Keep it complexity in check with pragmatic composable commerce – Composable commerce is the hottest thing in e-commerce right now, and for good reason. It promises increased flexibility, scalability, and agility, allowing businesses to build custom solutions that perfectly fit their needs. But with great power comes great complexity. Managing multiple integrations and ensuring data consistency across different systems can be a real headache.
That’s where pragmatic composability comes in. By taking a strategic approach to managing complexity, businesses can unlock the full potential of composable commerce without getting bogged down in technical challenges. This article will explore key strategies for achieving pragmatic composability and ensuring a smooth transition to a modern, flexible e-commerce architecture.
Composable Commerce
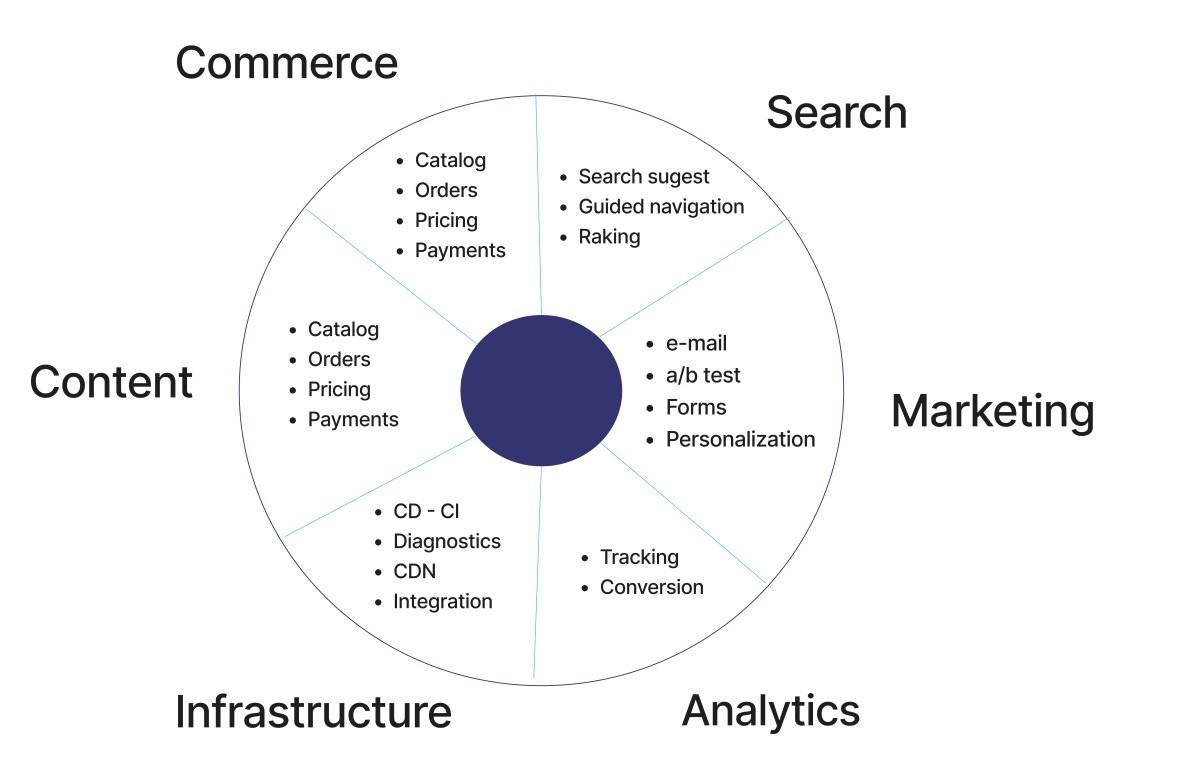
Forget the days of monolithic e-commerce platforms that felt like trying to squeeze a square peg into a round hole. Composable commerce is here, and it’s changing the game. Imagine a Lego set for your online store, where you can pick and choose the best-in-class components to create the perfect shopping experience.
Composable Commerce: A Paradigm Shift
Composable commerce is all about building your e-commerce ecosystem with independent, best-of-breed services that can be easily connected and integrated. It’s like building a custom car, where you can choose the engine, the body, the wheels, and the interior to create the exact ride you want. Traditional e-commerce platforms, on the other hand, are like buying a pre-configured car—you get what you get, and you can’t change much.
Real-World Applications of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce is being used by businesses across various industries to achieve specific goals. For example, a fashion retailer might use a composable commerce platform to connect its website with a social media platform, allowing customers to purchase items directly from their Instagram feed. A food delivery service might use a composable commerce platform to integrate with a third-party logistics provider to optimize delivery routes and reduce delivery times.
Benefits of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce offers a range of benefits that can help businesses achieve their e-commerce goals.
- Increased Flexibility: Businesses can easily adapt their e-commerce platform to meet changing customer needs and market trends. They can add new features, integrate new technologies, and experiment with new business models without having to rewrite their entire platform.
- Enhanced Scalability: Composable commerce platforms are designed to scale with your business. As your business grows, you can easily add new components and resources to handle the increased traffic and demand.
- Improved Agility: Businesses can respond quickly to market changes and competitor moves. They can launch new products and services faster, and they can adapt their marketing campaigns to changing customer preferences.
The Challenge of Complexity in Composable Commerce
While composable commerce promises a flexible and scalable future for businesses, it also introduces a new set of complexities that must be carefully addressed. The very nature of this architecture, with its modular and interconnected components, can create intricate challenges in implementation and management.
Managing Multiple Integrations
The modular nature of composable commerce requires businesses to integrate various best-of-breed solutions for different functionalities like product information management (PIM), order management systems (OMS), and customer relationship management (CRM). This integration process, while offering flexibility, can be complex and time-consuming. Each integration requires careful configuration and testing to ensure seamless data flow and functionality.
- Data Mapping and Transformation: Each system may use different data structures and formats, requiring complex mapping and transformation rules to ensure data consistency and accurate transfer between systems. This process can be particularly challenging when dealing with large volumes of data and complex business logic.
- API Management and Security: Composable commerce relies heavily on APIs for communication between different systems. Managing these APIs, including version control, security protocols, and performance optimization, is crucial for ensuring reliable and secure data exchange.
- Integration Testing and Maintenance: As the number of integrations grows, comprehensive testing becomes essential to ensure that all systems work together seamlessly. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and updates for each integrated system can add complexity and require careful coordination to avoid conflicts and downtime.
Data Consistency and Synchronization
With multiple systems working together, ensuring data consistency across all platforms is critical. Inconsistent data can lead to inaccurate reporting, poor customer experiences, and operational inefficiencies.
- Real-time Data Synchronization: Maintaining real-time data synchronization across different systems is essential for providing accurate and up-to-date information to customers and internal teams. This can be challenging with multiple integrations, especially when dealing with large volumes of data and complex business logic.
- Data Governance and Compliance: Ensuring data quality, security, and compliance with relevant regulations is paramount in a composable commerce environment. With data spread across multiple systems, managing data governance and compliance can be complex and require a comprehensive approach.
- Data Redundancy and Conflicts: Data redundancy can occur when multiple systems store the same information. This can lead to data inconsistencies and conflicts, requiring careful management to ensure data integrity and accuracy.
Impact on Development Costs, Time-to-Market, and Performance, Keep it complexity in check with pragmatic composable commerce
The complexity of composable commerce can significantly impact development costs, time-to-market, and overall performance.
- Increased Development Costs: The need for multiple integrations, complex data management, and extensive testing can increase development costs. This includes the cost of specialized expertise, integration tools, and ongoing maintenance.
- Extended Time-to-Market: The complexity of integrating and configuring multiple systems can extend the time required to launch new features or functionalities. This can impact a business’s ability to respond quickly to market changes and customer demands.
- Potential Performance Bottlenecks: Multiple integrations and complex data flows can create performance bottlenecks, especially if not carefully managed. This can lead to slow loading times, system outages, and a negative impact on customer experience.
Pragmatic Approaches to Managing Complexity: Keep It Complexity In Check With Pragmatic Composable Commerce
Composable commerce, while offering immense flexibility and customization, comes with its own set of complexities. To unlock the full potential of this approach, a well-defined strategy for managing these complexities is crucial. This strategy should focus on prioritizing and addressing key areas of complexity, leading to more streamlined and efficient implementations.
Prioritizing and Addressing Key Areas of Complexity
A framework for prioritizing and addressing complexity in composable commerce helps organizations navigate the intricacies of this approach. This framework provides a structured approach to identify and manage potential challenges, ultimately leading to smoother implementations.
- Understanding the Scope of Complexity: The first step is to identify and understand the specific areas of complexity within your composable commerce implementation. This could involve analyzing the number of systems involved, the integration points, the data flow, and the overall complexity of the business logic.
- Prioritizing Complexity Areas: Once you have identified the areas of complexity, prioritize them based on their potential impact on the project. For example, areas with high impact and high likelihood of causing issues should be addressed first.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: For each prioritized area of complexity, develop specific mitigation strategies. This could involve using pre-built integrations, adopting standardized APIs, implementing robust data management processes, or leveraging specialized tools for managing complex workflows.
- Continual Monitoring and Adjustment: The complexity of a composable commerce implementation can evolve over time. It’s crucial to have a process in place for continually monitoring the complexity landscape and making adjustments to your strategy as needed. This could involve regular assessments of the system, identifying new areas of complexity, and updating mitigation strategies accordingly.
Practical Tips and Best Practices
Several practical tips and best practices can help simplify composable commerce implementations and manage complexity effectively.
- Embrace Microservices: Microservices architecture is a key principle of composable commerce. Break down your functionality into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This approach can significantly reduce complexity by creating a more modular and manageable system.
- Adopt Standardized APIs: Using standardized APIs for communication between different services can significantly simplify integration processes. This reduces the need for custom development and ensures compatibility across different systems.
- Leverage Integration Platforms: Integration platforms are designed to streamline the process of connecting different systems. They provide pre-built connectors, data transformation capabilities, and tools for managing complex workflows.
- Focus on Data Management: Data is a crucial element of composable commerce. Implement robust data management processes to ensure data consistency, integrity, and accessibility across different systems.
- Automate Where Possible: Automation can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in managing complex systems. Automate tasks such as data synchronization, workflow management, and system monitoring to streamline operations.
Key Strategies for Achieving Pragmatic Composability
Navigating the complexity of composable commerce requires a strategic approach. By focusing on practicality and prioritizing the core business needs, organizations can unlock the true potential of composable architecture.
Strategies for Pragmatic Composability
To manage complexity, consider these key strategies:
- Start Small and Iterate: Begin with a focused implementation by integrating a few key components. This allows for controlled experimentation, learning, and gradual expansion.
- Prioritize Business Value: Align composable initiatives with specific business goals and challenges. This ensures that each integration delivers tangible benefits.
- Embrace Standardization and Best Practices: Adopt industry standards and best practices for APIs, data formats, and security. This facilitates seamless integration and reduces development time.
- Leverage Existing Infrastructure: Utilize existing systems and data whenever possible. This minimizes the need for costly and time-consuming infrastructure changes.
- Invest in Strong Governance and Documentation: Establish clear processes for managing integrations, dependencies, and changes. This ensures a well-defined and controlled ecosystem.
- Build a Skilled Team: Invest in training and development for your team to acquire the necessary skills in composable architecture, API management, and cloud technologies.
Strategies Explained
This table provides a deeper understanding of these strategies:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Start Small and Iterate | Begin with a limited number of integrations and gradually expand the scope. | Reduced complexity, faster time to value, lower risk. | May require careful planning and prioritization to ensure a coherent overall strategy. |
| Prioritize Business Value | Align composable initiatives with specific business goals and challenges. | Increased ROI, demonstrable impact on business outcomes. | Requires clear understanding of business needs and objectives. |
| Embrace Standardization and Best Practices | Adopt industry standards for APIs, data formats, and security. | Improved interoperability, reduced development time, enhanced security. | May require initial investment in learning and implementation. |
| Leverage Existing Infrastructure | Utilize existing systems and data whenever possible. | Reduced costs, faster deployment, minimized disruption. | May require careful evaluation of compatibility and potential limitations. |
| Invest in Strong Governance and Documentation | Establish clear processes for managing integrations, dependencies, and changes. | Increased control, reduced risk, improved maintainability. | Requires ongoing effort and commitment to maintain consistency. |
| Build a Skilled Team | Invest in training and development to acquire the necessary skills. | Improved implementation, enhanced problem-solving, greater agility. | May require budget allocation and time investment for training. |
Example of Pragmatic Composability
“A leading fashion retailer started with a simple integration of a new payment gateway to improve customer experience. They then gradually expanded to include a personalized recommendation engine and a loyalty program, iteratively building upon their initial success.”
The Future of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce is still in its early stages, but it’s already transforming the e-commerce landscape. The future of composable commerce is bright, with emerging trends and technologies poised to revolutionize how businesses operate and customers shop.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The future of composable commerce will be heavily influenced by emerging technologies. These technologies will enable businesses to build more personalized, engaging, and efficient e-commerce experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will play a crucial role in personalizing customer experiences, optimizing operations, and automating tasks. For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer support, while ML algorithms can analyze customer data to recommend relevant products and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT will connect physical and digital worlds, enabling businesses to gather real-time data about customer behavior and preferences. This data can be used to create personalized shopping experiences, optimize inventory management, and improve customer service.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can enhance security and transparency in e-commerce transactions. It can also be used to create decentralized marketplaces and enable new business models, such as subscription services and loyalty programs.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR technologies can create immersive shopping experiences that allow customers to visualize products in their own homes or try on clothes virtually. This can lead to increased engagement and conversion rates.
Predictions for the Evolution of Composable Commerce
Composable commerce is expected to continue evolving rapidly in the coming years. Here are some predictions about how it will impact the e-commerce landscape:
- Increased Adoption: More businesses will adopt composable commerce to gain greater flexibility, scalability, and agility. The growing demand for personalized customer experiences and the need to adapt to rapidly changing market conditions will drive this adoption.
- Headless Commerce Growth: Headless commerce, a key component of composable commerce, will become increasingly popular. This approach separates the front-end presentation layer from the back-end commerce logic, allowing businesses to create custom storefronts and integrate with a wider range of third-party applications.
- Rise of the “Composable” Business: Businesses will become more “composable” themselves, breaking down traditional silos and adopting a modular approach to their operations. This will enable them to respond quickly to changing market demands and build more agile and efficient business models.
Impact on Customer Experiences, Business Models, and Competition
Composable commerce will have a profound impact on customer experiences, business models, and industry competition:
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: Composable commerce will enable businesses to create highly personalized and engaging customer experiences. By leveraging data, AI, and other technologies, businesses can tailor product recommendations, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions to individual customer needs and preferences.
- New Business Models: Composable commerce will enable businesses to experiment with new business models, such as subscription services, marketplaces, and personalized shopping experiences. This will lead to increased innovation and competition in the e-commerce space.
- Increased Competition: Composable commerce will make it easier for new entrants to compete with established players. This is because composable platforms provide a more cost-effective and flexible way to build and launch e-commerce businesses. This will lead to increased competition and drive innovation in the industry.
In the end, achieving pragmatic composability is about finding the right balance between flexibility and control. By adopting a strategic approach to managing complexity, businesses can leverage the power of composable commerce to create seamless customer experiences, accelerate innovation, and drive business growth.
Building a complex e-commerce system can feel like trying to navigate the ocean without a map, but composable commerce can be your compass. It allows you to build your platform piece by piece, ensuring each component is flexible and adaptable. This approach is similar to the way Saildrone, a company known for its autonomous vessels, is building its latest innovation – saildrones first aluminum surveyor autonomous vessel splashes down for navy testing.
This vessel, designed for naval testing, is built with modular components, allowing for easy upgrades and modifications. By taking a similar approach, composable commerce empowers businesses to navigate the ever-changing e-commerce landscape with agility and efficiency.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News