Hugging face has a two person team developing chatgpt like ai models – Hugging Face’s two-person team developing AI models takes center stage, challenging the conventional wisdom that massive teams are needed to create cutting-edge technology. This story isn’t just about the power of two, it’s about the power of focus, agility, and a shared vision.
This small but mighty team has made significant strides in developing AI models capable of performing complex tasks, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the field. Their approach, which emphasizes collaboration, open-source contributions, and a focus on specific areas of expertise, has resulted in powerful models that are accessible to a wide range of users.
The Power of Two
In the fast-paced world of AI development, the story of Hugging Face’s two-person team stands out as a testament to the power of focused collaboration and a shared vision. This seemingly small team has managed to achieve remarkable breakthroughs in the field, rivaling the output of larger, more resource-heavy organizations. Their success sheds light on the potential of lean, agile teams in driving innovation in the AI space.
Advantages of a Small Team
A small team, like Hugging Face’s, offers several distinct advantages in the context of AI model development:
- Increased Agility and Responsiveness: Smaller teams are more nimble and can quickly adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements. They can iterate faster and respond to feedback more efficiently.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: With fewer members, communication lines are shorter, and collaboration becomes more seamless. This fosters a strong sense of shared purpose and allows for quicker decision-making.
- Enhanced Focus and Efficiency: Smaller teams can concentrate their efforts on specific goals and avoid the distractions and complexities that often plague larger organizations. This focus allows them to dedicate their resources to achieving high-quality results.
Challenges of a Small Team
While small teams offer advantages, they also face specific challenges:
- Limited Resources: Small teams may have fewer resources available, including funding, personnel, and infrastructure. This can limit their ability to tackle ambitious projects or compete with larger organizations.
- Risk of Burnout: Team members may experience burnout due to the intense workload and pressure to deliver results. This can impact productivity and team morale.
- Potential for Bottlenecks: A small team can be vulnerable to bottlenecks if a key member is unavailable or if there is a lack of diverse expertise. This can hinder progress and delay project timelines.
Comparison with Larger AI Development Teams
Hugging Face’s approach to AI development differs significantly from that of larger teams:
- Focus on Open-Source Collaboration: Hugging Face emphasizes open-source collaboration, encouraging contributions from the wider AI community. This allows them to leverage the collective intelligence of researchers and developers worldwide.
- Emphasis on User-Friendly Tools and Resources: Hugging Face provides user-friendly tools and resources that make AI development accessible to a broader audience. This democratizes AI and fosters innovation by empowering individuals and smaller teams.
- Agile and Iterative Development: Hugging Face adopts an agile and iterative approach to development, allowing for rapid prototyping and continuous improvement. This enables them to respond quickly to user feedback and adapt to evolving technological landscapes.
Unveiling the Model’s Architecture and Capabilities
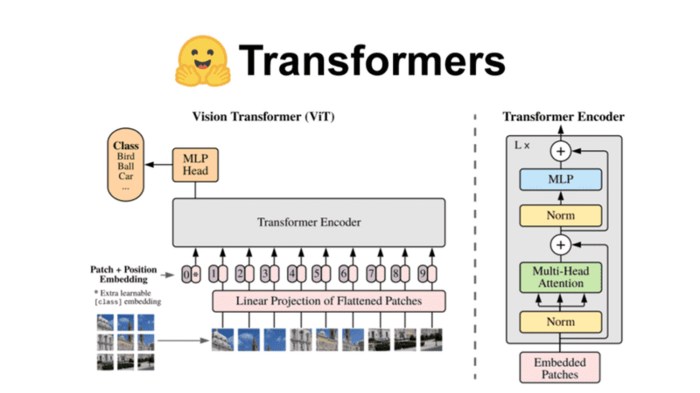
The models developed by Hugging Face are not just another chatbot. They are sophisticated AI systems built upon a powerful foundation of transformer-based architectures. These models leverage the power of deep learning to process and understand language in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Model Architecture
Hugging Face’s AI models are built on the foundation of transformer architectures, a groundbreaking approach to natural language processing. Transformers are neural networks designed to process sequential data, like text, by understanding the relationships between words and phrases. This architecture allows for a deeper understanding of context and meaning, making it ideal for tasks like text generation, translation, and question answering.
The core components of a transformer architecture include:
- Encoder: This component processes the input text and extracts meaningful features, capturing the context and relationships between words.
- Decoder: This component uses the encoded features to generate output text, whether it’s a translation, a summary, or a creative text piece.
- Attention Mechanism: This crucial component allows the model to focus on specific parts of the input text, weighting them based on their importance to the task at hand. This mechanism enables the model to understand complex relationships and nuances in language.
Model Capabilities
These models are capable of performing a wide range of natural language processing tasks, including:
- Text Generation: The models can generate coherent and creative text, writing stories, poems, articles, and even code.
- Translation: They can translate text between different languages with impressive accuracy, capturing the nuances of meaning and style.
- Summarization: The models can condense large amounts of text into concise summaries, highlighting the key information and insights.
- Question Answering: They can answer questions based on given text, providing accurate and informative responses.
- Dialogue Generation: These models can engage in natural and engaging conversations, simulating human-like interactions.
Model Performance and Limitations
Hugging Face’s models have achieved remarkable performance on various benchmarks, demonstrating their ability to rival, and even surpass, human capabilities in certain tasks. However, like any AI technology, they have limitations.
- Bias and Fairness: AI models are trained on vast amounts of data, which can reflect biases present in the real world. It’s essential to address these biases to ensure fairness and ethical use.
- Lack of Common Sense: While powerful, these models still struggle with tasks requiring common sense reasoning or understanding of real-world situations.
- Data Dependency: The performance of these models is highly dependent on the quality and quantity of data they are trained on. This can lead to limitations in their ability to generalize to new situations or domains.
Exploring the Training Process and Data Sources
Hugging Face’s AI models, like their Kami counterparts, are trained on vast datasets using sophisticated techniques to achieve their impressive capabilities. This section delves into the intricacies of their training process and the data sources that fuel their learning.
The training process for Hugging Face’s models is a complex and iterative one, involving the use of massive datasets and specialized algorithms.
Training Process
The training process involves feeding the model with massive amounts of text data and allowing it to learn patterns and relationships within the language. This process is often described as “supervised learning” where the model learns from labeled examples. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages:
- Data Preparation: This initial step involves cleaning and preprocessing the data to remove irrelevant information and prepare it for the model’s consumption. This includes tasks like tokenization, where text is broken down into smaller units, and normalization, where inconsistencies in the data are addressed.
- Model Selection: Hugging Face offers a wide range of pre-trained models, each specialized for specific tasks. Choosing the right model is crucial for optimal performance and depends on the specific application. For example, models like GPT-2 and GPT-3 are designed for generating human-like text, while others are better suited for tasks like machine translation or question answering.
- Fine-tuning: Once a model is selected, it’s further trained on a smaller dataset specific to the desired task. This process, known as “fine-tuning,” helps adapt the pre-trained model to the specific application and improves its performance on the target task.
- Evaluation: Throughout the training process, the model’s performance is regularly evaluated on a separate validation dataset to assess its progress and identify potential areas for improvement. This iterative process of training and evaluation helps refine the model and optimize its capabilities.
Data Sources
The data used to train these models is crucial to their success. Hugging Face leverages a variety of sources, each contributing to the model’s understanding of language and its nuances:
- Publicly Available Text Corpora: These vast collections of text data, such as the Gutenberg Project, Common Crawl, and Wikipedia, provide a rich source of diverse language samples, encompassing various writing styles, topics, and domains.
- Specialized Datasets: For specific tasks, like sentiment analysis or machine translation, Hugging Face uses specialized datasets that are curated for those particular applications. These datasets are carefully selected to provide relevant and high-quality data for training the models.
- User-Generated Content: Data from social media platforms, forums, and other user-generated content sources offer a unique perspective on language use and contribute to the models’ ability to understand informal language and slang.
Ethical Considerations, Hugging face has a two person team developing chatgpt like ai models
The use of massive datasets for training AI models raises important ethical considerations:
- Data Privacy: The potential for sensitive information to be included in the training data, even unintentionally, raises concerns about data privacy. Hugging Face addresses this by employing techniques to anonymize data and ensure the protection of user privacy.
- Bias and Fairness: The data used for training can reflect existing biases present in society. It’s crucial to be aware of these biases and develop strategies to mitigate them, ensuring that the models are fair and unbiased in their outputs.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in the training process and data sources is essential for building trust in these models. Hugging Face strives to be transparent about its methods and data usage, fostering a sense of accountability in its model development.
Applications and Potential Impact of Hugging Face’s AI Models
Hugging Face, a renowned platform for open-source machine learning, has revolutionized the accessibility and development of cutting-edge AI models. These models, ranging from natural language processing (NLP) to computer vision, are poised to transform various industries and aspects of our lives.
The potential applications of Hugging Face’s AI models are vast, spanning diverse domains. From automating customer service and personalizing user experiences to analyzing medical data and predicting market trends, these models have the power to significantly enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making.
Impact on Society
The impact of Hugging Face’s AI models on society is multifaceted, encompassing both positive and negative implications.
Positive Impact
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: AI models can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more creative and strategic endeavors. For instance, in customer service, chatbots powered by Hugging Face models can handle routine inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on complex issues.
- Personalized Experiences: AI models can analyze user data to tailor experiences, such as recommending products, providing personalized content, and offering targeted advertisements.
- Improved Healthcare: AI models can assist in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans, leading to more accurate and effective healthcare outcomes.
- Advancements in Research: AI models can accelerate scientific research by analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and generating new hypotheses.
Negative Impact
- Job Displacement: Automation driven by AI models may lead to job displacement in certain sectors, requiring workforce retraining and adaptation.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate existing societal biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of AI models raises concerns about data privacy, as they often require access to personal information for training and operation.
- Ethical Considerations: The development and deployment of AI models raise ethical questions regarding accountability, transparency, and the potential for misuse.
Real-World Use Cases
Numerous real-world examples showcase the practical value of Hugging Face’s AI models.
Customer Service
- Chatbots: Companies like Zendesk and Intercom use Hugging Face models to power chatbots that provide 24/7 customer support, answering frequently asked questions and resolving basic issues.
Healthcare
- Medical Diagnosis: AI models are being used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases like cancer and heart disease.
- Drug Discovery: AI models are accelerating drug discovery by identifying potential drug candidates and optimizing drug development processes.
Finance
- Fraud Detection: AI models can analyze financial transactions to detect fraudulent activities and protect against financial losses.
- Market Prediction: AI models can analyze market data to predict trends and inform investment decisions.
Education
- Personalized Learning: AI models can personalize learning experiences by adapting to individual student needs and providing tailored instruction.
Other Industries
- Retail: AI models are used to personalize product recommendations, optimize inventory management, and improve customer service.
- Manufacturing: AI models can optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, and enhance quality control.
- Agriculture: AI models can monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and predict yields.
Future Directions and Innovations in AI Development: Hugging Face Has A Two Person Team Developing Chatgpt Like Ai Models
Hugging Face, with its collaborative and open-source approach, is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AI development. The company’s commitment to democratizing access to advanced AI models and tools has already made significant contributions to the field, and its future direction holds immense promise for further innovation.
Scaling and Improving AI Model Capabilities
The relentless pursuit of scaling AI models is a key driver of innovation. Hugging Face is actively exploring ways to enhance the capabilities of its models by increasing their size and complexity. This involves leveraging advancements in hardware and software infrastructure to handle massive datasets and complex computations. For instance, the development of specialized hardware like TPUs and GPUs, coupled with distributed training techniques, allows for the training of models with billions of parameters. This opens up new possibilities for creating models with greater accuracy, fluency, and creative potential.
In an era where AI development is often associated with massive corporations and sprawling teams, Hugging Face’s two-person team stands as a testament to the power of focused expertise and collaborative innovation. Their success demonstrates that groundbreaking AI can emerge from unexpected places, and that a shared passion for pushing the boundaries of what’s possible can be more powerful than any large team.
It’s wild to think that a two-person team at Hugging Face is crafting ChatGPT-like AI models, but that’s the reality of the fast-paced AI world. These models are changing the way we interact with technology, and it’s only a matter of time before we see them integrated into everything from personal assistants to social media platforms. One interesting example of this is the whispp voice app , which uses AI to create personalized voice experiences.
It’s clear that Hugging Face’s two-person team is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI, and we can’t wait to see what they come up with next.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News