Global off grid solar sector – The global off-grid solar sector is a burgeoning force, bringing clean energy to remote communities and fostering a sustainable future. It’s a sector brimming with potential, fueled by the need for reliable energy access in underserved areas, and the growing demand for renewable energy solutions.
From powering homes in rural villages to supporting businesses in off-grid locations, off-grid solar technology is bridging the energy gap and empowering communities worldwide. This sector is a beacon of hope, offering a pathway towards a cleaner, more equitable energy landscape.
Market Overview
The global off-grid solar sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing demand for electricity in remote and underserved areas. The sector is characterized by its focus on providing clean and affordable energy solutions to populations without access to the traditional grid.
The off-grid solar market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, fueled by factors such as rising energy demand, declining costs of solar technology, and increasing government support for renewable energy initiatives.
Market Size and Growth Rate
The global off-grid solar market was valued at USD 10.4 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 30.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 15.3% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including:
- Increasing demand for electricity in rural areas, particularly in developing countries.
- Declining costs of solar technology, making it more affordable for off-grid applications.
- Government initiatives and subsidies to promote renewable energy adoption.
- Growing awareness of the environmental benefits of solar energy.
Key Trends in the Off-Grid Solar Sector
The off-grid solar sector is constantly evolving, with several key trends shaping its future:
- Integration of storage solutions: Battery storage systems are becoming increasingly popular, enabling off-grid systems to provide reliable power even during periods of low sunlight. This allows for greater energy independence and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Advancements in solar technology: Ongoing innovation in solar panel efficiency and design is driving down costs and improving performance, making off-grid solar systems more attractive for a wider range of applications.
- Rise of pay-as-you-go (PAYG) models: PAYG models are gaining traction, allowing consumers to access solar energy on a subscription basis. This approach removes the upfront cost barrier and makes solar energy more accessible to low-income households.
- Increased focus on mini-grids: Mini-grids are small-scale electricity networks that serve a localized area, often powered by renewable energy sources. They offer a viable solution for providing electricity to communities that are too far from the grid to be connected.
Drivers and Challenges
The off-grid solar sector is driven by a combination of factors, but it also faces several challenges:
Drivers
- Growing energy demand in remote areas: As populations grow and economies develop, the demand for electricity in remote and underserved areas is increasing. Off-grid solar provides a clean and affordable solution to meet this demand.
- Environmental concerns: The use of fossil fuels for electricity generation contributes to climate change. Off-grid solar is a clean and sustainable alternative that helps to reduce carbon emissions.
- Government support: Many governments are promoting renewable energy adoption through policies, subsidies, and financial incentives. This support is encouraging the growth of the off-grid solar sector.
Challenges
- High upfront costs: The initial investment in off-grid solar systems can be a barrier for some consumers, particularly in low-income communities.
- Lack of access to financing: Obtaining financing for off-grid solar projects can be challenging, especially in developing countries.
- Limited grid infrastructure: In many remote areas, the lack of grid infrastructure makes it difficult to connect to the electricity network. This creates a demand for off-grid solutions.
- Technological limitations: While off-grid solar technology has advanced significantly, there are still limitations in terms of storage capacity and reliability, especially in areas with high energy demands.
Market Landscape
The off-grid solar market is characterized by a diverse range of players, including:
- Solar panel manufacturers: Companies like JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, and LONGi Solar are major suppliers of solar panels for off-grid applications.
- Battery storage providers: Companies such as Tesla, LG Chem, and BYD provide battery storage solutions for off-grid systems.
- System integrators: Companies like Sunfridge, D.light, and BBOXX design and install off-grid solar systems for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- Finance providers: Companies like SolarAid, Off-Grid Solar Access (OGSA), and SunFunder provide financing options for off-grid solar projects.
These players are competing to capture market share in the rapidly growing off-grid solar sector. They are employing a variety of strategies, including:
- Product innovation: Developing new and improved solar technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Market expansion: Targeting new markets and expanding into underserved areas.
- Strategic partnerships: Collaborating with governments, NGOs, and other organizations to promote off-grid solar adoption.
- PAYG models: Offering flexible financing options to make solar energy accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Technology Landscape
The off-grid solar sector is a dynamic landscape, characterized by diverse technologies and ongoing innovation. These technologies play a crucial role in providing electricity access to remote and underserved communities, empowering them with clean and reliable energy.
Types of Off-Grid Solar Technologies
Different types of off-grid solar technologies cater to varying needs and contexts. Each technology comes with its advantages and disadvantages, influencing its suitability for specific applications.
- Standalone Solar Systems: These systems are self-contained, consisting of solar panels, batteries, inverters, and controllers. They are suitable for powering individual homes, small businesses, and off-grid communities. The main advantage of standalone systems is their independence from the grid, offering energy security. However, their initial cost can be high, and maintenance requires technical expertise.
- Solar Home Systems (SHS): These systems are designed for residential use, typically powering lighting, TVs, and small appliances. They are affordable and easy to install, making them popular in developing countries. SHS are known for their low maintenance requirements and long lifespan. However, they have limited power output, restricting their use to small loads.
- Hybrid Solar Systems: These systems combine solar energy with other energy sources, such as generators or batteries. They provide a more reliable and consistent power supply, especially in areas with intermittent solar irradiance. Hybrid systems offer flexibility and scalability, making them suitable for various applications. However, their complexity can increase maintenance costs and installation challenges.
Latest Advancements in Off-Grid Solar Technology
The off-grid solar sector is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to enhance efficiency, affordability, and reliability.
- Energy Storage: Advancements in battery technology, such as lithium-ion batteries, have significantly improved energy storage capacity and efficiency. This enables off-grid systems to store excess solar energy for use during periods of low irradiance or high demand, ensuring a more reliable power supply.
- Smart Grids: Smart grid technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and distributed energy resource management (DERM), are being integrated into off-grid systems. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of energy consumption, enhancing grid efficiency and reliability.
- Microgrids: Microgrids are small-scale, localized energy systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. They are becoming increasingly popular in off-grid applications, offering energy resilience and local control. Microgrids can integrate various renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and biomass, providing a more sustainable and diversified energy solution.
Role of Innovation in Driving the Growth of the Off-Grid Solar Sector
Innovation is a key driver of growth in the off-grid solar sector, enabling the development of more efficient, affordable, and accessible technologies.
- Improved Solar Panel Efficiency: Continuous advancements in solar panel technology, such as the development of higher-efficiency cells and innovative materials, have increased the energy output of solar panels. This has led to smaller, more compact systems with lower installation costs.
- Cost Reduction of Batteries: The declining cost of battery technology, driven by increased production and technological improvements, has made energy storage more affordable for off-grid applications. This has enabled the development of larger and more reliable off-grid systems.
- Smart Grid Integration: The integration of smart grid technologies into off-grid systems is transforming how energy is managed and distributed. This has enabled greater control, efficiency, and resilience, making off-grid systems more attractive for various applications.
Applications and Use Cases
Off-grid solar technology is not limited to a single application. It offers a versatile solution for diverse sectors, ranging from individual homes to large-scale industrial operations. The key to its widespread adoption lies in its ability to provide reliable and sustainable energy in areas where traditional grid infrastructure is either unavailable or unreliable.
Residential Applications
Off-grid solar systems have revolutionized the way people live in remote areas. They offer a clean and cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels, enabling access to electricity for lighting, cooking, and other essential household needs. These systems are particularly beneficial in regions with limited grid access, reducing reliance on expensive and polluting kerosene lamps or generators.
Commercial Applications, Global off grid solar sector
Off-grid solar systems are increasingly being adopted by businesses in remote areas, particularly in the tourism, hospitality, and retail sectors. These businesses rely on reliable power for operations, and off-grid solar provides a sustainable and cost-effective solution.
Industrial Applications
Off-grid solar systems are finding applications in various industries, including mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. These industries often operate in remote locations with limited grid access, making off-grid solar a crucial source of clean and reliable power.
Agricultural Applications
Off-grid solar systems are transforming agriculture, providing clean energy for irrigation, livestock management, and crop processing. Solar-powered pumps can provide water for irrigation, while solar-powered refrigerators can preserve perishable produce.
Key Use Cases for Off-Grid Solar
The table below highlights key use cases for off-grid solar in different sectors, outlining their specific needs and challenges:
| Sector | Use Case | Specific Needs | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | Lighting, cooking, refrigeration, and other household appliances | Reliable and affordable electricity | Initial investment costs, limited storage capacity, and maintenance requirements |
| Commercial | Powering businesses, hotels, restaurants, and shops | Consistent power supply, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness | Scalability, grid integration, and regulatory compliance |
| Industrial | Operating machinery, lighting, and other industrial processes | High power output, reliability, and safety | Large-scale installation, grid synchronization, and power management |
| Agricultural | Irrigation, livestock management, and crop processing | Water pumping, refrigeration, and lighting | Weather dependence, land availability, and maintenance requirements |
Impact on Sustainable Development and Poverty Alleviation
Off-grid solar plays a significant role in promoting sustainable development and alleviating poverty in developing countries. By providing access to clean and reliable energy, off-grid solar systems improve living standards, create economic opportunities, and empower communities.
“Off-grid solar energy has the potential to transform the lives of millions of people in developing countries by providing them with access to clean, reliable, and affordable energy.” – International Energy Agency (IEA)
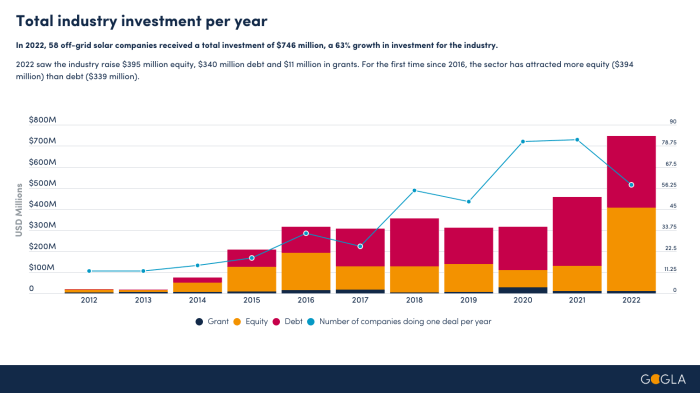
Financing and Investment: Global Off Grid Solar Sector
The off-grid solar sector relies heavily on diverse financing models to bridge the gap between demand and supply. Access to funding is crucial for project development, deployment, and expansion. The most common financing models include grants, loans, and equity investments, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Financing Models for Off-Grid Solar Projects
Various financing models are employed to support off-grid solar projects, each tailored to specific project needs and investor profiles.
- Grants: These are non-repayable funds provided by governments, NGOs, or philanthropic organizations to support projects aligned with their social or environmental objectives. Grants often target projects in underserved communities or those focusing on renewable energy adoption. Examples include the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and the World Bank’s Clean Technology Fund (CTF), which provide grants for off-grid solar projects in developing countries.
- Loans: Loans are repayable funds provided by financial institutions, development banks, or impact investors. These loans can be secured or unsecured, with interest rates and repayment terms varying depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness and project risk. The International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) offer loans for off-grid solar projects, facilitating access to capital for developers.
- Equity Investments: Equity investments involve acquiring ownership in a project in exchange for capital. Venture capitalists, private equity firms, and impact investors often participate in equity financing, seeking a return on their investment. Equity investments can provide significant capital for large-scale projects but also come with higher risk and a potential loss of control for the project owner.
Challenges and Opportunities for Investment
Attracting investment in the off-grid solar sector presents both challenges and opportunities.
- Challenges:
- High upfront costs: Off-grid solar projects require significant upfront capital for equipment, installation, and operating expenses, making them less attractive to investors seeking quick returns.
- Lack of access to credit: Limited access to affordable financing options, particularly in developing countries, can hinder project development.
- Market uncertainty: The nascent nature of the off-grid solar market, coupled with regulatory uncertainties and evolving technologies, can create investor hesitancy.
- Risk of technology obsolescence: Rapid advancements in solar technology can lead to early obsolescence of equipment, raising concerns about long-term project viability.
- Opportunities:
- Growing demand for clean energy: The increasing demand for affordable and reliable electricity in underserved communities presents a significant market opportunity for off-grid solar.
- Government support and policy frameworks: Many governments are enacting policies to promote renewable energy adoption, including incentives and subsidies for off-grid solar projects.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in solar technology, such as improved efficiency and lower costs, are driving greater investment in the sector.
- Emerging business models: Innovative business models, such as pay-as-you-go (PAYG) financing, are making off-grid solar more accessible to low-income households.
Major Investors in the Off-Grid Solar Market
| Investor | Investment Strategy | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| SunFunder | Provides debt financing and technical assistance to off-grid solar companies. | Solar home systems, mini-grids, and commercial and industrial solar projects. |
| SolarAid | Focuses on providing solar lanterns and home systems to off-grid communities in sub-Saharan Africa. | Combating poverty, improving education, and promoting sustainable development. |
| Acumen Fund | Invests in companies that provide affordable energy solutions to low-income populations. | Off-grid solar, clean water, and sanitation technologies. |
| The Shell Foundation | Supports initiatives that promote access to clean energy in developing countries. | Off-grid solar, renewable energy, and energy efficiency. |
| The World Bank | Provides loans, grants, and technical assistance for off-grid solar projects. | Expanding access to electricity in rural areas, promoting sustainable development, and mitigating climate change. |
Social and Environmental Impact
Off-grid solar energy has a significant impact on both the environment and society. Its ability to provide clean and reliable energy to remote areas, where access to electricity is limited, has the potential to transform lives and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Climate Change Mitigation
Off-grid solar systems play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuel-based energy sources. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems generate electricity without producing any harmful pollutants. The widespread adoption of off-grid solar technology can contribute significantly to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Energy Access
Off-grid solar provides access to electricity for millions of people in underserved communities around the world. This has a transformative impact on their lives, enabling them to access essential services such as education, healthcare, and communication. By bringing light and power to remote areas, off-grid solar empowers individuals and communities, fostering economic development and improving quality of life.
Poverty Reduction
Off-grid solar can contribute to poverty reduction by creating new economic opportunities. It enables small businesses to operate and grow, leading to job creation and increased income. The availability of electricity also reduces reliance on expensive and inefficient energy sources, freeing up household budgets and improving financial stability.
Waste Management
One of the challenges associated with off-grid solar deployment is the management of end-of-life solar panels. Improper disposal can release harmful chemicals into the environment. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to develop and implement robust recycling and disposal programs for solar panels.
Community Engagement
Successful off-grid solar projects require strong community engagement. It is crucial to involve local communities in the planning, implementation, and maintenance of these projects. This ensures that projects are tailored to local needs and that communities have a sense of ownership.
Examples of Successful Off-Grid Solar Projects
- The Barefoot College in India: This organization has trained over 10,000 women in rural communities to become solar engineers. These women have installed solar systems in their villages, bringing light and power to homes and schools. This project has empowered women, improved access to education, and contributed to a more sustainable future.
- The Lighting Africa initiative: This program, led by the World Bank, has helped to bring solar energy to millions of people in Africa. By providing financing and technical support to local businesses, Lighting Africa has created a market for solar products and services, contributing to economic growth and poverty reduction.
- The Global Off-Grid Lighting Association (GOGLA): GOGLA is a global network of companies and organizations working to promote off-grid solar solutions. It provides a platform for collaboration and knowledge sharing, helping to accelerate the adoption of off-grid solar technology.
The global off-grid solar sector is a testament to human ingenuity and a commitment to a sustainable future. With continued technological advancements, supportive policies, and increased investment, this sector has the potential to transform lives, empower communities, and pave the way for a brighter tomorrow.
The global off-grid solar sector is booming, with companies like Cesiumastro leading the charge in providing clean energy solutions to remote communities. But the industry is also facing challenges, like the recent accusations that a former Cesiumastro executive spilled trade secrets to an upstart competitor, Anysignal. This legal battle could have significant implications for the future of the off-grid solar market, potentially impacting the growth and development of innovative technologies in the sector.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News