EU DSA x RFI GenAI – a mouthful, right? But this trifecta is shaping the future of online content. The EU Digital Services Act (DSA) is setting the stage for responsible content moderation, while Request for Information (RFI) processes are actively seeking input on how Generative AI (GenAI) can play a role. Imagine a world where AI can help us filter harmful content, while also ensuring transparency and accountability. This is the future we’re navigating, and it’s a wild ride.
The DSA aims to create a safer online environment by requiring platforms to proactively address harmful content, increase transparency in their algorithms, and be accountable for their actions. Meanwhile, GenAI, with its ability to generate text, images, and even code, presents both exciting possibilities and potential risks. RFIs are crucial in this landscape, allowing policymakers to gather insights from experts and stakeholders on how to harness the power of GenAI while mitigating potential risks.
The EU Digital Services Act (DSA): Eu Dsa X Rfi Genai
The EU Digital Services Act (DSA) is a landmark piece of legislation that aims to regulate online platforms and services within the European Union. It seeks to create a safer and more transparent online environment for users while fostering innovation and competition among digital players.
Key Provisions of the DSA
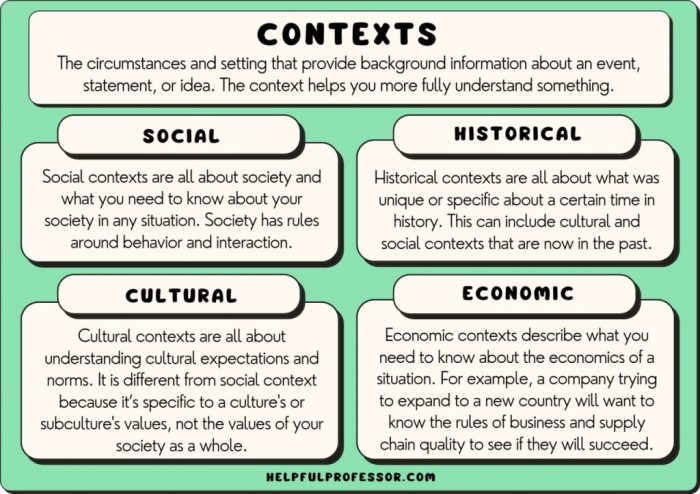
The DSA Artikels a comprehensive set of rules for online platforms, focusing on content moderation, transparency, and accountability.
- Content Moderation: The DSA requires platforms to take proactive measures to remove illegal content, such as hate speech, terrorist content, and child sexual abuse material. Platforms must also implement robust systems for reporting and removing harmful content, including mechanisms for users to appeal decisions.
- Transparency: The DSA mandates platforms to be transparent about their algorithms, content moderation policies, and user data practices. This includes providing users with clear information about how their data is collected, used, and shared. Platforms must also disclose their algorithms’ impact on content visibility and user engagement.
- Accountability: The DSA introduces stricter accountability measures for platforms. It empowers regulators to impose significant fines on platforms that violate the law, including penalties for failing to remove illegal content or for engaging in unfair practices.
Impact of the DSA on Online Platforms
The DSA has far-reaching implications for online platforms, both in terms of challenges and opportunities.
- Challenges:
- Increased Costs: Implementing the DSA’s requirements will likely involve significant investments for platforms, particularly in terms of content moderation, transparency reporting, and compliance with data protection rules.
- Operational Complexity: The DSA’s complex provisions and evolving regulatory landscape will require platforms to adapt their operations and processes, potentially leading to increased complexity and administrative burdens.
- Risk of Censorship: There are concerns that the DSA’s content moderation provisions could lead to over-censorship, potentially restricting freedom of expression and stifling legitimate online activities.
- Opportunities:
- Enhanced User Trust: By promoting transparency and accountability, the DSA could help build user trust in online platforms, fostering a more positive and engaging online environment.
- Increased Competition: The DSA’s provisions on unfair practices and algorithmic transparency could encourage competition among platforms, potentially leading to more diverse and innovative online services.
- Global Impact: The DSA’s success could inspire similar regulations in other jurisdictions, creating a more consistent and harmonized global regulatory framework for online platforms.
Comparison with Other Regulations
The DSA shares similarities with other regulations aimed at governing online platforms, such as the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) in the United States and the Network Enforcement Act (NetzDG) in Germany. However, the DSA stands out for its comprehensive scope, its focus on algorithmic transparency, and its stringent accountability measures.
- DMCA: The DMCA primarily focuses on copyright protection, while the DSA addresses a wider range of issues, including content moderation, transparency, and user data protection.
- NetzDG: The NetzDG targets hate speech and other forms of illegal content, but it lacks the DSA’s emphasis on algorithmic transparency and its robust accountability mechanisms.
RFI (Request for Information) and GenAI (Generative AI)
RFIs play a crucial role in the development and implementation of new technologies like Generative AI (GenAI). They serve as a vital tool for gathering information, understanding the landscape, and identifying potential challenges and opportunities.
The Role of RFIs in GenAI Development
RFIs are a valuable tool for understanding the current state of GenAI technology, identifying potential applications, and exploring the potential risks associated with its development and deployment. They provide a structured framework for gathering information from a wide range of stakeholders, including researchers, developers, industry experts, and policymakers.
- Identifying key players and technologies: RFIs help identify leading researchers, developers, and companies involved in GenAI research and development. This allows policymakers and industry leaders to understand the competitive landscape and identify potential collaborators.
- Exploring potential applications: RFIs can be used to gather information on the potential applications of GenAI across various sectors, including healthcare, education, entertainment, and finance. This helps policymakers and industry leaders understand the potential impact of GenAI on different industries and develop appropriate regulations and policies.
- Assessing potential risks: RFIs are essential for identifying potential risks associated with GenAI, such as bias, misinformation, and privacy concerns. This information helps policymakers and industry leaders develop mitigation strategies and safeguards to ensure the responsible development and deployment of GenAI.
Examples of RFIs in GenAI, Eu dsa x rfi genai
Numerous examples illustrate how RFIs have been used to gather information on GenAI applications and potential risks.
- The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) issued an RFI in 2022 seeking input on the development of guidelines for the responsible use of AI, including GenAI. The RFI aimed to gather information on best practices for developing and deploying AI systems that are trustworthy, fair, and unbiased.
- The European Union’s High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence (AI HLEG) issued an RFI in 2018 to gather information on the potential societal impact of AI. The RFI explored the potential benefits and risks of AI, including its impact on employment, privacy, and human rights.
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) has issued several RFIs on the topic of AI, including one in 2019 focused on the ethical implications of AI. The RFI sought input from experts and stakeholders on how to ensure that AI is developed and used in a responsible and ethical manner.
Implications of GenAI for Content Moderation and the DSA
GenAI presents both opportunities and challenges for content moderation and the implementation of the DSA’s requirements.
- Potential for automated content moderation: GenAI can be used to automate content moderation tasks, such as identifying and removing harmful content. This could help platforms more efficiently enforce their content policies and comply with the DSA’s requirements.
- Challenges in identifying AI-generated content: GenAI can be used to create realistic and convincing content, making it difficult to distinguish between human-generated and AI-generated content. This presents challenges for content moderation systems and could potentially lead to the spread of misinformation and disinformation.
- Potential for bias and discrimination: GenAI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on. This could lead to discriminatory outcomes in content moderation, where certain types of content are unfairly targeted or suppressed.
- Need for transparency and accountability: The use of GenAI in content moderation raises concerns about transparency and accountability. Platforms need to be transparent about their use of GenAI and ensure that their systems are fair and unbiased.
The intersection of the DSA, RFI, and GenAI is a complex dance, with each element influencing the others. This dynamic interplay is shaping the future of online content, with the potential to create a safer, more transparent, and more responsible digital world. As we move forward, it’s crucial to keep the conversation going, to involve diverse voices, and to ensure that technology serves humanity, not the other way around.
EU DSA and RFI GenAI are hot topics, and it’s no surprise that they’re making waves at TC Early Stage 2024. Want to dive deeper into these cutting-edge technologies? Check out the complete side events lineup at TC Early Stage 2024 for a glimpse into the future of tech. You’ll find discussions on everything from AI ethics to the impact of regulations on innovation, so get ready to be inspired!
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News