Smartphone Ownership Trends
The pervasiveness of smartphones in American society is undeniable, with a staggering 64% of adults now owning one. This remarkable statistic reflects a rapid evolution in technology adoption, transforming how we communicate, access information, and navigate our daily lives. To fully understand the significance of this trend, it’s essential to delve into the historical trajectory of smartphone ownership and analyze the factors driving its widespread acceptance.
Historical Growth of Smartphone Ownership
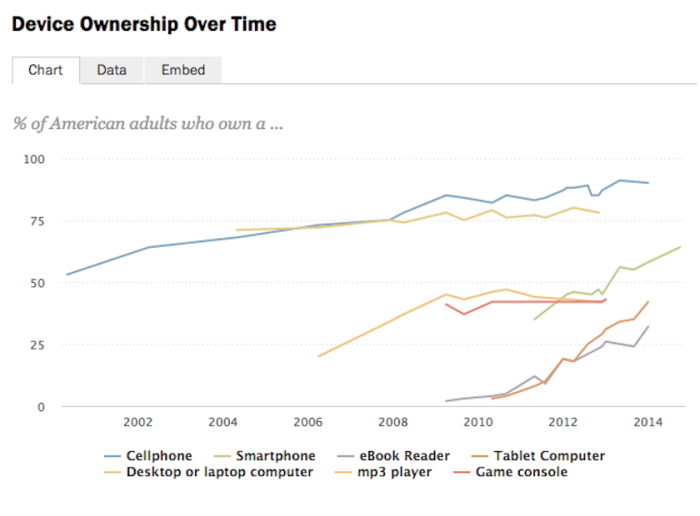
The rise of smartphone ownership in the United States has been nothing short of meteoric. While the first smartphones emerged in the late 1990s, their adoption was initially slow due to high prices and limited functionality. However, the introduction of the iPhone in 2007 marked a turning point, ushering in an era of sleek design, intuitive interfaces, and a wide array of apps. This innovation sparked a surge in demand, driving down prices and making smartphones accessible to a broader audience.
The Pew Research Center’s data paints a vivid picture of this rapid growth. In 2011, just 35% of adults owned a smartphone. This figure jumped to 56% by 2015 and reached 64% by 2023, indicating a consistent upward trend. This rapid adoption can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Affordability: Smartphone prices have steadily decreased over the years, making them more affordable for a wider range of consumers.
- Accessibility: The availability of affordable data plans and widespread cellular network coverage has made smartphones readily accessible.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in smartphone technology has led to enhanced features, improved performance, and greater functionality, further fueling adoption.
Smartphone Adoption Rate
The adoption rate of smartphones has outpaced that of other technologies, underscoring their transformative impact on society. For instance, it took roughly 75 years for the radio to reach 50% penetration in American households, while television took 13 years to achieve the same milestone. Smartphones, however, reached this benchmark in just five years, highlighting their unprecedented rate of adoption.
Smartphone Ownership Across Demographics
Smartphone ownership is not evenly distributed across all demographic groups. Notably, age plays a significant role in determining smartphone adoption rates. While nearly all young adults (98%) own a smartphone, this figure drops to 78% for adults aged 65 and older.
- Age: Smartphone ownership is significantly higher among younger generations, with nearly all young adults owning a smartphone, compared to older generations.
- Income: Higher-income households tend to have higher smartphone ownership rates than lower-income households.
- Education: Individuals with higher levels of education are more likely to own a smartphone than those with lower levels of education.
Factors Driving Smartphone Ownership
The widespread adoption of smartphones can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including:
- Affordability: As smartphone prices have decreased, they have become more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Accessibility: The availability of affordable data plans and widespread cellular network coverage has made smartphones readily accessible.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in smartphone technology has led to enhanced features, improved performance, and greater functionality, further fueling adoption.
- Social Connectivity: Smartphones have become essential tools for social interaction, allowing users to stay connected with friends and family through social media, messaging apps, and video calls.
- Information Access: Smartphones provide access to a vast array of information, news, and entertainment, making them invaluable tools for learning and staying informed.
- Convenience: Smartphones offer a wide range of functionalities, such as navigation, mobile payments, and online shopping, making them incredibly convenient for daily tasks.
Impact of Smartphone Ownership on Society
The ubiquity of smartphones has fundamentally altered communication patterns, social interactions, and access to information, profoundly impacting individuals and communities. This section delves into the multifaceted impact of widespread smartphone ownership on society.
Changes in Communication Patterns
Smartphones have revolutionized communication, enabling instant and pervasive connectivity.
- Increased Frequency and Reach: Smartphones facilitate frequent and widespread communication, allowing individuals to connect with friends, family, and colleagues across geographical boundaries with ease. This has led to a significant increase in the volume and frequency of communication, blurring the lines between personal and professional life.
- Shifting Communication Modes: Smartphones have introduced new modes of communication, such as instant messaging, video calls, and social media platforms, supplementing traditional forms like phone calls and emails. These new modes allow for more interactive and dynamic communication, facilitating real-time sharing of information, ideas, and experiences.
- Blurred Boundaries: The constant connectivity provided by smartphones has blurred the boundaries between work and personal life. Individuals are now expected to be available and responsive at all times, leading to increased stress and a sense of being constantly “on.” This constant connectivity can also contribute to feelings of social isolation and loneliness, as individuals may feel pressured to be constantly engaged with their devices.
Impact on Social Interactions and Relationships
Smartphones have significantly impacted social interactions and relationships, both positively and negatively.
- Enhanced Connections: Smartphones have facilitated stronger connections with friends and family, allowing for more frequent communication and the sharing of important life events. They have also enabled individuals to connect with people they might not otherwise have met, fostering new relationships and communities.
- Social Comparison and Competition: The curated and often idealized content shared on social media platforms can lead to feelings of social comparison and competition. Individuals may feel pressure to present a perfect image of themselves, leading to anxiety and dissatisfaction with their own lives.
- Distraction and Reduced Face-to-Face Interactions: Smartphones can be a source of distraction during social gatherings, leading to reduced face-to-face interactions and a decline in the quality of conversations. This can contribute to feelings of isolation and a lack of genuine connection with others.
Access to Information and Knowledge
Smartphones have democratized access to information and knowledge, providing individuals with unprecedented opportunities to learn and explore.
- Instant Access to Information: Smartphones provide instant access to a vast repository of information through search engines, news apps, and online libraries. This has empowered individuals to learn about a wide range of topics, stay informed about current events, and make informed decisions.
- Personalized Learning Experiences: Educational apps and online courses have made learning more accessible and personalized, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and on their own terms. This has opened up new possibilities for lifelong learning and skill development.
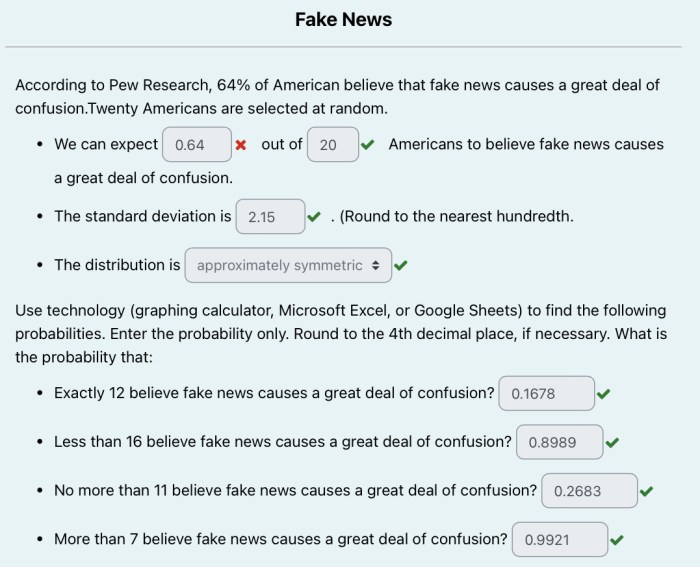
- Spread of Misinformation: While smartphones provide access to a wealth of information, they also contribute to the spread of misinformation and fake news. The rapid dissemination of information through social media platforms can lead to the amplification of false or misleading content, potentially impacting public opinion and decision-making.
Benefits and Challenges of Smartphone Ownership
Smartphone ownership offers numerous benefits, but it also presents challenges for individuals and communities.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Communication: Smartphones facilitate instant and widespread communication, enabling individuals to stay connected with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Access to Information: Smartphones provide instant access to a vast repository of information, empowering individuals to learn, stay informed, and make informed decisions.
- Convenience and Efficiency: Smartphones streamline daily tasks, such as shopping, banking, and navigation, making life more convenient and efficient.
- Entertainment and Recreation: Smartphones provide access to a wide range of entertainment options, including music, videos, games, and social media, making leisure time more engaging.
- Challenges:
- Addiction and Dependence: Excessive smartphone use can lead to addiction and dependence, negatively impacting mental health and well-being.
- Privacy Concerns: Smartphones collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
- Social Isolation and Loneliness: Constant connectivity can contribute to feelings of social isolation and loneliness, as individuals may feel pressured to be constantly engaged with their devices.
- Distraction and Reduced Productivity: Smartphones can be a source of distraction, impacting productivity and focus, especially in work and educational settings.
Smartphone Usage Patterns: Pew Research 64 Of Americans Now Own A Smartphone
Smartphones have become an integral part of modern life, influencing how we communicate, access information, and entertain ourselves. Understanding smartphone usage patterns provides insights into how individuals interact with technology and the evolving digital landscape.
Smartphone Activities
Smartphone usage patterns vary depending on individual preferences and needs. However, certain activities consistently dominate smartphone use. These include:
- Internet Browsing: Smartphones provide easy access to the internet, making it a primary activity for many users. Individuals use their phones to research topics, read news, shop online, and access entertainment content.
- Social Media: Social media platforms are highly popular on smartphones, allowing users to connect with friends and family, share updates, and consume content.
- Communication: Smartphones are primarily used for communication, including texting, voice calls, and video calls.
- Entertainment: Smartphones provide access to a wide range of entertainment options, including streaming services, games, and music apps.
- Productivity: Smartphones are also used for productivity tasks, such as email, calendar management, and note-taking.
Time Spent on Smartphone Applications
The time spent on different smartphone applications provides insights into users’ interests and priorities. For example, social media applications like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok often consume significant amounts of time, while productivity apps such as email clients and calendar apps might take up less time.
Smartphone Usage Patterns Across Demographics
Smartphone usage patterns vary across different age groups and demographic segments. For instance, younger generations tend to spend more time on social media and gaming apps, while older generations might use their smartphones primarily for communication and news consumption.
Average Daily Smartphone Usage Time
The table below illustrates the average daily smartphone usage time for different activities:
| Activity | Average Daily Usage Time (minutes) |
|---|---|
| Social Media | 60 |
| Internet Browsing | 45 |
| Communication | 30 |
| Entertainment | 30 |
| Productivity | 15 |
Smartphone Ownership and Digital Divide
The widespread adoption of smartphones has revolutionized communication and access to information. However, this digital revolution also highlights a growing concern: the potential for a digital divide based on smartphone ownership. This divide can exacerbate existing socioeconomic inequalities, limiting opportunities for individuals and communities without access to these devices and the internet services they enable.
Accessibility of Smartphones and Internet Services, Pew research 64 of americans now own a smartphone
The accessibility of smartphones and internet services varies significantly across different socioeconomic groups. Lower-income households are less likely to own smartphones and have access to reliable internet connections. This disparity is often attributed to several factors, including:
- Cost of Devices and Services: Smartphones and data plans can be expensive, particularly for families struggling to meet basic needs. The cost of internet access, especially high-speed broadband, can also be a significant barrier for low-income households.
- Digital Literacy: Individuals with limited digital literacy may find it challenging to navigate the complexities of smartphone usage and internet access. This can lead to feelings of frustration and discourage them from adopting these technologies.
- Geographic Location: Rural areas often have limited access to reliable internet infrastructure, making it difficult for residents to connect to the digital world.
Digital Literacy Levels
Digital literacy, the ability to effectively use technology for communication, information access, and problem-solving, is crucial for navigating the digital world. Studies have shown that smartphone owners generally have higher levels of digital literacy than non-owners. This gap in digital literacy can have significant consequences, impacting individuals’ ability to participate in online learning, access essential services, and engage in the digital economy.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Addressing the digital divide requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on:
- Affordable Devices and Services: Governments and private organizations can implement policies and programs to make smartphones and internet services more affordable for low-income households. This can include subsidies, discounts, and access to low-cost devices.
- Digital Literacy Training: Providing accessible digital literacy training programs can empower individuals with the skills needed to confidently use smartphones and the internet. This can involve workshops, online tutorials, and community-based initiatives.
- Infrastructure Development: Expanding internet infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, is essential to ensure equitable access to digital services. This includes investments in broadband networks and public Wi-Fi hotspots.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, businesses, and non-profit organizations can leverage resources and expertise to develop innovative solutions for bridging the digital divide.
Implications for Businesses and Industries
The widespread adoption of smartphones has fundamentally reshaped the business landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities for industries across the spectrum. From marketing and advertising to consumer behavior and the emergence of entirely new business models, smartphones have become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age.
Marketing and Advertising
Smartphones have revolutionized the way businesses market and advertise their products and services. The ubiquitous nature of these devices provides a constant channel for reaching consumers, allowing for targeted advertising based on demographics, interests, and location. Mobile advertising platforms have become increasingly sophisticated, enabling businesses to track user engagement and optimize campaigns in real time.
- Location-based advertising: Smartphones allow businesses to target consumers based on their physical location, sending relevant ads to people in specific areas. For example, a restaurant could send a promotional offer to users who are within a certain radius of its location.
- Personalized advertising: By leveraging user data collected through apps and browsing history, businesses can personalize advertising messages to individual users. This approach can increase engagement and conversion rates by tailoring ads to specific needs and preferences.
- Mobile apps: Businesses can create dedicated mobile apps to engage with customers, provide services, and promote their products. Apps offer a direct channel for communication, loyalty programs, and customer support.
Impact on Consumer Behavior and Purchasing Patterns
Smartphones have significantly influenced consumer behavior and purchasing patterns, empowering consumers with greater access to information, price comparisons, and product reviews. This has led to a shift in the power dynamic between businesses and consumers, forcing businesses to adapt to a more informed and demanding customer base.
- Research and comparison shopping: Consumers can easily research products and compare prices from different retailers using smartphone apps and websites. This has increased price transparency and put pressure on businesses to offer competitive prices and value.
- Online shopping: Smartphones have made online shopping more convenient and accessible, leading to a surge in e-commerce sales. Consumers can browse and purchase products from anywhere at any time.
- Social media influence: Social media platforms accessible through smartphones have become a powerful influence on consumer behavior. Reviews, recommendations, and influencer marketing can significantly impact purchasing decisions.
New Business Models and Services
The capabilities of smartphones have enabled the emergence of entirely new business models and services that cater to the unique needs and preferences of mobile users. These models leverage the portability, connectivity, and computing power of smartphones to create innovative solutions.
- Mobile payments: Smartphone-based payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay have revolutionized the way people make purchases, offering a convenient and secure alternative to traditional methods.
- On-demand services: The rise of ride-sharing services (Uber, Lyft), food delivery platforms (DoorDash, Grubhub), and home services marketplaces (TaskRabbit, Handy) has been driven by the convenience and accessibility of smartphone apps.
- Mobile gaming: Smartphones have become a major platform for gaming, with a growing market for mobile games and esports.
Industries Impacted by Smartphone Ownership
| Industry | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Increased competition from online retailers, pressure to offer competitive prices and customer experience | Enhanced customer engagement through mobile apps and loyalty programs, opportunities for personalized marketing and location-based promotions |
| Banking and Finance | Security concerns related to mobile payments and data breaches, need to adapt to changing customer expectations for digital banking services | Expansion of mobile banking services, development of innovative financial products and services for smartphone users |
| Healthcare | Challenges in integrating smartphone technology with existing healthcare systems, concerns about data privacy and security | Opportunities for telehealth and remote patient monitoring, personalized healthcare apps and wearable devices |
| Education | Digital divide issues, concerns about the impact of smartphones on student attention and learning | Use of smartphones for educational apps and online learning platforms, personalized learning experiences and access to educational resources |
| Travel and Hospitality | Increased competition from online travel agencies, need to adapt to changing customer expectations for booking and travel planning | Mobile booking platforms, personalized travel recommendations, location-based services for travelers |
Future of Smartphone Ownership
The ubiquitous presence of smartphones in our lives has undeniably revolutionized communication, information access, and daily routines. As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, the future of smartphone ownership holds exciting possibilities and potential challenges.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are poised to reshape the landscape of smartphone ownership and usage.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks promises significantly faster speeds and lower latency, enabling new applications and experiences. With 5G, smartphones will become even more powerful tools for gaming, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and cloud computing. The faster speeds will also facilitate the seamless streaming of high-quality video content and the development of more sophisticated mobile apps.
- Foldable Phones: Foldable phones are gaining traction, offering a larger screen experience in a compact form factor. This innovation has the potential to blur the lines between smartphones and tablets, offering users a versatile device for both work and entertainment. Foldable phones could become the preferred choice for professionals who require a larger screen for productivity tasks and for consumers who enjoy immersive multimedia experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into smartphones to enhance features like voice assistants, camera capabilities, and personalized recommendations. AI-powered smartphones can anticipate user needs, provide context-aware assistance, and improve overall efficiency. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated, they will further personalize the smartphone experience, creating a truly customized device for each user.
Challenges and Opportunities
The widespread adoption of smartphones presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers and service providers.
- Competition: The smartphone market is highly competitive, with established players like Apple and Samsung vying for market share. New entrants, particularly from China, are also making significant inroads. To stay ahead of the curve, manufacturers must continuously innovate and offer compelling features and functionalities that differentiate their products.
- Security and Privacy: As smartphones become more interconnected and store vast amounts of personal data, security and privacy concerns are paramount. Manufacturers and service providers must prioritize robust security measures to protect user data from cyber threats. Transparency and user control over data sharing are also essential to maintain trust and confidence in smartphone technology.
- Sustainability: The environmental impact of smartphone production and disposal is a growing concern. Manufacturers are under increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials, reducing energy consumption, and extending product lifecycles.
Long-Term Implications
The widespread adoption of smartphones has profound implications for society and the economy.
- Digital Divide: While smartphones have become ubiquitous in developed countries, there remains a significant digital divide in many parts of the world. Bridging this gap requires affordable access to devices and reliable internet connectivity.
- Economic Growth: Smartphones have fueled the growth of mobile-first businesses and industries. They have also empowered consumers with access to information, services, and opportunities.
- Social Impact: Smartphones have transformed social interactions, facilitating instant communication and the creation of online communities. However, they have also raised concerns about screen time, social isolation, and the potential for addiction.
Pew research 64 of americans now own a smartphone – As smartphone ownership continues to rise, it’s essential to understand its implications. The digital divide, the potential for information overload, and the evolving landscape of online privacy are just a few of the challenges we face. But amidst these challenges, there are also opportunities for innovation, social progress, and a more connected world. By understanding the trends and patterns of smartphone ownership, we can navigate this digital landscape with greater awareness and responsibility.
Pew Research found that 64% of Americans now own a smartphone, highlighting the massive shift towards mobile browsing. This makes it even more crucial for developers to prioritize security, as evidenced by the recent vulnerability found in Microsoft’s Spartan browser, microsofts spartan browser gets peeked at. With so many people accessing the internet on their phones, it’s essential to ensure their data is protected from potential threats.
This incident serves as a reminder that even seemingly secure browsers can be susceptible to vulnerabilities, emphasizing the importance of staying vigilant and keeping software updated.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News