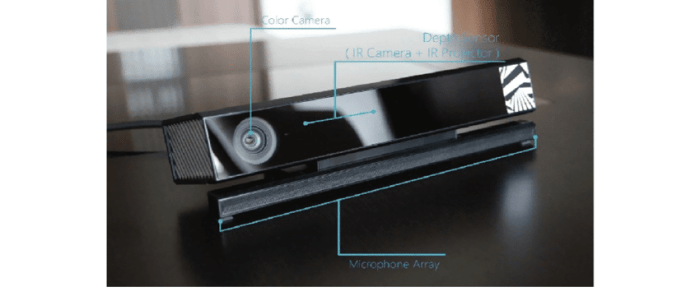
Kinect for Windows v2 Sensor Discontinuation: Kinect For Windows V2 Sensor No Longer Being Produced
The Kinect for Windows v2 sensor, a popular depth-sensing device that revolutionized human-computer interaction, has been discontinued. Microsoft officially announced the end of production for the sensor in 2017, marking the end of an era for this groundbreaking technology.
Reasons for Discontinuation
The decision to discontinue the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Shifting Market Dynamics: The market for depth-sensing technology evolved significantly since the Kinect’s initial release. The emergence of more affordable and versatile depth cameras, such as those based on the Intel RealSense technology, created increased competition for the Kinect.
- Declining Demand: As newer and more affordable alternatives became available, the demand for the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor declined. This decline in demand, coupled with the rising cost of manufacturing, made it commercially unsustainable for Microsoft to continue producing the sensor.
- Focus on Other Technologies: Microsoft shifted its focus to other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing. This strategic realignment led to a reduced emphasis on the Kinect, ultimately contributing to its discontinuation.
Timeline of the Kinect for Windows v2 Sensor
The Kinect for Windows v2 sensor had a significant impact on the field of human-computer interaction. Its lifecycle can be divided into several key stages:
- 2012: Microsoft released the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor, building upon the success of the original Xbox Kinect. The sensor offered advanced features like skeletal tracking, depth sensing, and color imaging, making it a popular choice for developers and researchers.
- 2014-2016: The Kinect for Windows v2 sensor gained widespread adoption across various industries, including healthcare, education, and gaming. Developers created numerous applications that leveraged the sensor’s capabilities, pushing the boundaries of human-computer interaction.
- 2017: Microsoft announced the discontinuation of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor. The company stated that it would continue to support the sensor, but would not be producing new units.
- 2017-Present: Despite the discontinuation, the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor remains a valuable tool for developers and researchers. However, the availability of the sensor is limited, and its future is uncertain.
Impact on Developers and Users
The discontinuation of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor presents a significant challenge for developers and users who have integrated it into their projects and workflows. While the sensor remains functional, its limited availability and lack of future support pose concerns for long-term sustainability.
Impact on Developers, Kinect for windows v2 sensor no longer being produced
Developers who rely on the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor for their projects face several challenges. The sensor’s discontinuation implies that:
- New development and integration: It becomes increasingly difficult to integrate the sensor into new projects, as obtaining the sensor may be challenging and there is no guarantee of future support or updates.
- Maintenance and support: Maintaining existing projects that rely on the sensor might become problematic, as finding replacements or workarounds for potential issues may be difficult.
- Long-term sustainability: Projects that rely on the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor may lack long-term sustainability, as the sensor’s discontinuation implies a limited lifespan for the technology.
Impact on Users
Users who utilize the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor for various applications, including gaming, accessibility, and research, face several challenges:
- Limited availability: Finding a new sensor may be challenging, as the discontinuation restricts its availability.
- Potential obsolescence: The sensor may become obsolete, leading to difficulties in finding replacements or maintaining existing applications.
- Lack of future updates: The sensor’s discontinuation implies a lack of future updates and support, potentially affecting its functionality and compatibility with newer systems.
Alternative Solutions
Several alternative solutions and technologies can replace the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor, providing developers and users with viable options for their projects and applications.
- Depth cameras: A variety of depth cameras from manufacturers like Intel RealSense, Orbbec, and Azure Kinect offer similar capabilities to the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor, providing depth sensing and skeletal tracking features.
- Computer vision libraries: OpenCV and other computer vision libraries provide tools for implementing various functionalities, including object detection, tracking, and gesture recognition, often relying on standard webcams.
- Machine learning models: Pre-trained machine learning models can be used for tasks like pose estimation, object recognition, and gesture recognition, eliminating the need for specialized hardware.
Legacy Support and Maintenance
Microsoft has made a commitment to providing ongoing support and maintenance for the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor, even though it’s no longer being produced. This commitment ensures that developers and users can continue to utilize the sensor and its capabilities for a considerable period.
However, maintaining compatibility and driver updates for a discontinued hardware product poses several challenges. The complexities of keeping the sensor functional in an ever-evolving technological landscape necessitate careful consideration of various factors.
Challenges of Maintaining Compatibility
Maintaining compatibility for a discontinued hardware product presents several challenges. These include:
- Operating System Updates: As Microsoft releases new versions of Windows, ensuring compatibility with the older Kinect for Windows v2 sensor requires extensive testing and potential driver updates. This is crucial to prevent compatibility issues that might arise from changes in the operating system’s core functionalities.
- Hardware and Software Ecosystem: The Kinect for Windows v2 sensor relies on a specific ecosystem of hardware and software components. Keeping these components synchronized and functional requires continuous maintenance and updates, particularly as new software libraries and hardware components are introduced.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Discontinued hardware often faces the challenge of security vulnerabilities. As new threats emerge, maintaining security patches and updates for the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor is crucial to protect users from potential risks.
Current Status of Software and Driver Updates
As of today, Microsoft continues to provide software and driver updates for the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor. These updates aim to address known issues, improve performance, and ensure compatibility with the latest versions of Windows. The updates are available through the official Microsoft website and are typically released periodically to address new issues or enhance functionality.
Future of Motion Sensing and Depth Perception
The discontinuation of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor marks a significant shift in the landscape of motion sensing and depth perception technologies. While Kinect has left its mark on various industries, the technology has evolved, paving the way for new and innovative solutions. This section explores the future of motion sensing and depth perception, examining alternative technologies and their potential applications.
Alternative Technologies for Motion Sensing and Depth Perception
The demise of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor has prompted the emergence of various alternative technologies for motion sensing and depth perception. These technologies offer distinct advantages and cater to specific application needs.
- Time-of-Flight (ToF) Sensors: ToF sensors measure the time it takes for a light pulse to travel to a target and return, providing depth information. These sensors are becoming increasingly popular due to their accuracy, reliability, and ability to operate in low-light conditions. ToF sensors find applications in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and gesture recognition systems.
- Structured Light Sensors: These sensors project a pattern of light onto a scene and analyze the distortions in the pattern to calculate depth. Structured light sensors offer high accuracy and are widely used in 3D scanning, facial recognition, and augmented reality (AR) applications.
- Stereo Vision Systems: Stereo vision systems use two cameras to capture images from slightly different perspectives. By comparing the images, these systems can determine depth information. Stereo vision systems are cost-effective and offer good performance, making them suitable for applications such as driver assistance systems and robot navigation.
- Computer Vision Algorithms: Advancements in computer vision algorithms have enabled the use of standard cameras for depth estimation. These algorithms analyze image features, such as texture and shadows, to infer depth information. Computer vision-based depth estimation is particularly useful for applications that require low-cost solutions, such as mobile phone cameras and virtual reality (VR) headsets.
Applications of Motion Sensing and Depth Perception
Motion sensing and depth perception technologies are poised to revolutionize various industries and applications, including:
- Healthcare: Motion sensing and depth perception are transforming healthcare by enabling advanced patient monitoring, rehabilitation, and surgical procedures. For example, depth cameras can track patient movements during physical therapy, providing real-time feedback and improving recovery outcomes. In surgery, depth cameras can assist surgeons with precise navigation and visualization, enhancing surgical accuracy and minimizing complications.
- Robotics: Motion sensing and depth perception are crucial for robots to interact with their environment safely and efficiently. Depth cameras allow robots to perceive their surroundings, avoid obstacles, and navigate complex environments. These technologies are essential for developing autonomous robots for tasks such as warehouse logistics, manufacturing, and home assistance.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Motion sensing and depth perception have revolutionized gaming and entertainment, providing immersive experiences and interactive gameplay. Depth cameras enable gesture recognition and body tracking, allowing users to control games and interact with virtual environments more naturally. This technology is also being used in VR and AR applications, creating highly realistic and engaging experiences.
- Security and Surveillance: Motion sensing and depth perception are used in security and surveillance systems to detect movement, identify objects, and monitor activities. Depth cameras can provide more accurate and reliable detection than traditional cameras, improving security measures and reducing false alarms.
- Automotive: Motion sensing and depth perception are essential for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Depth cameras enable features such as lane departure warning, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking, enhancing road safety and improving driving efficiency.
Impact on Gaming and Entertainment
The discontinuation of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor has significant implications for the gaming and entertainment industry, particularly in the realm of motion-controlled gaming and interactive experiences. This sensor played a crucial role in bringing immersive and engaging gameplay to life, and its absence will be felt by developers and gamers alike.
Impact on Gaming
The Kinect for Windows v2 sensor was instrumental in popularizing motion-controlled gaming. It allowed players to interact with games in a more intuitive and natural way, using their bodies as controllers. This technology led to the development of a wide range of games that leveraged body tracking, gesture recognition, and voice commands. Examples include:
- Dance Central: This popular dance game series utilized the Kinect sensor to track players’ movements and score their dance routines.
- Kinect Sports: This franchise featured various sports games that allowed players to control their virtual athletes using their bodies.
- Xbox Fitness: This fitness app used the Kinect sensor to track players’ movements and provide personalized workout routines.
The discontinuation of the Kinect sensor will likely lead to a decline in the development of new motion-controlled games. Developers may choose to focus on other input methods, such as traditional controllers or virtual reality headsets, which offer more established and mature technologies. However, the legacy of the Kinect sensor will continue to influence game design, as developers seek to incorporate natural and intuitive interactions into their games.
Alternative Motion Sensing Technologies
While the Kinect sensor is no longer in production, other motion sensing technologies are emerging to fill the void. These technologies offer similar capabilities for gaming and entertainment, but with varying levels of accuracy, cost, and accessibility. Some notable alternatives include:
- VR Headsets: Virtual reality headsets, such as the Oculus Quest 2 and the HTC Vive Pro 2, incorporate motion tracking sensors that allow players to move and interact with virtual environments using their bodies.
- Depth Cameras: Depth cameras, such as the Intel RealSense D435i, can capture depth information about a scene, enabling developers to create games that respond to players’ movements and gestures.
- Smartphone Cameras: Smartphones equipped with advanced cameras and motion tracking capabilities can be used for gaming and entertainment purposes.
The adoption of these alternative technologies will shape the future of motion sensing in gaming and entertainment. Developers will need to adapt their game designs to leverage the strengths and limitations of these new platforms.
Kinect for windows v2 sensor no longer being produced – While the discontinuation of the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor may seem like a setback, it also represents an opportunity for innovation. The emergence of new technologies and advancements in artificial intelligence and computer vision are paving the way for more advanced and sophisticated motion sensing and depth perception solutions. As we move forward, we can expect to see exciting new developments in this space, ushering in a new era of interactive experiences that will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Remember the Kinect for Windows v2 sensor? The one that let you control your PC with your body? Well, it’s officially been discontinued, leaving many gamers and developers scrambling for alternatives. It’s kind of like how Google’s wireless service will reportedly only work with the Nexus 6, googles wireless service will reportedly only work with the nexus 6 , leaving those with other devices in the lurch.
So, if you’re still clinging to your Kinect v2, it’s time to start thinking about the future – and maybe invest in a new gaming setup.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News