Robinhoods new gold card baas challenges and the tiny startup that caught stripes eye – Robinhood’s new Gold Card, BaaS challenges, and the tiny startup that caught Stripe’s eye are shaking up the financial landscape. This trifecta represents a shift towards a future where traditional banking is challenged by innovative fintech solutions. From Robinhood’s foray into the credit card market with a BaaS-powered offering to the intriguing startup that has caught the attention of a payments giant like Stripe, the financial world is abuzz with change.
This article delves into the intricacies of these developments, exploring the potential impact on consumers, businesses, and the industry as a whole. We’ll examine the key features of Robinhood’s Gold Card, the potential of BaaS to revolutionize financial services, and the startup’s unique proposition that has captured Stripe’s interest. Buckle up, because the future of finance is here, and it’s anything but ordinary.
Robinhood’s New Gold Card: A Game Changer?: Robinhoods New Gold Card Baas Challenges And The Tiny Startup That Caught Stripes Eye
Robinhood, the popular investing app, has expanded its services to include a new gold card, aiming to disrupt the traditional financial services landscape. The Gold Card, launched in partnership with a leading bank, promises a unique blend of financial benefits and user-friendly features, potentially attracting a diverse range of customers.
Impact on the Financial Services Landscape
Robinhood’s Gold Card has the potential to shake up the financial services industry by offering a compelling alternative to traditional bank cards and existing fintech offerings. The card’s focus on simplicity, transparency, and user-centric features could appeal to a generation of consumers accustomed to the intuitive interfaces of technology-driven platforms. By offering a seamless integration with Robinhood’s existing platform, the Gold Card could further solidify the company’s position as a one-stop shop for financial services.
Comparison with Existing Offerings
Robinhood’s Gold Card stands out from traditional bank cards by offering features often associated with fintech companies, such as:
- Simplified application process: Robinhood’s streamlined application process aims to make obtaining a credit card a faster and less cumbersome experience compared to traditional banks.
- Transparent fees and interest rates: Robinhood emphasizes transparency by clearly outlining fees and interest rates, eliminating the hidden charges often associated with traditional bank cards.
- Integration with existing platform: The Gold Card seamlessly integrates with Robinhood’s existing platform, allowing users to manage their finances, track spending, and access investment opportunities all in one place.
Compared to other fintech offerings, Robinhood’s Gold Card boasts several key advantages:
- Established brand recognition: Robinhood’s established brand recognition and loyal user base provide a significant advantage in attracting customers for the Gold Card.
- Wider range of financial services: Robinhood offers a broader range of financial services beyond credit cards, including investing, brokerage, and banking, providing a more comprehensive financial solution for its users.
- Strong focus on user experience: Robinhood’s user-centric approach extends to the Gold Card, emphasizing a seamless and intuitive experience for users.
Key Features and Benefits
The Gold Card offers several key features and benefits that make it attractive to potential users:
- Cashback rewards: The Gold Card offers cashback rewards on everyday purchases, allowing users to earn money back on their spending.
- Travel benefits: The card provides access to travel perks, such as airport lounge access and travel insurance, enhancing the overall travel experience.
- Early access to paychecks: Robinhood’s Gold Card allows users to access their paychecks early, providing financial flexibility and helping to avoid late fees.
- Built-in budgeting tools: The card comes with built-in budgeting tools, allowing users to track their spending and manage their finances effectively.
Target Market and Potential for Success
Robinhood’s Gold Card is targeted at a diverse audience, including:
- Millennials and Gen Z: These demographics are highly tech-savvy and prefer user-friendly platforms with transparent fees and convenient features.
- Existing Robinhood users: Robinhood’s existing user base provides a ready market for the Gold Card, offering a seamless integration with their existing financial services.
- Individuals seeking financial flexibility: The card’s features, such as early access to paychecks and built-in budgeting tools, appeal to individuals seeking greater control over their finances.
The success of Robinhood’s Gold Card hinges on its ability to effectively reach its target market and differentiate itself from existing offerings. By leveraging its established brand recognition, user-friendly platform, and unique features, Robinhood has a strong chance of capturing a significant share of the credit card market.
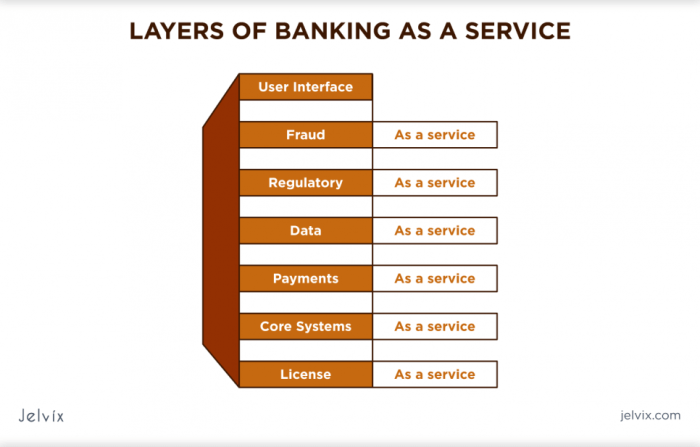
BaaS
The financial services industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving customer expectations, and a growing demand for innovative solutions. At the heart of this revolution lies Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS), a disruptive model that is reshaping the way financial institutions and businesses operate.
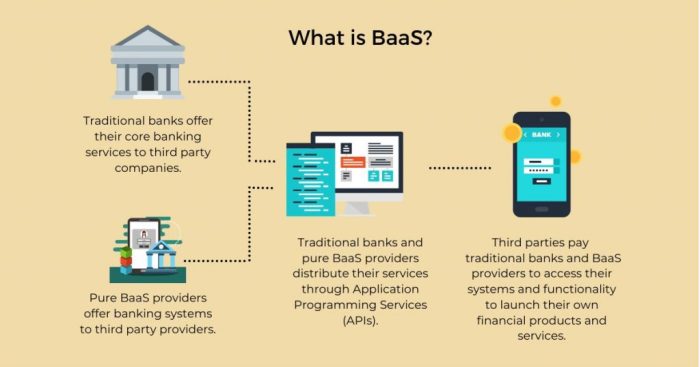
BaaS essentially enables non-financial companies to embed financial services directly into their existing platforms and applications. It empowers businesses to offer a range of financial products, such as payments, lending, and deposit accounts, without the need to build and maintain their own banking infrastructure.
Advantages of BaaS
The rise of BaaS has brought about significant advantages for both financial institutions and businesses.
- For Financial Institutions:
- Expanded Reach and Revenue Streams: BaaS allows financial institutions to extend their services to a broader customer base by partnering with non-financial businesses. This opens up new revenue streams and helps them compete more effectively in the evolving financial landscape.
- Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency: By leveraging BaaS platforms, financial institutions can reduce operational costs associated with building and maintaining their own infrastructure. They can also benefit from economies of scale and streamlined processes.
- Enhanced Innovation and Agility: BaaS platforms provide access to cutting-edge technology and APIs, enabling financial institutions to quickly develop and launch new products and services. This fosters innovation and agility in a rapidly changing market.
- For Businesses:
- Seamless Integration of Financial Services: BaaS allows businesses to seamlessly integrate financial services into their existing platforms, enhancing the customer experience and providing greater convenience. This can lead to increased customer engagement and loyalty.
- Improved Customer Acquisition and Retention: By offering financial services, businesses can attract new customers and retain existing ones. This can be particularly valuable for industries such as e-commerce, retail, and travel.
- Enhanced Revenue Generation: BaaS enables businesses to generate additional revenue streams by offering financial products and services. This can help them diversify their income and improve profitability.
Disadvantages of BaaS
While BaaS offers numerous advantages, it also presents some challenges that need to be considered.
- Security and Compliance Risks: BaaS platforms handle sensitive financial data, making security and compliance a paramount concern. Businesses and financial institutions must ensure that robust measures are in place to protect customer information and comply with relevant regulations.
- Data Privacy and Ownership: The use of BaaS platforms raises questions about data privacy and ownership. Businesses and financial institutions need to have clear agreements in place regarding data sharing, access, and control.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating BaaS platforms into existing systems can be complex and require significant technical expertise. Businesses and financial institutions need to carefully assess their technical capabilities and resources before adopting BaaS.
Examples of BaaS
BaaS is already being adopted by a wide range of companies and industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Fintech Companies: Fintech startups like Stripe, Plaid, and Wise are leading the charge in BaaS, offering a range of financial services to businesses through APIs and other integrations.
- E-commerce Platforms: E-commerce giants like Amazon and Shopify are incorporating BaaS into their platforms, enabling merchants to offer payment processing, lending, and other financial services to their customers.
- Retailers: Traditional retailers are also embracing BaaS to enhance their customer experience. For example, Walmart offers a financial services platform that allows customers to manage their finances, make payments, and access credit.
- Travel and Hospitality: Companies in the travel and hospitality industry are using BaaS to provide booking and payment solutions, as well as loyalty programs and other value-added services.
Growth and Challenges of the BaaS Market
The BaaS market is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years, driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of digital financial services, the rise of open banking, and the growing demand for personalized financial solutions.
- Market Size and Growth: The global BaaS market is projected to reach a value of over $100 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of over 20% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of BaaS by businesses across various industries.
- Key Trends: Some key trends shaping the BaaS market include the emergence of specialized BaaS platforms for specific industries, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into BaaS solutions, and the increasing focus on regulatory compliance and data security.
- Challenges: Despite its immense potential, the BaaS market faces several challenges, including the need for greater interoperability between different platforms, the complexity of integrating BaaS solutions into existing systems, and the potential for regulatory hurdles.
Tiny Startup Catches Stripe’s Eye: What’s the Buzz?
In the ever-evolving world of fintech, where innovation is paramount, a tiny startup has managed to capture the attention of a giant like Stripe. This is not just another news story; it’s a testament to the disruptive power of fresh ideas and the potential of niche solutions to revolutionize established markets.
The Startup and Its Business Model
The startup that has caught Stripe’s eye is called “Xentral”. This German-based company has carved a niche in the world of business-to-business (B2B) payment processing. Xentral’s business model is centered around offering a unified platform for managing and automating B2B payments. This platform goes beyond traditional payment processing; it integrates seamlessly with other essential business functions, such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer relationship management (CRM). This all-in-one approach allows businesses to streamline their operations and significantly reduce the complexities associated with B2B payments.
Stripe’s Interest in Xentral, Robinhoods new gold card baas challenges and the tiny startup that caught stripes eye
Stripe’s interest in Xentral stems from several key factors:
- Growing B2B Payment Market: The B2B payment market is experiencing explosive growth, fueled by the increasing adoption of digital technologies and the need for faster, more efficient payment solutions. Xentral’s platform addresses this demand head-on, offering a comprehensive and integrated solution for B2B payments.
- Focus on Automation: Xentral’s platform is built on automation, allowing businesses to eliminate manual processes and reduce errors. This resonates with Stripe’s mission of simplifying payments and empowering businesses to focus on their core operations.
- Integration with Other Systems: Xentral’s ability to integrate seamlessly with other business systems is a major advantage. This integration allows businesses to avoid the headaches of managing multiple platforms and data silos, making it a highly attractive solution for businesses looking to optimize their operations.
Xentral’s Competitive Landscape and Potential Impact
Xentral operates in a competitive landscape dominated by established players like PayPal, Square, and Adyen. These players have vast resources and extensive networks, but they primarily focus on consumer payments. Xentral’s focus on B2B payments, coupled with its innovative platform and integration capabilities, gives it a distinct advantage in this growing market.
Xentral vs. Established Players
| Feature | Xentral | PayPal | Square | Adyen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | B2B Payments | Consumer and B2B Payments | Consumer and B2B Payments | Consumer and B2B Payments |
| Platform Integration | High | Limited | Limited | Moderate |
| Automation Capabilities | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Target Market | Businesses | Individuals and Businesses | Individuals and Businesses | Businesses |
Xentral’s potential impact on the industry is significant. By providing a comprehensive and integrated solution for B2B payments, Xentral can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency for businesses of all sizes. This can lead to increased adoption of digital payments and a more robust B2B payment ecosystem.
The Rise of Fintech and the Future of Traditional Banking
The emergence of fintech companies like Robinhood has dramatically reshaped the financial landscape, challenging the traditional banking industry’s dominance. Fintech’s innovative solutions, coupled with their customer-centric approach, have disrupted traditional banking models, forcing incumbents to adapt and innovate to remain competitive. This shift has profound implications for the future of financial services, paving the way for a more inclusive, accessible, and technologically advanced banking ecosystem.
The Impact of Fintech on Traditional Banking
Fintech companies like Robinhood have disrupted traditional banking by offering innovative and user-friendly financial services. Their strengths lie in their ability to leverage technology to provide seamless experiences, lower costs, and cater to a wider range of customers. For instance, Robinhood’s commission-free stock trading platform has attracted millions of new investors, particularly millennials and Gen Z, who were previously underserved by traditional brokerage firms. This has forced established players to adapt their offerings and embrace technology to remain competitive.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Traditional Banks and Fintech Companies
Traditional banks possess a significant advantage in terms of established infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and customer trust built over decades. However, they often struggle to keep up with the rapid pace of technological innovation and cater to the evolving needs of digitally savvy customers. Fintech companies, on the other hand, are agile and innovative, leveraging technology to offer personalized and efficient services. However, they face challenges in terms of regulatory compliance, securing funding, and building trust with customers.
- Traditional Banks:
- Strengths: Established infrastructure, regulatory compliance, customer trust, strong brand reputation.
- Weaknesses: Slow to adapt to technological advancements, complex and bureaucratic processes, limited digital offerings, high fees.
- Fintech Companies:
- Strengths: Agile and innovative, user-friendly technology, lower costs, personalized services, focus on customer experience.
- Weaknesses: Regulatory compliance challenges, limited access to capital, lack of established brand reputation, potential security risks.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Financial Services
The future of financial services is being shaped by several key trends, including:
- Mobile Payments: The rise of mobile payments, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, has significantly increased the convenience and speed of transactions, making traditional banking methods less relevant.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming financial services by automating tasks, personalizing customer experiences, and improving fraud detection. For example, AI-powered chatbots are being used to provide instant customer support, while AI algorithms are analyzing data to identify potential fraud and credit risks.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology, the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies, offers secure and transparent transaction processing, which could revolutionize financial services. This technology has the potential to streamline cross-border payments, reduce settlement times, and enhance data security.
Timeline of Fintech’s Evolution and Impact on Banking
The evolution of fintech has been a gradual process, with each wave of innovation building upon the previous one. This timeline highlights key milestones and their impact on the banking landscape:
| Year | Milestone | Impact on Banking |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Emergence of online banking and financial websites | Increased convenience and accessibility of banking services. |
| 2000s | Growth of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms | Disrupted traditional lending models by connecting borrowers and lenders directly. |
| 2010s | Rise of mobile payments and financial apps | Shifted customer preferences towards digital and mobile-first experiences. |
| 2020s | Integration of AI, blockchain, and other emerging technologies | Enhanced security, efficiency, and personalization in financial services. |
The convergence of Robinhood’s Gold Card, BaaS, and the startup that has caught Stripe’s eye signals a new era in financial services. This era is characterized by innovation, disruption, and the relentless pursuit of better solutions for consumers and businesses. As these trends continue to evolve, it’s clear that the traditional banking landscape is facing a significant challenge, and the winners will be those who embrace the future of finance with agility and foresight.
Robinhood’s foray into the banking-as-a-service (BaaS) world with their new gold card has been met with some challenges, while a tiny startup called Threads is finally testing a recent filter for search results , which might make it easier to find what you’re looking for. Meanwhile, a tiny startup called Stripe is making waves in the payment processing space, attracting attention from giants like Robinhood.
This begs the question: can a small startup like Stripe really compete with established players in the fintech arena?
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News