Tesla Model S Wireless Security Vulnerabilities
The Tesla Model S, a luxurious electric vehicle, has been lauded for its performance and technology. However, like any connected device, it is susceptible to wireless security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities could allow hackers to gain unauthorized access to the vehicle’s systems, potentially compromising its security and user privacy.
Wireless Attack Methods
Hackers can exploit several wireless attack methods to compromise a Tesla Model S. These methods include:
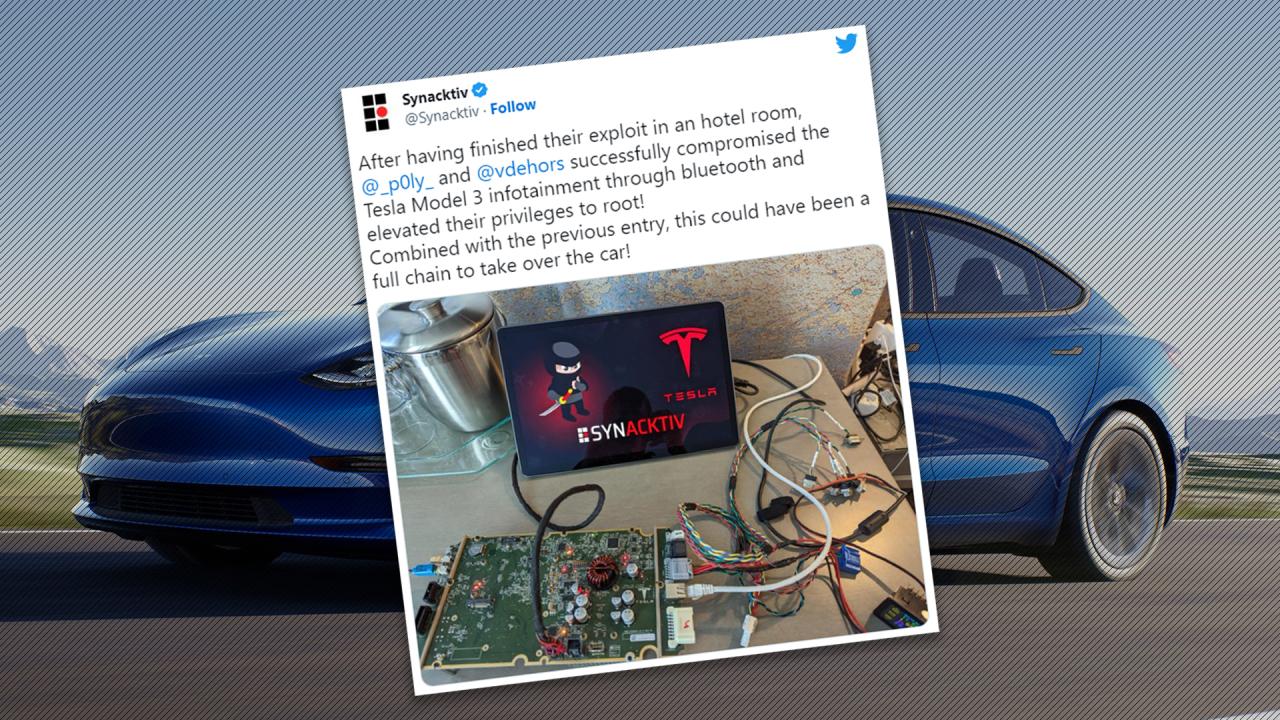
- Bluetooth Hacking: Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the vehicle’s Bluetooth system to gain access to its infotainment system, potentially allowing them to control certain functions, such as music playback, or even steal sensitive data.
- Wi-Fi Hacking: Tesla Model S vehicles connect to Wi-Fi networks, making them vulnerable to Wi-Fi hacking. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in the Wi-Fi network or the vehicle’s Wi-Fi connectivity to intercept data or gain access to the vehicle’s internal systems.
- Cellular Network Attacks: The Tesla Model S uses cellular networks for communication and data transfer. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in the cellular network or the vehicle’s cellular connectivity to intercept data or gain access to the vehicle’s internal systems.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Tesla vehicles receive OTA updates for software updates and bug fixes. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in the OTA update process to inject malicious code into the vehicle’s software, potentially compromising its security.
Hacking Methods and Techniques: Hacker S Wireless Attack Tesla Model S
While Tesla vehicles are known for their advanced technology and safety features, they are not immune to security vulnerabilities, particularly when it comes to wireless attacks. These attacks can exploit weaknesses in the car’s communication protocols and software, potentially allowing hackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or even control the vehicle remotely.
Steps Involved in a Wireless Attack
A typical wireless attack on a Tesla Model S often involves a series of steps, starting with reconnaissance and ending with data exfiltration.
- Reconnaissance: This initial phase involves gathering information about the target vehicle, such as its location, model, and communication protocols. Hackers may use publicly available resources, social media, or even physical surveillance to gather this information.
- Exploitation: Once the hacker has gathered sufficient information, they can begin exploiting vulnerabilities in the vehicle’s wireless communication system. This might involve identifying and exploiting known security flaws in the car’s software, or using social engineering techniques to trick the owner into providing access.
- Data Exfiltration: Once the hacker has gained access to the vehicle’s systems, they can exfiltrate data, such as personal information, location data, or even sensitive vehicle data. This data can then be used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft, blackmail, or even vehicle theft.
Real-World Examples of Wireless Attacks
While specific details of wireless attacks targeting Tesla vehicles are often kept confidential for security reasons, there have been documented cases of attacks on similar systems. For instance, in 2015, researchers demonstrated the ability to remotely control a Jeep Cherokee through its infotainment system, highlighting the potential for wireless attacks on connected vehicles.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Successful Wireless Attack, Hacker s wireless attack tesla model s
Imagine a scenario where a hacker targets a Tesla Model S parked in a public garage. Using publicly available information, the hacker identifies the car’s model, year, and communication protocols. They then exploit a known vulnerability in the car’s software, allowing them to gain remote access to the vehicle’s systems.
Once inside, the hacker can access the vehicle’s GPS data, tracking the owner’s movements and potentially sharing this information with others. They could also manipulate the car’s controls, such as the brakes, steering, or even the doors, potentially causing harm or theft.
This scenario highlights the potential risks associated with wireless attacks on connected vehicles. While Tesla and other car manufacturers are constantly working to improve security, it’s crucial to be aware of these vulnerabilities and take steps to mitigate them.
Impact and Mitigation Strategies
A successful wireless attack on a Tesla Model S could have severe consequences, ranging from vehicle control hijacking to data theft and privacy breaches. These attacks could lead to dangerous situations on the road, compromise sensitive personal information, and cause financial losses. Understanding the potential impact and implementing mitigation strategies is crucial to protect Tesla owners and their vehicles.
Potential Consequences of Wireless Attacks
The consequences of a successful wireless attack on a Tesla Model S can be far-reaching and potentially dangerous. Here are some key impacts:
- Vehicle Control Hijacking: An attacker could gain unauthorized control over the vehicle’s critical functions, such as steering, acceleration, braking, and even the infotainment system. This could lead to accidents, injuries, or even fatalities.
- Data Theft: Attackers could steal sensitive data stored in the vehicle’s systems, including personal information, driving records, and even financial data. This could result in identity theft, financial fraud, and privacy violations.
- Privacy Breaches: Hackers could access and monitor the vehicle’s sensors and cameras, potentially compromising the privacy of the occupants. This could involve tracking their movements, recording conversations, or even accessing live video feeds.
- Remote Vehicle Immobilization: Attackers could disable the vehicle remotely, rendering it inoperable. This could lead to inconvenience, financial losses, and potential safety risks, especially in emergencies.
- Ransomware Attacks: Hackers could hold the vehicle’s systems hostage, demanding a ransom to regain control. This could result in significant financial losses and disruptions to daily life.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with wireless attacks, Tesla owners and the company must implement a multi-layered approach. This includes:
- Software Updates: Tesla regularly releases software updates to address security vulnerabilities and enhance the vehicle’s defenses. Owners should install these updates promptly to ensure their vehicles are protected against the latest threats.
- Hardware Modifications: Some hardware modifications can further enhance the vehicle’s security. These include:
- Signal Jammers: These devices can block wireless signals from reaching the vehicle, preventing attackers from establishing a connection.
- Faraday Cages: These enclosures block electromagnetic radiation, effectively shielding the vehicle’s systems from wireless attacks.
- Security Best Practices: Tesla owners should adopt security best practices to minimize their risk of being targeted by attackers:
- Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for all Tesla accounts and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for all Tesla accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, as they are often vulnerable to attacks.
- Regularly Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Monitor the vehicle’s systems for any unusual behavior or signs of unauthorized access.
Risk Mitigation Table
The following table summarizes the potential risks associated with each identified vulnerability and Artikels corresponding mitigation strategies:
| Vulnerability | Potential Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unsecured Wi-Fi Connection | Data theft, unauthorized access to vehicle systems | Use strong passwords, enable encryption, avoid public Wi-Fi networks |
| Outdated Software | Exploitation of known vulnerabilities | Install software updates promptly |
| Weak Authentication Mechanisms | Unauthorized access to vehicle systems | Enable two-factor authentication, use strong passwords |
| Vulnerable Communication Protocols | Data interception, manipulation of vehicle commands | Use secure communication protocols, encrypt data transmissions |
| Lack of Security Awareness | Unintentional exposure to attacks | Educate Tesla owners on security best practices |
The Role of Technology and Regulations
The advancement of technology has significantly impacted the automotive industry, leading to the emergence of connected vehicles, including Tesla models. These vehicles are equipped with advanced technologies that enhance driving experience and safety, but also introduce new security vulnerabilities that require innovative solutions. This section explores the role of emerging technologies in mitigating wireless security risks in connected vehicles and examines the current regulatory landscape surrounding vehicle cybersecurity.
Emerging Technologies for Enhanced Wireless Security
Emerging technologies play a crucial role in bolstering wireless security in connected vehicles. They offer innovative approaches to address vulnerabilities and enhance protection against cyberattacks.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms can be employed to detect anomalies and suspicious activities in vehicle networks. These technologies can analyze real-time data from sensors and vehicle systems to identify potential threats and trigger appropriate countermeasures.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s decentralized and tamper-proof nature can be leveraged to secure vehicle data and transactions. It can create a secure and immutable record of vehicle operations, making it difficult for hackers to manipulate or alter critical information.
- Secure Hardware and Software: Advanced hardware and software security measures are essential for protecting connected vehicles. This includes implementing secure boot processes, encryption protocols, and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: OTA updates allow manufacturers to patch vulnerabilities and improve security in real-time. By continuously updating vehicle software, manufacturers can address new threats and enhance overall system resilience.
Regulatory Landscape of Vehicle Cybersecurity
The automotive industry is facing growing pressure from regulatory bodies to address cybersecurity concerns. Regulations are evolving to ensure the safety and security of connected vehicles.
- United States: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has issued guidelines for cybersecurity in connected vehicles, focusing on risk management, vulnerability assessments, and incident response. The agency is also working on developing specific regulations for vehicle cybersecurity.
- European Union: The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to vehicle data, requiring manufacturers to implement robust security measures to protect personal information. The EU is also developing specific regulations for vehicle cybersecurity, including the Cybersecurity Act, which aims to enhance cybersecurity in critical infrastructure, including connected vehicles.
- Global Harmonization: There is a growing trend towards global harmonization of vehicle cybersecurity regulations. International organizations like the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) are working to develop standardized cybersecurity requirements for connected vehicles, promoting interoperability and global consistency.
Timeline of Wireless Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures
The automotive industry has witnessed a continuous evolution of wireless security vulnerabilities and countermeasures. This timeline highlights key milestones in the development of secure Tesla vehicles:
| Year | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | First Tesla Model S released | Initial models lacked robust cybersecurity features, making them susceptible to attacks. |
| 2015 | Tesla introduces over-the-air updates | OTA updates allow Tesla to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security in real-time. |
| 2016 | Researchers demonstrate hacking of Tesla Model S | Researchers demonstrated the ability to remotely control a Tesla Model S, highlighting the need for improved cybersecurity. |
| 2017 | Tesla enhances security measures | Tesla implements additional security features, including encryption protocols and intrusion detection systems. |
| 2019 | NHTSA issues guidelines for vehicle cybersecurity | NHTSA guidelines encourage manufacturers to implement robust cybersecurity measures, including vulnerability assessments and incident response plans. |
| 2020 | Tesla continues to improve cybersecurity | Tesla continues to invest in research and development to enhance vehicle security, including implementing AI and ML algorithms for threat detection. |
Hacker s wireless attack tesla model s – The vulnerabilities exposed in Tesla Model S vehicles serve as a stark reminder that the pursuit of technological advancement must be accompanied by unwavering commitment to security. As connected vehicles become increasingly sophisticated, the threat landscape evolves, demanding a proactive approach to cybersecurity. This article has shed light on the complexities of wireless attacks targeting Tesla vehicles, highlighting the importance of ongoing research, collaboration, and robust mitigation strategies. By understanding the risks and implementing appropriate measures, we can pave the way for a future where connected vehicles offer both convenience and security, empowering drivers and passengers alike.
The news of a hacker’s wireless attack on a Tesla Model S sent shivers down the spines of tech enthusiasts, highlighting the vulnerability of even the most advanced vehicles. While we’re grappling with the implications of such attacks, news of the Pixel XL appearing on Geekbench reminds us that the tech world is constantly evolving. This new development could signal the arrival of a powerful new smartphone, but it also serves as a reminder that we must remain vigilant about cybersecurity, especially in a world where even our cars are becoming connected.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News