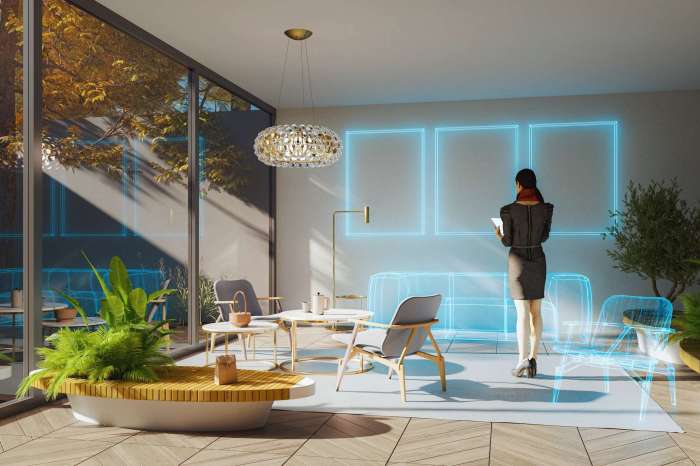
Metas augments place digital objects around your physical space – Imagine walking down the street and seeing a virtual storefront pop up on your phone, showcasing the latest fashion trends. Or, envision stepping into a museum and being guided by a holographic tour guide, providing fascinating insights about the exhibits. This is the world of metas, a technology that seamlessly blends the physical and digital realms by placing digital objects within our physical space. Metas, like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), have the potential to revolutionize how we interact with the world around us.
Metas can be used in various industries, from retail to healthcare. Imagine using metas to create immersive shopping experiences, where customers can virtually try on clothes or see how furniture would look in their homes. In education, metas could bring history lessons to life, allowing students to explore ancient ruins or interact with historical figures. The possibilities are endless, and the impact on user experience is profound.
The Concept of “Metas”
Imagine a world where your physical space is seamlessly integrated with digital objects, creating a dynamic and interactive environment. This is the world of “metas,” a technology that bridges the gap between the physical and digital realms by augmenting our physical spaces with digital objects.
Metas offer a unique approach to interacting with digital information and experiences, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. They provide a platform for digital objects to exist and interact with our physical environment, enhancing our perception and interaction with the world around us.
Metas Compared to Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Metas are distinct from augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), though they share some commonalities. While AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, metas go beyond simple overlays, allowing digital objects to exist and interact within the physical space. VR, on the other hand, immerses users in entirely virtual environments, creating a separate digital reality.
Metas differ from AR and VR in the following ways:
- Persistence: Metas create persistent digital objects within the physical space, unlike AR overlays that disappear when the device is turned off. These objects can be accessed and interacted with by multiple users over time.
- Interactivity: Metas allow for a more interactive and dynamic experience than AR, enabling digital objects to respond to user actions and physical environment changes.
- Physical Integration: Metas seamlessly integrate digital objects with the physical world, blurring the lines between the two, unlike VR that creates a separate digital environment.
Applications of Metas
Imagine a world where digital objects seamlessly blend with your physical surroundings, enhancing your everyday experiences. Metas, the digital augmentations that place virtual objects in your real-world environment, are poised to revolutionize how we interact with our physical spaces. These applications can be found across various industries, from retail to education and healthcare, transforming user experiences and creating a more interactive and immersive reality.
Applications in Retail
Metas can transform the retail landscape by providing customers with an interactive and engaging shopping experience. For example, imagine walking into a furniture store and seeing a virtual couch placed in your living room using your smartphone. You can interact with the virtual couch, change its color, fabric, and even try out different configurations, all without physically moving the furniture. This immersive experience can help customers visualize how the furniture would look in their homes, making the purchasing decision easier and more informed.
- Virtual Product Demonstrations: Metas can be used to create virtual product demonstrations, allowing customers to interact with products in a realistic and engaging way. For instance, a car dealership could use metas to create a virtual test drive experience, allowing customers to explore the car’s interior and exterior, experience its features, and even take it for a virtual spin.
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: Metas can personalize the shopping experience by providing customers with tailored recommendations and information based on their preferences. For example, a clothing store could use metas to create a virtual fitting room, allowing customers to try on different outfits and see how they look without actually having to try them on.
- Interactive Store Displays: Metas can be used to create interactive store displays that provide customers with information about products and services. For instance, a grocery store could use metas to create a virtual aisle that displays recipes and nutritional information about the products on the shelf.
Applications in Education
Metas can revolutionize education by creating immersive and engaging learning environments. Imagine students learning about the human body by interacting with a virtual 3D model, dissecting it virtually, and exploring its different organs and systems. This interactive learning experience can make education more engaging and accessible, helping students understand complex concepts in a more intuitive way.
- Interactive Learning Experiences: Metas can be used to create interactive learning experiences that bring textbooks and classroom lessons to life. For instance, a history class could use metas to recreate historical events, allowing students to experience them firsthand.
- Virtual Field Trips: Metas can be used to take students on virtual field trips to places they might not otherwise be able to visit, such as museums, historical sites, or even other planets. This can help students learn about different cultures, environments, and historical periods in a more immersive and engaging way.
- Personalized Learning: Metas can be used to personalize the learning experience by providing students with tailored content and feedback based on their individual needs and learning styles. This can help students learn at their own pace and focus on the areas where they need the most support.
Applications in Healthcare
Metas can transform healthcare by providing patients with more personalized and effective care. Imagine a doctor using metas to view a patient’s medical records and 3D scans, allowing them to diagnose and treat conditions more accurately. This can help patients receive better care, faster diagnoses, and more effective treatments.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Metas can be used to monitor patients remotely, allowing healthcare professionals to track their vital signs, activity levels, and other important data. This can help identify potential health problems early and provide patients with the care they need, even if they are not physically present at a healthcare facility.
- Virtual Rehabilitation: Metas can be used to create virtual rehabilitation programs that help patients recover from injuries or illnesses. This can involve using metas to guide patients through physical exercises, provide feedback on their progress, and motivate them to stay on track.
- Medical Training: Metas can be used to train medical professionals in a safe and realistic environment. This can involve using metas to simulate surgical procedures, allowing trainees to practice their skills without putting patients at risk.
Hypothetical Application of Metas in Hospitality
Imagine a hotel that uses metas to enhance the guest experience. Guests could use their smartphones to access virtual concierge services, view interactive maps of the hotel, and even order room service with a few taps on their screen. The hotel could also use metas to create virtual tours of the city, providing guests with information about local attractions and activities.
- Virtual Concierge Services: Guests could use metas to access a virtual concierge, providing them with information about the hotel, local attractions, and services. The virtual concierge could also help guests book reservations, make arrangements for transportation, and answer any questions they might have.
- Interactive Maps and Navigation: Guests could use metas to navigate the hotel and its surroundings, with interactive maps showing them the location of amenities, restaurants, and other points of interest. This could be especially helpful for guests who are unfamiliar with the area.
- Personalized Guest Experiences: The hotel could use metas to personalize the guest experience, providing them with tailored recommendations and information based on their preferences. For instance, the hotel could use metas to recommend restaurants, activities, and attractions that are aligned with the guest’s interests.
- Virtual Tours: The hotel could use metas to create virtual tours of the city, providing guests with information about local attractions and activities. This could help guests plan their trip and discover new things to see and do.
Technological Components of Metas
Metas, the fusion of the physical and digital worlds, rely on a sophisticated blend of technologies to bridge the gap between these realms. The magic behind metas lies in the seamless integration of sensors, cameras, and specialized software, working in tandem to capture and display digital objects in physical spaces.
Sensors: The Eyes of Metas
Sensors are the vital eyes of metas, gathering data from the physical environment and translating it into actionable information for the digital world. These sensors act as intermediaries, perceiving the physical space and feeding the information back to the system for processing and display.
- Motion Sensors: These sensors detect movement within a space, allowing metas to respond dynamically to user interactions and create interactive experiences. For example, a motion sensor could trigger the display of a virtual object as a person approaches it, enhancing engagement and immersion.
- Proximity Sensors: These sensors measure the distance between objects, enabling metas to create context-aware experiences. Imagine walking past a virtual billboard in a metas environment; a proximity sensor could activate a closer view of the content as you approach, creating a more immersive and personalized experience.
- Environmental Sensors: These sensors collect data about the physical environment, such as temperature, humidity, and light levels. This information can be used to create more realistic and dynamic metas experiences, adjusting the display of digital objects based on the surrounding environment.
Cameras: The Lens of Reality
Cameras play a crucial role in metas, capturing the physical environment and providing the foundation for overlaying digital objects. These cameras act as the lens through which the digital world is projected onto the physical space, creating a seamless blend of reality and virtuality.
- Depth Cameras: These cameras capture depth information, enabling metas to accurately place digital objects in the physical space. By understanding the distance between objects, metas can create realistic and immersive experiences, ensuring that virtual objects appear correctly in relation to real-world objects.
- High-Resolution Cameras: These cameras capture high-quality images, providing detailed information about the physical environment. This allows metas to render digital objects with greater accuracy and realism, enhancing the overall experience and minimizing the perception of a jarring transition between the physical and digital worlds.
- 360-Degree Cameras: These cameras capture the entire surrounding environment, enabling metas to create immersive experiences that extend beyond a single viewpoint. Imagine exploring a virtual museum exhibit; a 360-degree camera would allow you to move freely and view the exhibit from any angle, providing a truly immersive experience.
Software: The Brain of Metas
Software acts as the brain of metas, orchestrating the interaction between the physical and digital worlds. It processes data from sensors and cameras, interprets user input, and renders digital objects onto the physical space.
- Computer Vision Algorithms: These algorithms analyze images captured by cameras, identifying objects and features within the physical space. This information allows metas to accurately place digital objects within the environment, ensuring that they appear realistically in relation to real-world objects.
- Real-Time Rendering Engines: These engines generate and display digital objects in real-time, responding dynamically to user input and environmental changes. This ensures that metas experiences are smooth and responsive, minimizing lag and creating a seamless transition between the physical and digital worlds.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Software: This software overlays digital objects onto the physical world, creating a blended experience that seamlessly integrates both realms. AR software is the core technology behind metas, enabling the fusion of the physical and digital worlds.
Challenges and Opportunities
The integration of these technologies presents both challenges and opportunities for the future of metas.
- Computational Power: Processing data from sensors and cameras, rendering digital objects in real-time, and maintaining a seamless user experience requires significant computational power. This poses a challenge for widespread adoption, as current devices may lack the processing capabilities to support complex metas applications.
- Data Privacy and Security: Metas applications collect and process large amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security. It is crucial to develop robust data protection measures to ensure user privacy and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- User Experience: Designing intuitive and engaging user experiences is crucial for the success of metas. This requires careful consideration of user interactions, interface design, and the overall flow of information between the physical and digital worlds.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Metas applications should be accessible to all users, regardless of their physical abilities or disabilities. This requires careful design and development to ensure that all users can participate in and benefit from the metaverse experience.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Metas need to seamlessly integrate with existing physical infrastructure and digital systems. This requires interoperability standards and protocols to ensure that different metas applications can communicate and exchange data effectively.
User Interaction with Metas
Metas bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds, allowing users to interact with digital objects in their physical spaces. This interaction is not limited to viewing; users can manipulate, control, and even engage with these objects in ways that blur the lines between reality and virtuality.
Methods of User Interaction with Metas
The way users interact with metas is diverse and evolving, encompassing various methods that leverage different senses and technologies.
- Gestures: Users can interact with metas using natural hand gestures, such as pointing, swiping, and grabbing. This intuitive approach makes metas accessible and engaging, especially for tasks like controlling virtual objects, navigating menus, or selecting items. For instance, a user might point at a virtual map displayed on their kitchen table to zoom in on a specific location or use a swiping gesture to scroll through a list of virtual documents.
- Voice Commands: Voice interaction with metas enables hands-free control and allows for natural communication with digital objects. Users can speak commands, ask questions, or give instructions to metas, streamlining tasks and enhancing accessibility. Imagine controlling the lighting in your living room by simply saying “Dim the lights,” or asking your virtual assistant for weather updates without having to touch a device.
- Touch Interfaces: Touch-based interaction with metas allows users to physically engage with digital objects by touching or manipulating them directly. This can be achieved through various technologies, such as touchscreens, haptic feedback devices, or even augmented reality (AR) interfaces. Users can, for example, touch a virtual product on their table to examine its details or use a haptic feedback device to feel the texture of a virtual fabric.
| Method | Description | Example | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestures | Using hand movements to control metas | Pointing at a virtual map to zoom in | Intuitive, natural, hands-free | Limited accuracy, potential for misinterpretation |
| Voice Commands | Speaking to interact with metas | Asking a virtual assistant for weather updates | Hands-free, convenient, natural communication | Privacy concerns, potential for misinterpretation |
| Touch Interfaces | Physically touching metas to interact with them | Touching a virtual product to examine details | Immersive, tactile feedback, precise control | Limited range of motion, potential for discomfort |
Ethical Considerations of Metas
Metas, with their ability to seamlessly blend the digital and physical realms, present a unique set of ethical challenges. While the potential benefits are undeniable, it’s crucial to address the potential downsides to ensure responsible development and implementation. This section delves into the ethical considerations surrounding metas, exploring concerns related to privacy, data security, and accessibility.
Privacy Concerns
The integration of digital objects into physical spaces raises significant privacy concerns. Metas have the potential to collect vast amounts of personal data, including location, movement patterns, and even biometric information. This data collection can be intrusive and raise concerns about how it is used, stored, and protected.
- Data Collection and Usage: Metas can collect data about users’ physical movements, interactions with digital objects, and even their physiological responses. This data can be used for various purposes, including targeted advertising, personalized experiences, and even surveillance. It’s crucial to establish clear guidelines for data collection and usage, ensuring transparency and user consent.
- Data Security and Privacy: The security of personal data collected by metas is paramount. Data breaches or unauthorized access can have severe consequences for users’ privacy. Robust security measures, including encryption and access controls, are essential to protect sensitive information.
- Anonymity and Pseudonymity: Metas can potentially erode anonymity and pseudonymity in physical spaces. Users may be tracked and identified based on their interactions with digital objects, raising concerns about privacy and freedom of movement.
Data Security and Trust
The security of data collected and processed by metas is crucial for maintaining user trust. Data breaches or unauthorized access can have serious consequences, including identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
- Data Encryption and Access Control: Metas should employ strong encryption methods to protect user data during transmission and storage. Access controls should be implemented to restrict access to sensitive information only to authorized personnel.
- Data Retention and Deletion: Clear policies regarding data retention and deletion are essential. Users should have the right to access, modify, or delete their data.
- Data Sharing and Transparency: Data sharing practices should be transparent and subject to user consent. Users should be informed about how their data is being used and shared with third parties.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Metas have the potential to enhance accessibility and inclusivity by providing new ways for people with disabilities to interact with the physical world. However, it’s crucial to ensure that metas are designed and implemented in a way that is accessible to all.
- Universal Design: Metas should be designed according to universal design principles, ensuring that they are usable and accessible to people with a wide range of abilities.
- Assistive Technologies: Integration with assistive technologies, such as screen readers and voice control systems, is essential for users with visual or mobility impairments.
- Inclusive Design: Metas should be designed to cater to diverse user needs and preferences, including those with cognitive disabilities or language barriers.
Future of Metas: Metas Augments Place Digital Objects Around Your Physical Space
The future of metas technology holds immense potential for transforming how we interact with the physical world and digital information. Metas have the potential to become ubiquitous, seamlessly blending the digital and physical realms and creating entirely new experiences.
Evolution of Metas
The future of metas will see them evolve into more sophisticated and integrated systems. This evolution will be driven by advancements in several key areas, including:
- Increased computational power and processing speeds: As computing power continues to increase, metas will be able to process and analyze data more efficiently, enabling them to provide more complex and responsive interactions.
- Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML will play a crucial role in enhancing the intelligence and adaptability of metas. Metas will learn from user interactions and adapt to individual preferences, making them more personalized and intuitive.
- Improved sensor technologies: Advances in sensor technologies will allow metas to gather more accurate and detailed information about the physical environment, enabling them to provide more contextualized and relevant information and experiences.
- Integration with other technologies: Metas will increasingly integrate with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR), creating a more immersive and connected experience.
Timeline of Key Milestones
The development of metas technology is expected to progress through several key milestones:
- Near-term (2023-2027): Focus on refining existing metas technologies, improving user experience, and expanding applications in specific industries such as healthcare, education, and retail.
- Mid-term (2028-2032): Emergence of more sophisticated and integrated metas systems, with a greater emphasis on personalization, interoperability, and seamless integration with other technologies.
- Long-term (2033 onwards): Widespread adoption of metas in various aspects of daily life, creating a truly blended reality where digital objects and information are seamlessly integrated with the physical world.
Potential Applications of Metas
The future applications of metas are vast and diverse. Metas will have a significant impact on various industries, including:
- Healthcare: Metas can be used to provide personalized healthcare experiences, including virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and augmented reality surgery.
- Education: Metas can enhance learning by creating immersive educational environments, providing interactive simulations, and offering personalized learning paths.
- Retail: Metas can revolutionize the shopping experience by providing virtual try-on capabilities, personalized recommendations, and interactive product demonstrations.
- Manufacturing: Metas can be used for remote collaboration, training, and maintenance, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Entertainment: Metas can create immersive gaming experiences, interactive entertainment, and personalized content recommendations.
Ethical Considerations, Metas augments place digital objects around your physical space
As metas technology evolves, it’s crucial to address ethical considerations to ensure responsible development and deployment. These considerations include:
- Privacy: Metas collect vast amounts of data about users and their surroundings. It’s essential to ensure that this data is collected and used ethically and responsibly.
- Security: Metas systems need to be secure to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access or manipulation.
- Accessibility: Metas should be accessible to all users, regardless of their physical abilities or technological literacy.
- Bias: Metas systems need to be designed and trained to avoid biases that could discriminate against certain groups of users.
As metas technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds. Metas have the potential to reshape how we interact with our environment, offering a richer and more engaging experience. The future of metas is bright, and it’s exciting to imagine how this technology will continue to shape our lives.
Meta’s vision of placing digital objects around your physical space is getting closer to reality, but it’s a reminder of the need for sustainable tech. Thankfully, companies like Fairphone are leading the way with their commitment to repairable devices. Their latest offering, fairphone launches easy to repair earbuds , is a step in the right direction, ensuring we can enjoy the future of tech without sacrificing the planet.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News