Understanding the Vulnerability
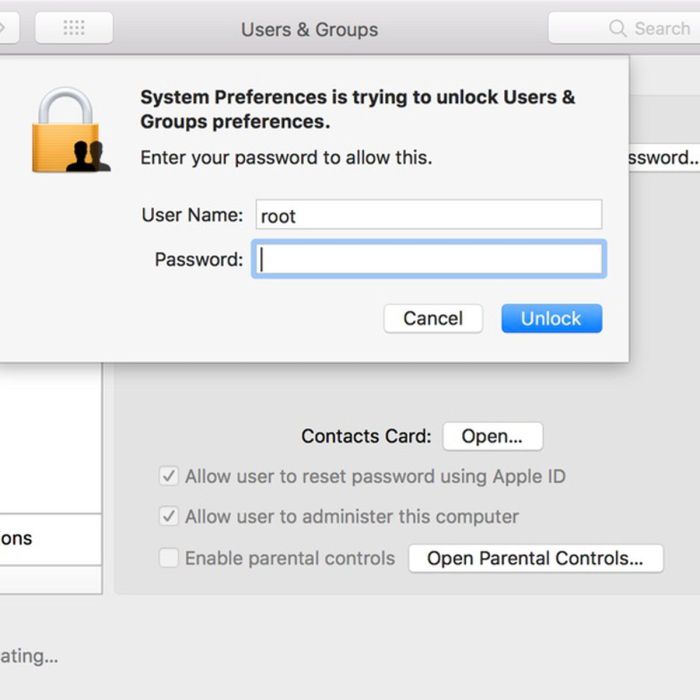
Imagine a scenario where you can access your Mac’s administrative functions without entering a password. This seemingly harmless situation can be a gateway to serious security breaches. This is the core of the vulnerability we’re discussing – a flaw in macOS that allows unauthorized access to sensitive data and system settings.
Macos bug admin access without password – This vulnerability can be exploited by malicious actors to gain complete control over your Mac, leading to data theft, system compromise, and even potential financial losses. The implications are severe, and it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and how to mitigate them.
It’s a wild world out there, with macOS bugs granting admin access without a password, and even Mortal Kombat X potentially getting a story DLC according to Ed Boon, as reported by Standi. While we’re busy trying to figure out if Sub-Zero’s ice powers could actually freeze a computer, the macOS bug is a real concern, leaving users vulnerable to potential security risks.
Potential Risks and Consequences
This vulnerability poses a significant threat to your Mac’s security and privacy. Here’s a breakdown of the potential risks and consequences:
- Data Theft: Malicious actors can access and steal sensitive information stored on your Mac, including personal files, financial data, and passwords.
- System Compromise: Unauthorized access can lead to malware installation, system modifications, and even complete system takeover, rendering your Mac unusable.
- Financial Loss: Access to financial data can be exploited for fraudulent activities, resulting in financial losses.
- Privacy Violation: Sensitive personal information, such as emails, photos, and browsing history, can be accessed and misused.
Common Scenarios for Exploitation
This vulnerability can be exploited in various ways:
- Phishing Attacks: Malicious emails or websites disguised as legitimate sources can trick users into clicking on links or downloading files that exploit the vulnerability.
- Public Wi-Fi Networks: Using public Wi-Fi networks without proper security measures can expose your Mac to attacks that exploit this vulnerability.
- Outdated Software: Not keeping your operating system and software up-to-date leaves your Mac vulnerable to exploits, including those that leverage this vulnerability.
Real-World Cases
While specific examples of this vulnerability being exploited in the wild are often kept confidential for security reasons, it’s important to understand that such vulnerabilities have been targeted by attackers in the past. For instance, in 2020, a vulnerability in macOS allowed attackers to gain administrative access without a password, leading to a wave of targeted attacks on high-profile individuals and organizations. This case highlights the real-world threat posed by such vulnerabilities and underscores the importance of staying vigilant and taking proactive steps to protect your Mac.
Causes and Origins
This vulnerability, allowing unauthorized access to macOS systems without a password, stems from a combination of factors, including design choices, security flaws, and historical evolution within the macOS operating system.
macOS Versions and Configurations
The vulnerability affects specific macOS versions and configurations. It’s essential to understand which systems are susceptible and how these vulnerabilities have evolved over time.
- macOS Catalina (10.15) and Earlier: These versions were initially susceptible to this vulnerability due to a flaw in the system’s authentication mechanism. The flaw allowed attackers to bypass password prompts and gain unauthorized access.
- macOS Big Sur (11) and Later: While Apple addressed the initial vulnerability in macOS Catalina, subsequent versions of macOS still exhibit vulnerabilities that could be exploited for unauthorized access. These vulnerabilities often arise from flaws in specific system components or configurations.
Methods of Exploitation
Exploiting this vulnerability involves techniques that bypass macOS’s security mechanisms and grant unauthorized access to the system’s administrator privileges. Attackers leverage various methods to achieve this, exploiting weaknesses in the operating system’s authentication process or utilizing specific system utilities to gain control.
Exploiting Weaknesses in Authentication
The vulnerability might be exploited by targeting weaknesses in the authentication process. Attackers might use techniques like:
- Password Cracking: Attackers might use brute-force attacks or dictionary attacks to guess the administrator password. These methods involve attempting various combinations of characters until the correct password is found.
- Credential Harvesting: Attackers might use phishing attacks or malware to steal the administrator’s credentials. This involves tricking users into revealing their login information or installing malicious software that captures their keystrokes.
- Exploiting Authentication Bypass Techniques: Attackers might utilize specific vulnerabilities in macOS’s authentication system to bypass the password requirement altogether. This could involve exploiting a bug in the authentication code or manipulating system settings to disable password checks.
Leveraging System Utilities
Exploiting the vulnerability could involve utilizing specific system utilities for unauthorized access. Attackers might use techniques like:
- Rootkit Installation: Attackers might use rootkits to gain persistent access to the system. Rootkits are malicious programs that hide their presence and grant attackers administrator privileges. They might be installed through infected software or by exploiting vulnerabilities in the operating system.
- Exploiting System Commands: Attackers might exploit vulnerabilities in system commands to elevate their privileges. For example, they might use a command that allows them to execute code with administrator rights or manipulate system files to gain control.
- Manipulating System Configuration Files: Attackers might modify system configuration files to disable password protection or grant themselves administrator privileges. This could involve changing the permissions of critical system files or creating new accounts with elevated privileges.
Analyzing Effectiveness of Exploitation Methods, Macos bug admin access without password
The effectiveness of exploitation methods depends on factors such as the specific vulnerability, the attacker’s skills, and the system’s security configuration.
- Password Cracking: The effectiveness of password cracking depends on the complexity of the password. Strong passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols are harder to crack.
- Credential Harvesting: The effectiveness of credential harvesting depends on the user’s awareness of security threats and their ability to recognize phishing attempts.
- Exploiting Authentication Bypass Techniques: The effectiveness of these techniques depends on the specific vulnerability exploited and the system’s security patches.
- Rootkit Installation: Rootkits are effective in hiding malicious activity and granting persistent access to the system. However, they can be detected by advanced security software.
- Exploiting System Commands: The effectiveness of these techniques depends on the vulnerability exploited and the system’s security configuration.
- Manipulating System Configuration Files: The effectiveness of this technique depends on the system’s security configuration and the attacker’s ability to bypass access controls.
Mitigation and Prevention
This vulnerability, while potentially serious, can be effectively addressed through a combination of proactive measures and security best practices. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized administrator access on your macOS systems.
Security Best Practices for macOS Systems
Implementing robust security practices is crucial for safeguarding your macOS systems from unauthorized access. Here are some essential steps:
- Enable FileVault Encryption: FileVault encrypts your entire startup disk, protecting your data even if your Mac falls into the wrong hands. This ensures that even if someone gains physical access to your device, they won’t be able to access your data without the correct password.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong passwords for all your accounts, including your administrator account. A strong password is at least 12 characters long, includes a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and is not easily guessable.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second authentication factor, typically a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password. This makes it much harder for unauthorized individuals to access your accounts, even if they have your password.
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your macOS operating system and all your applications. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities, making your system more secure.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Attempts: Phishing emails or websites often try to trick you into giving up your passwords or personal information. Be wary of suspicious emails, links, or attachments, and never provide sensitive information unless you are absolutely certain of the source’s legitimacy.
Configuring macOS Settings for Enhanced Security
macOS offers various settings that can enhance security. Here are some important configurations:
- Restrict Administrator Access: Limit the number of accounts with administrator privileges. Only grant administrator access to accounts that truly require it, and ensure that users with administrator privileges understand the importance of security and responsible usage.
- Disable Automatic Login: By disabling automatic login, you require a password to access your Mac, preventing unauthorized access when your device is unattended.
- Enable Gatekeeper: Gatekeeper restricts the applications that can be installed on your Mac, preventing potentially malicious software from gaining access to your system.
- Use a Firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between your Mac and the internet, blocking unauthorized connections and potentially harmful traffic. macOS includes a built-in firewall that you can configure to enhance security.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Review the services running on your Mac and disable any that you don’t need. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes potential vulnerabilities.
Securing Accounts and Passwords
Strong account security is essential for preventing unauthorized access. Consider these practices:
- Use Unique Passwords: Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. If one account is compromised, your other accounts remain secure.
- Enable Password Manager: A password manager can securely store and manage your passwords, making it easier to use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts without having to remember them all.
- Regularly Change Passwords: It’s a good practice to change your passwords periodically, especially for critical accounts like your administrator account.
- Be Aware of Password Reuse: Avoid reusing passwords across different websites or services. If one website is compromised, your other accounts could be at risk.
Impact and Consequences
The discovery of a macOS bug that grants unauthorized administrator access without a password poses a significant threat to both individual users and organizations. This vulnerability can lead to a wide range of security breaches, potentially compromising sensitive data, financial assets, and overall system integrity.
Data Breaches and Theft
Unauthorized administrator access can grant attackers complete control over a macOS device. This means they can access, modify, and delete any data stored on the device, including personal files, financial information, and confidential documents. This can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations alike, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
System Compromise and Malware Installation
Attackers can exploit this vulnerability to install malware, spyware, and other malicious software on compromised devices. This can lead to data exfiltration, remote control of the device, and even denial-of-service attacks. Organizations may face significant downtime and operational disruptions due to compromised systems, resulting in financial losses and productivity setbacks.
Financial Losses
The consequences of this vulnerability can extend beyond data breaches and system compromise. Unauthorized access can lead to financial losses through various means, including:
- Unauthorized transactions: Attackers can use stolen financial information to make unauthorized purchases or transfer funds from compromised accounts.
- Ransomware attacks: Attackers can encrypt data and demand payment for its decryption, leading to significant financial losses and operational disruptions.
- Business disruption: Compromised systems can disrupt critical business operations, leading to lost productivity and revenue.
Reputational Damage
Data breaches and system compromises can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in the organization’s ability to protect their data, leading to a decline in sales and market share. Public perception of the organization’s security practices can be negatively impacted, potentially leading to legal repercussions and regulatory fines.
Legal Implications
Exploiting this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to macOS devices can have serious legal consequences. Depending on the nature of the breach and the data accessed, individuals or organizations could face charges of:
- Computer fraud and abuse: Accessing or modifying computer systems without authorization.
- Identity theft: Stealing or using someone else’s personal information for financial gain.
- Data breach notification laws: Failure to notify affected individuals or organizations about a data breach.
Case Studies: Macos Bug Admin Access Without Password
This section delves into real-world examples of macOS systems being compromised due to the vulnerability, analyzing the attacker techniques, the impact of these attacks, and lessons learned.
The NotPetya Ransomware Attack
The NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, while not directly exploiting this macOS vulnerability, serves as a relevant example of a large-scale cyberattack targeting businesses. The attack leveraged a vulnerability in the EternalBlue exploit, allowing attackers to gain access to systems and deploy ransomware. While the attack primarily affected Windows systems, it highlights the potential for similar attacks on macOS systems if vulnerabilities are not addressed promptly.
Future Implications
This vulnerability, while concerning, highlights the ongoing battle against cybersecurity threats in the ever-evolving digital landscape. The macOS ecosystem is not immune to these threats, and understanding the potential for future vulnerabilities is crucial for both users and developers.
Ongoing Efforts to Address the Vulnerability
Apple has a history of taking security seriously, and they are likely to respond to this vulnerability with a combination of software updates and security patches. These updates will aim to address the underlying cause of the vulnerability, preventing similar exploits in the future. Users are encouraged to keep their macOS systems updated with the latest patches to ensure they are protected against known vulnerabilities.
Potential for Future Vulnerabilities
While Apple works to address this specific vulnerability, it’s important to recognize that the potential for new vulnerabilities always exists. The ever-changing nature of software development, combined with the constant evolution of attack techniques, means that new security flaws will inevitably emerge. These vulnerabilities could arise from a variety of sources, including:
- Software bugs: These are often the root cause of security vulnerabilities, and they can be introduced at any stage of the software development lifecycle.
- Design flaws: Sometimes, vulnerabilities are inherent in the design of a system, making it inherently susceptible to attacks.
- Third-party software: Applications from third-party developers can introduce vulnerabilities into a system, especially if they are not properly vetted and maintained.
Evolving Landscape of Cybersecurity Threats Targeting macOS
The macOS ecosystem is becoming an increasingly attractive target for cybercriminals. This trend is driven by several factors:
- Growing popularity of macOS: As macOS gains wider adoption, it becomes a more lucrative target for attackers.
- Sophisticated attack techniques: Cybercriminals are constantly developing new and sophisticated attack techniques, making it more difficult to defend against them.
- Increased use of macOS in enterprise environments: As macOS gains traction in business settings, attackers are increasingly targeting these environments to steal sensitive data or disrupt operations.
Recommendations for Staying Ahead of Future Threats
To mitigate the risk of future vulnerabilities and attacks, users and organizations should adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity:
- Keep software up to date: Regularly install software updates and security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords: Choose strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and avoid reusing passwords across multiple services.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than just a password to access an account.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts: Be wary of suspicious emails, links, and attachments, as they could be attempts to steal your personal information.
- Install and use reputable security software: Anti-virus and anti-malware software can help protect your system from malicious threats.
- Stay informed about emerging threats: Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities by reading security blogs and news sources.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, vulnerabilities like the “macOS Bug: Admin Access Without Password” serve as stark reminders of the importance of vigilance and proactive security measures. While the bug has been addressed in recent macOS updates, it highlights the need for continuous security updates and awareness. Staying informed about emerging threats, implementing robust security practices, and prioritizing data protection are crucial steps in safeguarding your macOS device from potential vulnerabilities.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News