allow law enforcement to access encrypted data with appropriate legal authorization. | Some police chiefs have publicly called for legislation that would mandate backdoors in encryption technologies, arguing that such measures are necessary to prevent serious crimes and terrorism. |
| Supporter of Balanced Approach | Police chiefs who support a balanced approach recognize the importance of both privacy and public safety. They advocate for solutions that enable law enforcement to access encrypted data in specific circumstances while preserving the privacy of law-abiding citizens. | These police chiefs may support proposals that involve developing technical solutions that allow for targeted access to encrypted data, such as with a warrant or court order, or that focus on enhancing law enforcement’s capabilities in utilizing metadata and other investigative techniques. |
| Concerned about Privacy Implications | Police chiefs who are concerned about the privacy implications of lawful access argue that weakening encryption could have unintended consequences, potentially leading to increased surveillance and abuse of power. They believe that alternative solutions, such as focusing on investigative techniques and intelligence gathering, should be prioritized. | Some police chiefs have expressed concerns that mandating backdoors in encryption technologies could undermine the security and privacy of all users, not just criminals. They advocate for a more nuanced approach that respects individual privacy while still enabling law enforcement to effectively investigate crimes. |
Balancing Privacy and Security
The implementation of end-to-end encryption (E2EE) presents a significant challenge in balancing individual privacy with public safety. While E2EE enhances individual privacy by protecting communications from unauthorized access, it also creates a potential obstacle for law enforcement agencies seeking lawful access to encrypted data in criminal investigations. Finding a balance between these competing interests is crucial for ensuring a secure and just society.
Framework for Balancing Privacy and Security
A framework for balancing privacy and security in the context of E2EE should be based on the following principles:
- Transparency and Accountability: Law enforcement agencies should be transparent about their data access requests and the legal basis for them. This transparency fosters public trust and accountability, ensuring that lawful access is not abused.
- Necessity and Proportionality: Access to encrypted data should only be granted when it is strictly necessary for legitimate law enforcement purposes and proportionate to the seriousness of the crime under investigation. This principle helps prevent overreach and safeguards individual privacy.
- Independent Oversight: An independent body should oversee lawful access requests to ensure they comply with legal and ethical standards. This oversight mechanism helps protect against arbitrary or discriminatory access.
- Minimization of Data Retention: Law enforcement agencies should only retain encrypted data for as long as necessary for the investigation and should securely destroy it afterward. This minimizes the potential for misuse or abuse of the data.
- Strong Legal Framework: A clear and robust legal framework should govern lawful access to encrypted data, defining the scope of access, the procedures for obtaining it, and the safeguards for protecting privacy.
Potential Solutions and Compromises
Several potential solutions and compromises can address the concerns of both privacy advocates and law enforcement agencies:
- Key Escrow: This approach involves storing encryption keys in a secure third-party location, allowing authorized access to encrypted data in specific circumstances. However, key escrow raises concerns about privacy and security, as it creates a single point of failure and potential for abuse.
- Backdoors: This approach involves building intentional vulnerabilities into encryption systems, allowing law enforcement agencies to access encrypted data. Backdoors are highly controversial, as they undermine the security of encryption and create a potential for misuse by malicious actors.
- Limited Access with Judicial Oversight: This approach involves granting law enforcement agencies access to encrypted data only under specific circumstances and with rigorous judicial oversight. This approach balances the need for lawful access with the protection of individual privacy.
- Data Retention Requirements: This approach involves requiring service providers to retain encrypted data for a specified period, allowing law enforcement agencies to access it if needed. This approach raises concerns about privacy, as it creates a potential for surveillance and abuse of data.
- Enhanced Cooperation and Collaboration: Increased collaboration between law enforcement agencies and technology companies can help develop solutions that balance privacy and security. This collaboration can involve sharing best practices, developing technical solutions, and working together to address emerging threats.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding lawful access to encrypted data are complex and far-reaching.
- Right to Privacy: Individuals have a fundamental right to privacy, which includes the right to communicate securely and privately. Lawful access to encrypted data can infringe on this right, potentially chilling free speech and inhibiting legitimate activities.
- Potential for Abuse: Access to encrypted data can be abused by law enforcement agencies, potentially leading to surveillance, harassment, and discrimination. This potential for abuse raises serious ethical concerns about the use of lawful access powers.
- Impact on Society: The balance between privacy and security has a profound impact on society. Overly restrictive access to encrypted data can hinder innovation, stifle free speech, and erode trust in government. Conversely, unrestricted access to encrypted data can undermine privacy, erode civil liberties, and create a surveillance society.
Balancing Privacy and Security: A Visual Representation
[Insert image of a scale with “Privacy” on one side and “Security” on the other. The scale is balanced, but the image should convey the complexities of achieving this balance. The image should also include elements representing various factors, such as technology, law enforcement, individual rights, and public safety, to highlight the interconnected nature of the issue.]Technological Solutions
The quest for lawful access to encrypted communications without compromising end-to-end encryption (E2EE) has spurred the development of various technological solutions. These solutions aim to strike a delicate balance between security, privacy, and law enforcement needs.
These solutions aim to enable lawful access without compromising the security of E2EE, and they present both opportunities and challenges.
Solutions for Lawful Access
The following are some potential technological solutions that have been proposed or explored:
- Key Escrow: This approach involves storing encryption keys in a secure, trusted third-party location, such as a government agency. Law enforcement could then request access to these keys with proper authorization. However, key escrow raises concerns about privacy and security. A breach of the escrow system could compromise the security of all encrypted communications. Additionally, there is a risk of government overreach and misuse of access to keys.
- Temporary Decryption: In this approach, users temporarily decrypt their communications for authorized access. This could be achieved through a mechanism where a user grants temporary access to their encrypted data for a specific period and for a defined purpose. This approach would require users to trust the system and the authorities involved. It also raises concerns about potential misuse and the difficulty of ensuring the temporary decryption mechanism is truly secure and tamper-proof.
- Trusted Third-Party Access: This involves the use of a trusted third party to facilitate lawful access. This third party could be a technology company, a designated government agency, or a combination of both. This approach requires careful consideration of the trustworthiness and accountability of the third party. It also raises concerns about potential conflicts of interest and the possibility of abuse.
- Specialized Encryption Algorithms: This involves the development of encryption algorithms that incorporate backdoors or mechanisms for lawful access. However, the introduction of backdoors could weaken the security of the entire system, making it vulnerable to malicious actors. Additionally, the creation of such algorithms raises ethical concerns about the potential for misuse and the erosion of trust in E2EE.
- Metadata Analysis: Instead of decrypting the content of communications, law enforcement could focus on analyzing metadata associated with the communication. This includes information like the sender, receiver, timestamp, and location of the communication. Metadata analysis can provide valuable insights into criminal activity without compromising the privacy of the communication content. However, metadata analysis can still be revealing and raise privacy concerns, especially when combined with other data sources.
Feasibility and Drawbacks of Technological Solutions
The feasibility and potential drawbacks of these solutions vary widely.
- Key Escrow: While technically feasible, key escrow raises significant concerns about privacy and security. A breach of the escrow system could compromise the security of all encrypted communications. Additionally, there is a risk of government overreach and misuse of access to keys.
- Temporary Decryption: This approach requires users to trust the system and the authorities involved. It also raises concerns about potential misuse and the difficulty of ensuring the temporary decryption mechanism is truly secure and tamper-proof.
- Trusted Third-Party Access: This approach requires careful consideration of the trustworthiness and accountability of the third party. It also raises concerns about potential conflicts of interest and the possibility of abuse.
- Specialized Encryption Algorithms: The introduction of backdoors could weaken the security of the entire system, making it vulnerable to malicious actors. Additionally, the creation of such algorithms raises ethical concerns about the potential for misuse and the erosion of trust in E2EE.
- Metadata Analysis: While metadata analysis can provide valuable insights into criminal activity without compromising the privacy of the communication content, it can still be revealing and raise privacy concerns, especially when combined with other data sources.
Examples of Existing or Proposed Technologies
Several existing or proposed technologies aim to address the lawful access challenge:
- The UK’s Investigatory Powers Act (IPA): This legislation requires telecommunications companies to provide technical assistance to law enforcement agencies, including access to encrypted communications. The IPA has been criticized for its potential impact on privacy and security.
- The US CLOUD Act: This legislation allows US law enforcement to request data from foreign companies, even if the data is stored outside the US. The CLOUD Act has raised concerns about the potential for extraterritorial surveillance and the erosion of data privacy.
- The EU’s ePrivacy Regulation: This regulation aims to strengthen data protection rights in the EU, including the right to privacy in electronic communications. The ePrivacy Regulation could potentially create challenges for law enforcement agencies seeking access to encrypted communications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Technological Approaches
- Key Escrow:
- Advantages: Allows for direct access to encrypted data with proper authorization.
- Disadvantages: Raises significant privacy and security concerns, potential for government overreach and misuse.
- Temporary Decryption:
- Advantages: Allows for temporary access to encrypted data for specific purposes.
- Disadvantages: Requires user trust, potential for misuse, difficulty in ensuring security.
- Trusted Third-Party Access:
- Advantages: Can facilitate lawful access with the involvement of a trusted entity.
- Disadvantages: Requires careful consideration of trustworthiness and accountability, potential for conflicts of interest.
- Specialized Encryption Algorithms:
- Advantages: Could potentially provide lawful access without compromising the security of the entire system.
- Disadvantages: Raises ethical concerns about misuse, weakens overall security, erodes trust in E2EE.
- Metadata Analysis:
- Advantages: Provides insights into criminal activity without compromising the privacy of the communication content.
- Disadvantages: Can still raise privacy concerns, especially when combined with other data sources.
The Future of E2EE and Lawful Access: E2ee Police Chiefs Lawful Access
The landscape of end-to-end encryption (E2EE) and lawful access is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing societal norms, and evolving legal frameworks. This dynamic interplay raises crucial questions about the future of privacy, security, and the balance between these competing interests.
Emerging Technologies and the E2EE Landscape, E2ee police chiefs lawful access
The emergence of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing, will significantly impact the E2EE landscape.
- AI-powered encryption: AI algorithms could be used to create more robust and sophisticated encryption methods, making it even more challenging for law enforcement to access encrypted data. This could lead to a future where even the most advanced decryption techniques are rendered ineffective.
- Blockchain-based communication: Blockchain technology can enable secure and decentralized communication networks, potentially circumventing traditional surveillance methods. These networks could operate outside the control of governments and law enforcement agencies, creating new challenges for lawful access.
- Quantum computing: The development of quantum computers could eventually break current encryption methods, rendering E2EE ineffective. However, this technology is still in its early stages, and its impact on E2EE remains uncertain.
Evolving Legal and Ethical Frameworks
The legal and ethical frameworks surrounding lawful access are constantly evolving, reflecting the changing technological landscape and societal values.
- International cooperation: Increased cooperation between countries is crucial to establish common standards for lawful access in the digital age. This requires addressing issues of jurisdiction, data sovereignty, and cross-border data transfer.
- Balancing privacy and security: Striking a balance between individual privacy and national security remains a critical challenge. Governments must ensure that lawful access measures are proportionate, necessary, and respect fundamental rights.
- Transparency and accountability: Law enforcement agencies must be transparent about their use of lawful access measures and accountable for their actions. This includes establishing clear procedures for obtaining and using encrypted data, as well as providing oversight mechanisms to prevent abuse.
The Future of the Debate
The debate between privacy advocates and law enforcement agencies regarding E2EE and lawful access is likely to intensify in the future.
- Privacy advocates: Privacy advocates will continue to push for stronger encryption and privacy protections, arguing that E2EE is essential for safeguarding individual freedoms and protecting sensitive information. They will likely advocate for legislative and technological solutions that prioritize privacy over access.
- Law enforcement agencies: Law enforcement agencies will continue to argue for the need for lawful access to encrypted data to investigate crimes and protect public safety. They will likely seek to implement technological solutions that allow for lawful access while preserving privacy.
Timeline of Key Milestones
The history of E2EE and lawful access is marked by a series of key milestones and events that have shaped the current debate.
- 1970s: The development of public-key cryptography revolutionized encryption technology, making it possible for secure communication without sharing secret keys. This marked the beginning of the modern era of E2EE.
- 1990s: The rise of the internet and digital communication led to widespread adoption of encryption technologies, raising concerns about lawful access for law enforcement agencies.
- 2000s: The development of strong encryption algorithms, such as AES and RSA, made it increasingly difficult for law enforcement to decrypt encrypted data. This led to calls for backdoors and other measures to provide lawful access.
- 2010s: The rise of mobile messaging apps and social media platforms with E2EE capabilities, such as WhatsApp and Signal, further intensified the debate about lawful access.
- 2020s: The ongoing debate about E2EE and lawful access continues to evolve, with new technologies and legal challenges emerging. The future of this debate will be shaped by the balance between privacy and security, the role of emerging technologies, and the evolving legal and ethical frameworks.
The debate surrounding E2EE, police chiefs, and lawful access is far from over. Finding a solution that balances individual privacy with the need for effective law enforcement is a delicate tightrope walk. While technology continues to evolve, so too must our understanding of the complexities of privacy and security in the digital age. The future of E2EE and lawful access remains uncertain, but one thing is clear: this is a conversation we can’t afford to ignore.
The debate over E2EE and police chiefs’ lawful access is a complex one, with strong arguments on both sides. While ensuring public safety is paramount, the potential for privacy breaches and abuse of power must be carefully considered. Meanwhile, in the tech world, Sona, a frontline workforce management platform, has just raised $27.5 million with eyes on US expansion.
This news highlights the growing importance of efficient workforce management, a critical factor in ensuring effective policing and public safety. Ultimately, finding the right balance between security and privacy will be crucial in navigating the future of E2EE and law enforcement.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News