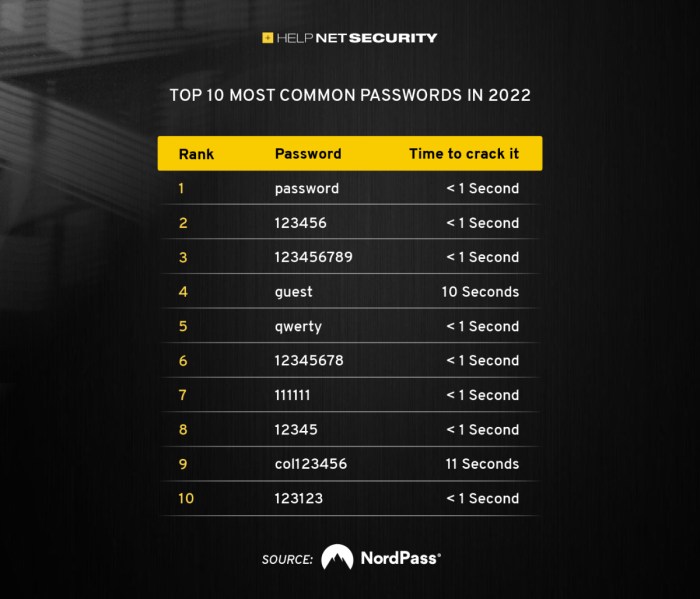
The Rise of “123456”
The year 2017 saw “123456” reign supreme as the most common password, a title it has held for several years. This simple sequence of numbers, seemingly innocuous, represents a fascinating phenomenon in the digital landscape, a story of human behavior, technological limitations, and the enduring struggle for online security.
The History of “123456”
The origins of “123456” as a common password can be traced back to the early days of computing. In the 1980s, personal computers began to enter homes, and users were often required to create passwords to access their systems. The concept of password security was still in its infancy, and users were not accustomed to the complexities of creating strong and unique passwords. “123456” and similar simple sequences were easy to remember and type, making them a natural choice for many users.
Factors Contributing to its Popularity in 2017
Several factors contributed to the continued popularity of “123456” in 2017.
- Ease of Use: “123456” is exceptionally easy to remember and type, especially for users who are not familiar with password security best practices.
- Inertia: Many users simply stick with passwords they have used for years, even if they are aware of the security risks. This “inertia” can be attributed to a lack of awareness, convenience, or simply a reluctance to change ingrained habits.
- Limited Password Complexity Requirements: Some websites and applications have relatively lax password requirements, allowing users to choose weak passwords like “123456”. This lack of enforcement contributes to the persistence of simple passwords.
Examples of “123456” in Use
The pervasiveness of “123456” is evident in various contexts.
- Data Breaches: “123456” has been a common password found in numerous data breaches, including the infamous Yahoo! breach of 2016, which exposed over 3 billion accounts.
- Password Cracking: “123456” is often the first password that hackers try when attempting to crack into accounts. Its simplicity makes it vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where hackers systematically try different combinations until they find the correct password.
- Public Awareness: The prevalence of “123456” has led to public awareness campaigns urging users to choose stronger passwords. However, despite these efforts, the use of “123456” persists.
Simplicity vs. Security: Most Common Password Of 2017 Wont Surprise You
The ease of remembering “123456” is undeniable, but it comes at a significant cost in terms of security. This simple password, often considered the most common, is incredibly vulnerable to hacking attempts. The consequences of using such a simple password can be severe, ranging from compromised online accounts to identity theft.
Reasons for Choosing Simple Passwords
People often choose simple passwords for various reasons. The main reasons include:
- Ease of Recall: Simple passwords are easy to remember and type, particularly for individuals who manage multiple online accounts. This convenience can be a significant factor for many users.
- Habit and Familiarity: Many individuals have been using the same simple password for years, forming a habit that is difficult to break. This familiarity can make it seem less risky, even though it is not.
- Lack of Awareness: Some users may not fully understand the risks associated with using weak passwords. They may underestimate the sophistication of hacking techniques and the potential consequences of compromised accounts.
The Evolution of Password Practices
The world of online security is in constant flux, and password practices are no exception. Since 2017, the landscape has seen significant shifts, driven by evolving threats, technological advancements, and a growing awareness of cybersecurity best practices.
Password Managers and Multi-Factor Authentication, Most common password of 2017 wont surprise you
Password managers and multi-factor authentication have become indispensable tools in bolstering online security.
Password managers, like LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane, store and manage your passwords securely, eliminating the need to remember numerous complex credentials. They generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise your data.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification before granting access to an account. This could involve a combination of something you know (password), something you have (phone), or something you are (fingerprint).
MFA is a powerful deterrent against unauthorized access, as even if an attacker manages to obtain your password, they would still need to bypass the second authentication factor.
The Importance of Strong, Unique Passwords
Using strong, unique passwords for different accounts is crucial for maintaining robust online security.
- Strong Passwords: A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using common words, personal information, or easily guessable sequences.
- Unique Passwords: Using the same password for multiple accounts is a major security risk. If one account is compromised, attackers could gain access to all your other accounts using the same password.
By adopting these practices, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyberattacks and safeguard their online presence.
The Impact of Data Breaches
The prevalence of “123456” as the most common password in 2017 served as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in weak password practices. Data breaches involving this ubiquitous password highlighted the critical need for stronger password security measures, not just for individuals but for organizations as well. These breaches revealed the real-world consequences of using simple passwords and underscored the importance of robust security protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
Real-World Consequences of Simple Passwords in Data Breaches
The use of “123456” in data breaches has had far-reaching consequences, impacting individuals, businesses, and even governments. Here are some examples:
- Identity Theft: In numerous data breaches, individuals using “123456” have fallen victim to identity theft, where criminals gain access to their personal information, including credit card details, Social Security numbers, and addresses. This can lead to financial losses, damage to credit scores, and even legal repercussions.
- Financial Losses: Companies that have suffered data breaches due to the use of simple passwords have faced significant financial losses. These losses can stem from stolen funds, legal expenses, reputational damage, and the cost of implementing new security measures. For instance, the 2017 Equifax data breach, which involved millions of compromised accounts, cost the company billions of dollars in settlements and regulatory fines.
- National Security Risks: In cases where government agencies or critical infrastructure are compromised due to weak passwords, national security risks can arise. Hackers can gain access to sensitive data, disrupt essential services, or even compromise national security systems. The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, which targeted healthcare systems and other critical infrastructure, exploited vulnerabilities in outdated software and weak passwords, highlighting the potential for national security threats.
The Future of Password Security
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so are the methods used to protect our online identities. While passwords have long been the cornerstone of security, their limitations are becoming increasingly apparent. Data breaches, sophisticated hacking techniques, and the growing complexity of online services have forced us to re-evaluate the effectiveness of traditional password-based authentication. The future of password security lies in embracing innovative technologies and practices that enhance security while simplifying the user experience.
Emerging Technologies and Practices
The future of password security is not about replacing passwords altogether but about augmenting them with more robust security measures. Emerging technologies and practices are being developed to address the vulnerabilities associated with traditional passwords.
- Passwordless Authentication: This approach eliminates the need for passwords altogether, relying on alternative methods like biometrics (fingerprint scanning, facial recognition), security keys, or one-time passcodes. Passwordless authentication enhances security by eliminating the risk of password compromise through phishing or brute-force attacks. For example, Google’s Titan Security Key, a physical security key, offers a highly secure way to authenticate into online accounts.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access. This can involve a combination of something the user knows (password), something the user has (phone), and something the user is (biometrics). MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one factor is compromised.
- Password Managers: Password managers store and manage passwords securely, eliminating the need for users to remember complex passwords for every online account. They generate strong, unique passwords for each service and automatically fill in login credentials, making it easier for users to adopt secure practices. Popular password managers include LastPass, 1Password, and Dashlane.
- Behavioral Biometrics: This technology analyzes user behavior patterns, such as typing speed, mouse movements, and keystroke dynamics, to identify legitimate users. Behavioral biometrics can detect suspicious activity and prevent unauthorized access, even if a password is stolen.
- Passwordless Authentication with Biometrics: This technology combines the strengths of both passwordless authentication and biometrics, providing a highly secure and user-friendly authentication experience. For instance, Apple’s Face ID and Touch ID utilize facial and fingerprint recognition to unlock devices and authenticate into accounts.
Most common password of 2017 wont surprise you – The prevalence of “123456” as the most common password in 2017 serves as a stark reminder of the importance of strong password security. It’s a wake-up call for individuals and organizations alike to prioritize online security and implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. While “123456” may be a relic of the past, the lessons it teaches are still relevant today. In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, choosing strong, unique passwords is more crucial than ever. So, ditch the simple passwords and embrace the complexity; your online security depends on it.
Remember that time in 2017 when “123456” was the most common password? Yeah, we all knew that was coming. It’s like the gaming world releasing a classic like super bomberman r switch updated – nostalgic, predictable, and still totally fun. But just like we need to switch up our passwords, maybe it’s time for a new, exciting bomberman game to blow us away.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News