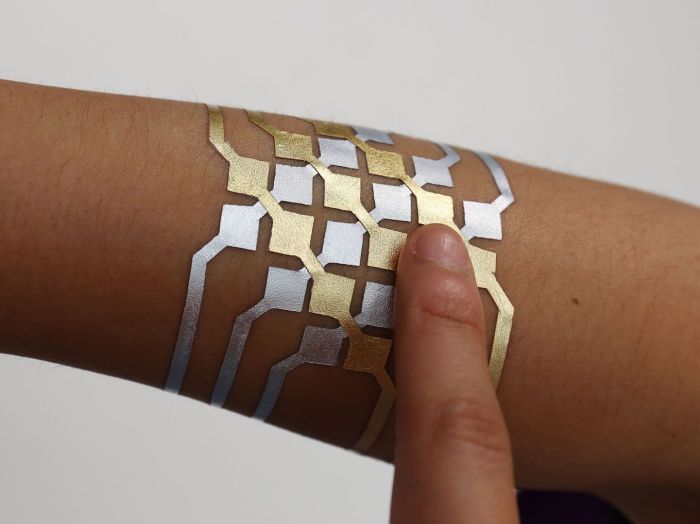
The Rise of Smart Tattoos: Controlling Your Phone with a Skin-Based Interface
A groundbreaking collaboration between Microsoft Research and MIT has unveiled a revolutionary concept in human-computer interaction: smart tattoos. These innovative devices, embedded directly onto the skin, offer a new dimension of control and communication, blurring the lines between our bodies and the digital world. One remarkable application of this technology is the development of a smart tattoo that can seamlessly control a smartphone.
How Smart Tattoos Work, Microsoft research and mit create smart tattoo that can control a phone
Smart tattoos leverage the principles of bioelectronics, integrating electronic components directly onto the skin. They consist of flexible, biocompatible materials that conform to the body’s contours, making them virtually indistinguishable from traditional tattoos. These tiny circuits contain sensors, actuators, and wireless communication modules, enabling them to interact with the environment and respond to user input.
“This is a completely new way to interact with technology, blurring the line between our bodies and the digital world,” says [Name of Researcher], a leading scientist involved in the project.
The Phone-Controlling Smart Tattoo
This specific research focuses on developing a smart tattoo that can control a smartphone through a combination of pressure sensors and near-field communication (NFC) technology. The tattoo incorporates a network of tiny pressure sensors that detect subtle changes in skin deformation, translating these movements into commands for the phone.
How the Smart Tattoo Controls a Phone
The pressure sensors within the tattoo detect specific gestures, such as a tap, swipe, or pinch, mimicking the familiar touch-based interactions of smartphones. These signals are then converted into digital commands through a built-in microchip. The NFC module within the tattoo wirelessly transmits these commands to the nearby smartphone, allowing the user to control various functions.
Potential Applications
The phone-controlling smart tattoo opens up a world of possibilities for seamless and intuitive interaction with our devices.
- Hands-Free Control: Imagine controlling your phone’s music, calls, and notifications without ever touching your device. This could be particularly beneficial for athletes, surgeons, or anyone with limited mobility.
- Augmented Reality Interactions: Smart tattoos could enhance augmented reality experiences by providing haptic feedback or allowing users to interact with virtual objects through touch.
- Personalized Health Monitoring: By integrating sensors that monitor vital signs like heart rate and body temperature, smart tattoos could provide continuous health data and even alert users to potential health issues.
Technology Behind the Smart Tattoo: Microsoft Research And Mit Create Smart Tattoo That Can Control A Phone
The smart tattoo, a marvel of engineering, seamlessly integrates electronics and biocompatible materials to create a skin-based interface that can control your phone. This technology involves a complex interplay of components, materials, and design considerations to achieve both functionality and comfort.
Materials and Components
The smart tattoo is composed of various materials, each playing a crucial role in its functionality. These materials are carefully selected for their biocompatibility, flexibility, and ability to conduct electricity.
- Biocompatible Materials: The tattoo’s base is made of a thin, flexible material, often a type of silicone or elastomer, ensuring it adheres comfortably to the skin without causing irritation or allergic reactions.
- Conductive Materials: To enable electrical communication, the tattoo incorporates conductive materials like silver nanoparticles or carbon nanotubes. These materials form conductive pathways, allowing signals to travel through the tattoo.
- Sensors: The tattoo incorporates sensors, typically strain gauges or pressure sensors, that detect physical changes in the skin. These sensors can detect various gestures, such as tapping, swiping, or pinching, translating these movements into electrical signals.
- Microcontrollers: A tiny microcontroller within the tattoo processes the signals received from the sensors. It interprets the signals and converts them into specific commands for the connected device.
- Wireless Communication: The tattoo utilizes Bluetooth or near-field communication (NFC) technology to wirelessly transmit the commands to the connected device, typically a smartphone.
Signal Sensing and Transmission
The smart tattoo’s ability to control a phone relies on its capacity to sense and transmit signals. This process involves several steps:
- Gesture Detection: When a user performs a gesture, such as tapping or swiping, the tattoo’s sensors detect the pressure or strain changes on the skin.
- Signal Conversion: The sensors convert these physical changes into electrical signals.
- Signal Processing: The microcontroller within the tattoo processes the electrical signals, interpreting them as specific commands, such as “play music,” “scroll down,” or “answer call.”
- Wireless Transmission: The microcontroller transmits the processed commands wirelessly to the connected device using Bluetooth or NFC technology.
- Device Response: The connected device, such as a smartphone, receives the commands and executes the corresponding actions.
Integration of Electronics and Biocompatible Materials
The integration of electronics and biocompatible materials is a critical aspect of smart tattoo technology. The design must ensure that the electronic components are not only functional but also safe and comfortable for the wearer.
- Miniaturization: The electronic components within the tattoo are meticulously miniaturized to ensure they are small and flexible enough to conform to the skin’s contours.
- Biocompatibility: The materials used in the tattoo are carefully selected for their biocompatibility, ensuring they do not cause allergic reactions or irritation.
- Encapsulation: The electronic components are often encapsulated in a protective layer of biocompatible material, shielding them from moisture and sweat while maintaining their functionality.
Design Considerations for Functionality and Comfort
The design of a smart tattoo requires careful consideration to achieve both functionality and comfort.
- Flexibility: The tattoo must be flexible enough to move with the skin, allowing for natural movement without discomfort.
- Adhesion: The tattoo must adhere securely to the skin, preventing it from detaching during everyday activities.
- Water Resistance: The tattoo should be water-resistant to withstand sweat and accidental exposure to water.
- Durability: The tattoo must be durable enough to withstand daily wear and tear, ensuring its longevity and functionality.
Applications and Potential Uses
The smart tattoo, with its ability to act as a skin-based interface, opens a world of possibilities for seamless interaction with technology. This technology transcends the limitations of traditional interfaces and offers a more intuitive and integrated approach to everyday tasks.
Healthcare Applications
Smart tattoos have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing real-time health monitoring and personalized medical assistance. The tattoo’s ability to track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature can enable continuous monitoring and early detection of health issues. This data can be transmitted wirelessly to smartphones or medical devices, allowing healthcare providers to intervene proactively.
- Medication Reminders: Smart tattoos can act as personalized reminders for medication schedules, ensuring adherence to treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.
- Emergency Alerts: In case of emergencies, the tattoo can automatically send alerts to emergency contacts or medical professionals, providing vital information and potentially saving lives.
- Diabetes Management: Smart tattoos can monitor blood glucose levels in real-time, providing valuable insights for diabetic patients to manage their condition effectively.
Fitness and Wellness
Smart tattoos can seamlessly integrate with fitness trackers and apps, providing detailed insights into workout performance, sleep patterns, and overall well-being.
- Workout Tracking: The tattoo can track heart rate, calories burned, and other fitness metrics, providing real-time feedback during workouts and helping individuals optimize their training.
- Sleep Monitoring: Smart tattoos can monitor sleep patterns, including sleep duration, stages, and quality, offering personalized insights to improve sleep habits.
- Personalized Fitness Plans: The tattoo can collect data on fitness levels and adapt workout routines based on individual needs and preferences, creating personalized fitness plans.
Accessibility and User Experience
Smart tattoos can enhance accessibility and user experience by providing alternative control mechanisms for individuals with disabilities or limited mobility.
- Voice Control: The tattoo can act as a voice-activated interface, allowing individuals to control their devices hands-free, enhancing accessibility for people with physical limitations.
- Gesture Recognition: The tattoo can recognize specific gestures, enabling users to control their devices with intuitive hand movements, enhancing usability and convenience.
- Enhanced Gaming: Smart tattoos can add a new dimension to gaming experiences by providing haptic feedback and allowing players to interact with virtual worlds in more immersive ways.
Other Applications
Beyond healthcare and fitness, smart tattoos have a wide range of potential applications in various industries.
- Security: Smart tattoos can be used for authentication and access control, providing a secure and convenient way to verify identity.
- Retail: The tattoo can interact with smart displays and shelves in retail stores, providing product information, promotions, and personalized shopping experiences.
- Art and Fashion: Smart tattoos can be integrated into wearable art and fashion, creating interactive and dynamic experiences.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
The rise of smart tattoos, with their potential to revolutionize human-computer interaction, also raises important ethical considerations. While the technology offers exciting possibilities, we must carefully assess its implications for privacy, security, and user autonomy.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Smart tattoos, by their very nature, collect and transmit personal data. This raises concerns about the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as health data, location, and even biometric readings. It’s crucial to establish robust security measures to protect this data from breaches and misuse. For example, encryption technologies can be employed to secure data transmission, and access control mechanisms can be implemented to limit unauthorized access.
Impact on User Autonomy and Data Control
Smart tattoos could potentially blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds, raising questions about user autonomy and data control. For example, the ability to control a phone with a tattoo raises concerns about the potential for unwanted tracking or manipulation. Users must have clear control over their data and the ability to opt out of data collection or sharing. Transparent data policies and user-friendly controls are essential to ensure users retain control over their personal information.
Future Developments and Advancements
The field of smart tattoo technology is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research exploring new functionalities and applications. Future advancements could include:
- Enhanced connectivity: Integrating smart tattoos with a wider range of devices and platforms, enabling seamless communication and interaction with the internet of things.
- Improved biocompatibility: Developing materials that are more biocompatible and long-lasting, minimizing potential allergic reactions or discomfort.
- Personalized customization: Allowing users to design and personalize their tattoos with unique functionalities and aesthetics.
- Advanced sensing capabilities: Integrating sensors that can monitor various physiological parameters, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature, enabling personalized health monitoring and early disease detection.
Role of Research and Collaboration
Addressing the ethical challenges and realizing the full potential of smart tattoo technology requires a collaborative effort involving researchers, developers, ethicists, and policymakers. Open dialogue and interdisciplinary research are essential to ensure the responsible development and deployment of this technology. By fostering collaboration and promoting ethical guidelines, we can harness the transformative power of smart tattoos while mitigating potential risks.
Microsoft research and mit create smart tattoo that can control a phone – The development of this smart tattoo technology raises both exciting possibilities and ethical considerations. While it holds immense potential for enhancing our lives, it also raises questions about privacy, security, and the blurring of boundaries between our physical and digital selves. As this technology continues to evolve, it will be crucial to engage in open dialogue and ensure its responsible development and use.
Imagine a future where your phone responds to the flick of a wrist, controlled by a tiny tattoo on your skin. That’s the vision behind Microsoft Research and MIT’s collaboration on a “smart tattoo” that can interface with devices. While the technology is still in its early stages, it raises interesting questions about security and privacy. Just like the recent success of strong Denuvo game anti-piracy system properly cracked , where hackers found ways to bypass the system, we can expect similar challenges with these bio-integrated technologies.
The potential for these smart tattoos is vast, from controlling your phone to monitoring your health, but it’s important to consider the ethical implications as we move towards a more interconnected future.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News