Understanding Website Redirects
Website redirects are a common occurrence in the online world, directing users from one web address to another. While redirects are often a seamless and necessary part of the internet experience, they can also be exploited for malicious purposes. Understanding the different types of redirects and their implications is crucial for navigating the digital landscape safely and effectively.
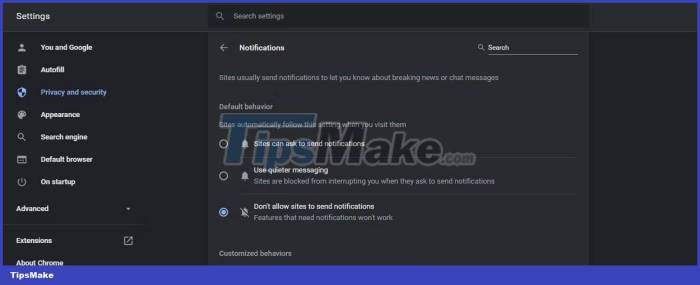
Legitimate Website Redirects, Google chrome block unexpected website redirects
Legitimate redirects are intended to improve user experience or enhance website functionality. These redirects are often implemented for purposes, mobile optimization, or to update website addresses.
Here are some common reasons for legitimate website redirects:
* Optimization: Redirects can be used to consolidate website content, ensuring search engines index the most relevant pages. For example, if a website has multiple pages with similar content, a redirect can be used to direct users to the most comprehensive page, improving ranking.
* Mobile Optimization: Redirects can ensure that users are directed to the appropriate mobile version of a website, providing a better user experience on mobile devices.
* Website Updates: When a website changes its domain name or structure, redirects can be used to ensure that users are directed to the correct location. For example, if a website moves from www.example.com to www.newexample.com, a redirect can be implemented to automatically direct users to the new address.
Malicious Website Redirects
Malicious redirects are used by cybercriminals to exploit users and gain unauthorized access to their information or devices. These redirects can be used for phishing attacks, malware distribution, or to redirect users to websites containing inappropriate or harmful content.
Here are some examples of malicious redirects:
* Phishing Attacks: Malicious redirects can be used to direct users to fake websites that mimic legitimate websites, such as banks or online retailers. These fake websites may ask users to enter sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details, which can then be stolen by cybercriminals.
* Malware Distribution: Malicious redirects can be used to direct users to websites containing malicious software, such as viruses or spyware. When users visit these websites, their devices may become infected with malware, potentially leading to data loss, identity theft, or financial losses.
* Inappropriate Content: Malicious redirects can also be used to direct users to websites containing inappropriate or harmful content, such as pornography, hate speech, or violence. These websites may expose users to offensive or dangerous content, or they may be used to spread misinformation or propaganda.
Google Chrome’s Security Features
Google Chrome is renowned for its robust security features, playing a crucial role in safeguarding users from malicious website redirects and other online threats. These features work diligently behind the scenes to ensure a safe browsing experience.
Safe Browsing
Google Chrome’s Safe Browsing feature is a fundamental defense against unexpected website redirects. This feature utilizes a vast database of known malicious websites, constantly updated by Google’s security experts. When you visit a website, Chrome checks its URL against this database. If the site is identified as malicious, Chrome will block access and display a warning message, preventing you from being redirected to a harmful destination.
Phishing and Malware Protection
Chrome’s Phishing and Malware Protection feature is another vital shield against website redirects. It goes beyond simply checking URLs; it analyzes the content of websites to identify potential threats. Phishing websites often mimic legitimate sites to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Chrome’s protection detects these attempts by analyzing the website’s code and content, looking for telltale signs of phishing, such as suspicious links, unusual formatting, or requests for personal data.
How Google Chrome’s Security Features Work Together
Google Chrome’s security features work in concert to create a comprehensive defense against unexpected website redirects. Safe Browsing acts as the first line of defense, blocking access to known malicious sites. If a website is not flagged by Safe Browsing, Chrome’s Phishing and Malware Protection kicks in, scrutinizing the content for potential threats. If either feature detects a malicious redirect, Chrome will block the redirect and warn the user.
Updates and Improvements
Google Chrome’s security features are constantly evolving to stay ahead of the ever-changing threat landscape. Google’s security team continuously updates the Safe Browsing database with new malicious websites and phishing techniques. Additionally, Chrome receives regular security updates that enhance its phishing and malware detection capabilities. These updates ensure that Chrome remains a reliable and secure browser, capable of protecting users from unexpected website redirects and other online threats.
Identifying and Addressing Unexpected Redirects: Google Chrome Block Unexpected Website Redirects
You’re cruising the web, clicking on a link, and suddenly you’re on a completely different website. Or, you’re trying to access your favorite online store, but the page takes forever to load, and you’re bombarded with pop-ups. These are classic signs of unexpected website redirects, and they can be a real pain. But don’t worry, there are steps you can take to identify and address these issues.
Unexpected website redirects can be a symptom of various problems, from simple glitches to malicious attacks. Knowing how to spot them and handle them effectively can help you stay safe online.
Identifying Unexpected Redirects
Unexpected redirects can manifest in various ways, and it’s crucial to recognize these warning signs.
- URL Changes: The most obvious sign is a change in the website’s URL in your browser’s address bar. If you click on a link expecting to land on a specific website, but the URL changes to something completely different, you might be dealing with a redirect.
- Unexpected Pop-Ups: A sudden barrage of pop-ups, especially those unrelated to the website you’re visiting, can be a sign of a redirect. These pop-ups often contain advertisements, surveys, or even malware.
- Slow Loading Times: If a website takes an unusually long time to load, especially if it’s usually quick, it might be a sign of a redirect. The redirect process can add extra time to the loading process.
- Unfamiliar Website Content: If the content on the website you land on is completely different from what you expected, or if it seems irrelevant to the link you clicked, you might be dealing with a redirect.
Addressing Unexpected Redirects
Once you’ve identified an unexpected redirect, there are a few steps you can take to address it.
- Close the Browser Tab: The simplest solution is often the best. Close the browser tab or window where you encountered the redirect. This will stop the redirect and prevent any further issues.
- Check the URL: Look carefully at the URL in your browser’s address bar. If it looks suspicious or doesn’t match the website you intended to visit, don’t proceed.
- Use a Different Browser: Try accessing the website using a different web browser. This can help you determine if the redirect is specific to your current browser or a more widespread issue.
- Clear Browser Cache and Cookies: Sometimes, outdated cached data or cookies can cause unexpected redirects. Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies can resolve this issue.
- Run a Malware Scan: If you suspect a malicious redirect, run a full malware scan on your computer. This can help identify and remove any malware that might be causing the issue.
Verifying Website Redirects
Not all redirects are malicious. Some are legitimate, like when you’re redirected to a secure version of a website (HTTPS). However, it’s essential to verify the legitimacy of any redirect to ensure your safety.
- Check the URL: The URL should start with “https://” for a secure website. Make sure the website’s domain name is correct and matches the website you intended to visit.
- Look for Security Certificate: A padlock icon in your browser’s address bar and “https://” at the beginning of the URL indicate a secure connection. You can click on the padlock icon to view the website’s security certificate and verify its legitimacy.
Preventing Unexpected Redirects
Here are some proactive measures you can take to minimize the risk of encountering unexpected redirects:
- Use Strong Passwords: Strong passwords make it harder for hackers to gain access to your accounts, which can be a source of malicious redirects.
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Software updates often include security patches that can fix vulnerabilities that hackers exploit to cause redirects.
- Be Cautious of Links: Be wary of clicking on links from unknown sources or suspicious emails. Always double-check the URL before clicking.
Protecting Yourself from Malicious Redirects
While website redirects can be a legitimate part of web browsing, malicious redirects are a common tactic used by cybercriminals to steal your personal information or infect your device with malware. Understanding how these attacks work and taking precautions can help you stay safe online.
Common Tactics Used by Attackers
Attackers use various methods to trick users into visiting malicious websites. Some of the most common tactics include:
- Phishing Emails: These emails often appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks, social media platforms, or government agencies. They may contain malicious links that, when clicked, redirect you to a fake website designed to steal your login credentials or other sensitive information.
- Social Media Scams: Malicious links can be shared on social media platforms, disguised as news articles, promotions, or even funny videos. Clicking on these links can redirect you to a website designed to steal your data or install malware on your device.
- Compromised Websites: Legitimate websites can be compromised by hackers, allowing them to inject malicious code that redirects visitors to malicious websites. This can happen without the website owner’s knowledge.
The Importance of Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software play a crucial role in protecting your computer from malicious redirects and other online threats. These programs scan your computer for malware and can block attempts to redirect you to malicious websites. They also help to identify and remove any malware that may have already infected your system.
Identifying and Avoiding Phishing Emails and Websites
Recognizing phishing emails and websites is essential to protect yourself from malicious redirects. Here are some key indicators to watch out for:
- Suspicious Links: Be cautious of links that look unusual or are embedded in emails from unknown senders. Hover your mouse over the link to see the actual URL before clicking.
- Grammar and Spelling Errors: Phishing emails often contain grammatical errors or misspellings, which can be a sign that the email is not legitimate.
- Urgent Requests: Phishing emails may try to create a sense of urgency, urging you to click on a link or provide personal information immediately.
- Fake Websites: Pay attention to the website’s URL. Malicious websites may have URLs that are similar to legitimate websites but with slight variations. Check for the “https” prefix and a valid security certificate.
Staying Safe Online
In addition to using antivirus and anti-malware software, there are other steps you can take to protect yourself from malicious redirects:
- Avoid Suspicious Links: Do not click on links from unknown senders or that appear suspicious.
- Keep Your Software Up-to-Date: Regularly update your operating system, web browser, and other software to patch security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Be Cautious About What Information You Share Online: Avoid sharing personal information, such as your passwords, credit card numbers, or Social Security number, on websites you don’t trust.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create unique, strong passwords for all your online accounts and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code sent to your phone or email in addition to your password when logging in to your accounts.
Google chrome block unexpected website redirects – Navigating the digital world can be a minefield of unexpected redirects. But with Google Chrome’s vigilant security features, you can rest assured that your online experience is protected from malicious actors. By understanding the signs of unexpected redirects, following our tips, and staying informed about the latest threats, you can confidently explore the internet without fear. Remember, a little knowledge goes a long way in keeping your online life secure.
Ever get that annoying “redirect loop” in Chrome? It’s like your browser is stuck in a never-ending game of “who’s got the remote.” Sometimes, it’s a sign of malware, but other times, it’s just a website being a bit… overzealous. Remember when Nintendo was cracking down on any talk about the NX? nintendo clamping down on nx talk Maybe those redirects are just a website’s way of keeping a secret, just like Nintendo! Whatever the reason, hopefully, you can clear the redirect loop and get back to browsing.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News