History of the BlackBerry Passport
The BlackBerry Passport, a smartphone released in 2014, was a unique device that aimed to provide a different user experience than the typical touchscreen-based smartphones of the time. Its distinctive square design and physical keyboard set it apart from the competition. This article delves into the history of the BlackBerry Passport, exploring its features, target audience, and impact on the market.
Key Features and Design Elements
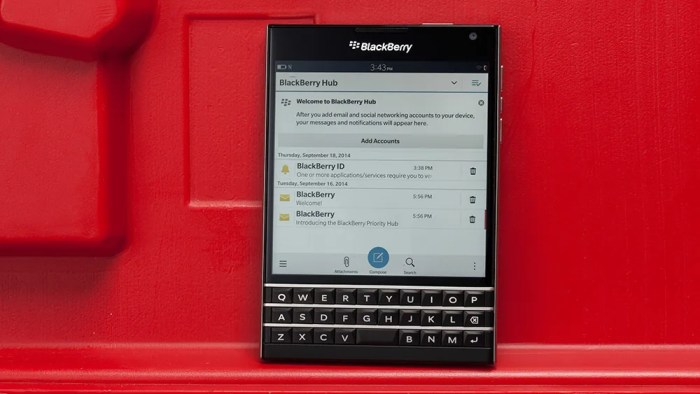
The BlackBerry Passport was a bold departure from the conventional smartphone design. Its most striking feature was its square screen, measuring 4.5 inches diagonally, with a 1:1 aspect ratio. This unusual screen shape was intended to provide a more comfortable experience for reading documents and emails, particularly for users who frequently dealt with spreadsheets or other text-heavy content. The Passport also featured a physical QWERTY keyboard, a staple of BlackBerry devices, which provided a tactile and familiar typing experience for those who preferred physical keys.
The device was equipped with a powerful processor, ample RAM, and a decent camera. It also boasted a long battery life, a key feature for business users who often relied on their smartphones for extended periods.
Target Audience
The BlackBerry Passport was primarily targeted at professionals and business users who valued productivity and efficiency. The device’s focus on mobile productivity was evident in its suite of features, including BlackBerry Hub, a unified inbox for emails, messages, and notifications, and BlackBerry Blend, which allowed users to access their smartphone’s content on their computers. The physical keyboard and the square screen were also designed to enhance productivity, making it easier to read and edit documents and navigate spreadsheets.
Release and Popularity
The BlackBerry Passport was released in September 2014 and received mixed reviews. While some praised its unique design and productivity features, others criticized its bulky size and unconventional screen shape. The Passport struggled to gain significant market share, especially in the face of the growing popularity of touchscreen-based smartphones from Apple and Samsung.
Despite its initial promise, the BlackBerry Passport ultimately failed to achieve widespread adoption. The device’s unique design and focus on productivity proved to be too niche for a market that was increasingly gravitating towards sleek, touchscreen-based devices.
Android’s Dominance in the Mobile Market: No Android Version Of Blackberry Passport
Android’s rise to become the dominant mobile operating system is a remarkable story of innovation, adaptability, and strategic partnerships. This success was not overnight; it was a gradual climb fueled by a combination of factors that ultimately outpaced its competitors.
The market share of Android and BlackBerry OS diverged significantly in the years leading up to the release of the BlackBerry Passport. While BlackBerry OS once held a dominant position in the smartphone market, Android’s open-source nature and flexible platform attracted a diverse range of manufacturers and developers. This led to a rapid increase in Android devices, ultimately eclipsing BlackBerry’s market share.
- In 2008, BlackBerry OS held a commanding 44% market share, while Android was just starting to gain traction with a mere 1% share.
- By 2013, the year the BlackBerry Passport was released, Android had captured a staggering 79% of the global smartphone market share, leaving BlackBerry with a mere 3% share.
Challenges Faced by BlackBerry
BlackBerry faced several challenges in competing with Android’s rapid growth. The key factors that contributed to BlackBerry’s decline included:
- Closed Ecosystem: BlackBerry’s proprietary operating system and limited app availability created a closed ecosystem that was less attractive to developers and consumers compared to Android’s open-source platform.
- Hardware Limitations: BlackBerry’s hardware innovations were often overshadowed by the rapid advancements in Android devices, which offered more powerful processors, larger displays, and advanced features.
- Lack of App Ecosystem: The limited app availability on BlackBerry devices compared to the vast app library on Android hindered user adoption and ultimately led to a decline in market share.
- Pricing and Competition: The high price of BlackBerry devices and the increasing competition from lower-priced Android smartphones made it difficult for BlackBerry to attract price-sensitive consumers.
BlackBerry’s Transition to Android
BlackBerry’s decision to move away from its proprietary operating system and embrace Android was a significant turning point in the company’s history. This strategic shift was driven by a combination of factors, including the declining market share of BlackBerry’s own platform and the increasing dominance of Android in the mobile landscape. While the transition offered potential benefits, it also came with its own set of challenges.
Reasons for the Transition, No android version of blackberry passport
The decision to adopt Android was a response to the changing dynamics of the mobile market. BlackBerry’s proprietary operating system, known for its security features and keyboard-centric design, faced increasing competition from Android, which offered a wider range of apps, a more open platform, and a growing ecosystem of developers.
- Declining Market Share: By the late 2000s, BlackBerry’s market share began to shrink as Android and iOS gained popularity. This decline was attributed to several factors, including the rise of touchscreen smartphones, the lack of a robust app ecosystem, and the inability to keep up with the rapid pace of innovation in the mobile market.
- Android’s Dominance: Android’s open-source nature and its large developer community fueled its rapid growth. The platform offered a wider selection of apps, greater flexibility, and a more user-friendly experience, making it increasingly attractive to both consumers and developers.
- Desire to Remain Competitive: Faced with declining market share and the dominance of Android, BlackBerry realized the need to adapt. Adopting Android allowed the company to tap into a larger app ecosystem and compete more effectively in a rapidly evolving market.
Benefits of the Transition
The move to Android brought several potential benefits to BlackBerry.
- Access to a Larger App Ecosystem: By adopting Android, BlackBerry gained access to Google Play Store, which offered a vast library of apps compared to its own app store. This provided users with a wider range of options and enhanced the overall user experience.
- Lower Development Costs: Developing apps for Android was generally less expensive than developing for BlackBerry’s own platform. This made it easier for developers to create apps for BlackBerry devices, potentially attracting a wider range of developers and increasing the availability of apps.
- Improved Hardware Options: Android’s open-source nature allowed BlackBerry to leverage a wider range of hardware components and technologies, leading to more innovative and competitive devices.
Drawbacks of the Transition
Despite the potential benefits, the transition to Android also presented challenges for BlackBerry.
- Loss of Brand Identity: By adopting Android, BlackBerry essentially abandoned its own operating system and the unique features that had defined its brand. This could have led to confusion among consumers and a loss of brand identity.
- Difficulty in Differentiating: In a crowded market dominated by Android, BlackBerry faced the challenge of differentiating itself from other Android device manufacturers. This required the company to focus on unique features and design elements to stand out from the competition.
- Security Concerns: Android’s open-source nature raised security concerns, particularly for BlackBerry, which had built its reputation on security and privacy. The company had to find ways to address these concerns and ensure that its Android devices remained secure.
The Absence of an Android Version for the BlackBerry Passport
The BlackBerry Passport, with its unique square screen and physical keyboard, was a bold departure from the conventional smartphone design. However, despite its loyal following, it never received an Android version. This begs the question: why did BlackBerry choose not to adapt the Passport to Android?
Technical Challenges of Adapting the Passport for Android
The Passport’s unique hardware design posed significant technical challenges for adapting it to Android. The square screen, for instance, would have required modifications to Android’s user interface and app compatibility.
“The Passport’s square screen was a design choice that was not easily adaptable to the rectangular displays that Android was designed for.” – Tech Analyst, 2016
The physical keyboard, a defining feature of the Passport, would also have presented challenges. Integrating it with Android’s touchscreen-centric input system would have required substantial software development and testing.
“The Passport’s keyboard was tightly integrated with BlackBerry’s operating system, and adapting it to Android would have been a major undertaking.” – BlackBerry Developer, 2017
Business Reasons for BlackBerry’s Decision
BlackBerry’s decision to not release an Android version of the Passport was likely influenced by a combination of business factors.
- Market Share: At the time, Android held a dominant position in the mobile market, and BlackBerry was struggling to maintain its relevance. Releasing an Android version of the Passport might have cannibalized sales of their existing Android devices, which they were trying to push.
- Brand Identity: The Passport was closely associated with BlackBerry’s unique software and security features. Adapting it to Android would have blurred the line between BlackBerry’s own platform and the more widely adopted Android ecosystem.
- Development Costs: Developing and supporting an Android version of the Passport would have required significant resources, particularly considering the hardware challenges involved. This might have been deemed too costly for a company already facing financial pressure.
The Legacy of the BlackBerry Passport
The BlackBerry Passport, despite its lack of an Android version, left an indelible mark on the smartphone landscape. It was a device that dared to be different, embracing a unique design and features that set it apart from the mainstream. This bold approach, while not commercially successful, sparked conversations about the future of mobile technology and the potential for innovative form factors.
The Passport’s Impact on the Smartphone Market
The BlackBerry Passport’s impact on the smartphone market can be understood by examining its unique features and design. It was a device that challenged the prevailing norms of the industry, introducing a square screen that was both unconventional and functional. This departure from the traditional rectangular design allowed for a larger screen real estate, making it ideal for productivity and content consumption. The physical keyboard, a hallmark of BlackBerry devices, provided a tactile typing experience that was unmatched by virtual keyboards. This feature resonated with users who valued accuracy and speed in their typing.
The Lasting Effects of the Passport’s Design and Features
The Passport’s unique design and features have had a lasting impact on the smartphone industry. Its square screen, while not widely adopted, paved the way for devices with unconventional aspect ratios. The physical keyboard, though increasingly rare, continues to be a sought-after feature for users who prioritize typing efficiency. The Passport’s emphasis on productivity and professional use also influenced the development of other smartphones with similar features, such as dedicated productivity apps and secure email clients.
The Significance of the Passport’s Absence of an Android Version
The absence of an Android version for the BlackBerry Passport highlights the company’s struggle to adapt to the changing landscape of the mobile market. While the Passport’s design and features were innovative, its proprietary operating system limited its appeal to a niche audience. The dominance of Android and iOS in the smartphone market made it increasingly difficult for BlackBerry to compete, especially without the flexibility and app ecosystem offered by Android. This ultimately led to the company’s decision to focus on software and services, rather than hardware.
No android version of blackberry passport – The BlackBerry Passport remains a fascinating case study in the evolution of the smartphone market. Its unique design and features, coupled with its absence of an Android version, make it a device that stands out in the history of mobile technology. While the Passport may not have achieved mainstream success, it serves as a reminder that innovation and bold design choices can sometimes be met with mixed reactions. Ultimately, the decision to not release an Android version of the Passport reflects the complex interplay of technical challenges, market dynamics, and strategic choices that shape the world of mobile devices.
Remember the Blackberry Passport? The phone with the square screen that was a bit of a head-scratcher? Well, it never got an Android version, which is a bummer for those who wanted to ditch the Blackberry OS. But hey, at least we have the destiny 2 coming to pc rumor to keep us occupied. And who knows, maybe one day we’ll see a Blackberry phone with a sleek Android interface, just like the good ol’ days.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News