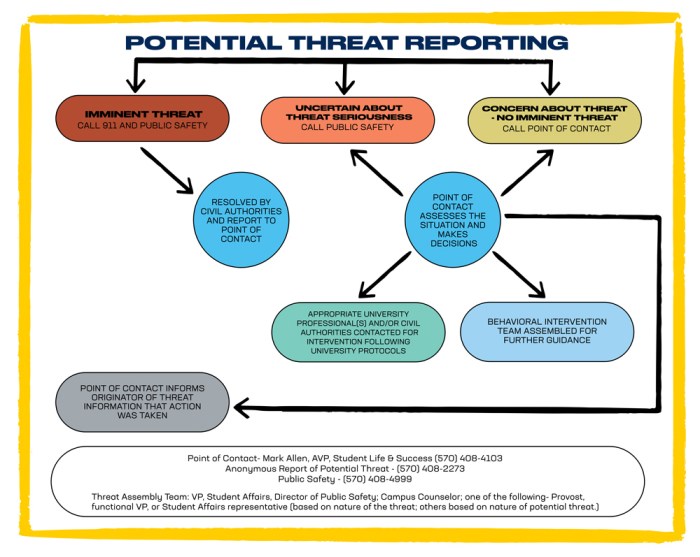
Security Company Behavioral Security: A New Era of Protection – Gone are the days of relying solely on fences, cameras, and guards. The security landscape is evolving, and with it, the need for a more nuanced approach to safeguarding people and assets. Enter behavioral security, a revolutionary concept that leverages the power of data analytics, machine learning, and human psychology to create a more proactive and intelligent security system.
Behavioral security goes beyond the traditional focus on physical barriers and access control. It recognizes that human behavior is a critical factor in security, and that understanding and predicting human actions can be a powerful tool for preventing threats and mitigating risks. By analyzing patterns in behavior, security companies can identify potential threats before they escalate, allowing them to intervene proactively and prevent incidents from occurring.
Applications of Behavioral Security in Security Companies: Security Company Behavioral Security
Security companies can leverage behavioral security principles to enhance their services by understanding and analyzing human behavior in various security contexts. This approach helps identify potential threats, mitigate risks, and improve overall security effectiveness.
Risk Assessment
Behavioral security can be integrated into risk assessments by analyzing the behavior of individuals and groups to identify potential vulnerabilities. This approach considers factors such as:
- Past behavior: Analyzing historical data on individuals or groups can reveal patterns that indicate potential risks. For example, a security company might analyze past incidents of theft or vandalism to identify individuals or groups with a history of such behavior.
- Social dynamics: Understanding the social dynamics within a group can provide insights into potential risks. For example, a security company might analyze the relationships between employees to identify potential conflicts or vulnerabilities.
- Environmental factors: Analyzing the environment in which individuals operate can provide insights into potential risks. For example, a security company might analyze the physical layout of a facility to identify potential security weaknesses.
Threat Detection
Behavioral security can be used to detect threats by analyzing the behavior of individuals and groups in real-time. This approach can identify suspicious activity, such as:
- Unusual behavior: Observing individuals who deviate from typical patterns of behavior can indicate potential threats. For example, a security company might use video surveillance to detect individuals who are acting suspiciously, such as lingering near restricted areas or attempting to bypass security measures.
- Social engineering attempts: Detecting attempts to manipulate individuals or groups to gain access to sensitive information or systems. For example, a security company might train employees to recognize and report social engineering attempts, such as phishing emails or phone calls.
- Cybersecurity threats: Analyzing user behavior on computer systems to identify potential threats. For example, a security company might use software to detect unusual activity, such as unauthorized login attempts or data exfiltration attempts.
Incident Response
Behavioral security can be used to improve incident response by understanding the behavior of individuals involved in security incidents. This approach can help to:
- Identify perpetrators: Analyzing the behavior of individuals involved in an incident can help to identify the perpetrators. For example, a security company might analyze security camera footage to identify individuals who were present at the scene of a crime.
- Determine motives: Understanding the motives of perpetrators can help to prevent future incidents. For example, a security company might analyze the behavior of individuals involved in a data breach to understand why they committed the crime.
- Develop effective response strategies: Understanding the behavior of individuals involved in an incident can help to develop effective response strategies. For example, a security company might analyze the behavior of individuals involved in a hostage situation to determine the best course of action.
Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a large corporation experiencing a series of internal data breaches. The security company investigating the incidents utilizes behavioral security principles to analyze the behavior of employees. They discover that a disgruntled employee with access to sensitive data has been exhibiting suspicious behavior, such as working late hours, accessing restricted files outside of work hours, and engaging in online activities related to data theft. This behavioral analysis provides critical evidence, leading to the identification and apprehension of the perpetrator, preventing further data breaches.
Key Components of Behavioral Security
Behavioral security relies on a combination of advanced technologies and strategic approaches to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential security threats based on human behavior.
Data Analytics for Behavioral Pattern Identification
Data analytics plays a crucial role in identifying and analyzing behavioral patterns that might indicate security risks. By collecting and analyzing data from various sources, including security cameras, access control systems, and network logs, security professionals can identify anomalies and deviations from typical behavior.
- Identifying Unusual Activity: Data analytics helps in identifying unusual activity patterns, such as frequent access attempts outside regular work hours, unusual file downloads, or unusual network traffic. These anomalies can be early indicators of potential threats like data breaches or insider attacks.
- Analyzing User Behavior: Security teams can analyze user behavior patterns to identify potential risks. For example, a sudden change in login frequency or an increase in the number of failed login attempts could indicate a compromised account or an attempt to gain unauthorized access.
- Correlating Data: Data analytics enables the correlation of data from different sources, providing a comprehensive view of potential threats. For instance, correlating access logs with camera footage can help identify individuals who accessed restricted areas or interacted with sensitive equipment without authorization.
Integration of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly being integrated into behavioral security systems to automate threat detection and response.
- Automated Threat Detection: ML algorithms can be trained on historical data to identify patterns indicative of malicious activity. Once trained, these algorithms can automatically detect anomalies and alert security teams in real time.
- Predictive Analytics: AI-powered predictive analytics can analyze data to anticipate future threats. By identifying trends and predicting potential vulnerabilities, security teams can proactively mitigate risks before they materialize.
- Adaptive Security: AI can dynamically adapt security measures based on evolving threat landscapes and user behavior. This enables organizations to maintain a proactive and responsive security posture.
Best Practices for Data Collection and Interpretation
Collecting and interpreting behavioral data requires a delicate balance between security and privacy.
- Transparency and Consent: Organizations should be transparent about their data collection practices and obtain explicit consent from individuals whose data is being collected. This fosters trust and ensures ethical data handling.
- Data Minimization: Only collect and analyze data that is relevant and necessary for security purposes. Avoid collecting excessive or unnecessary personal information.
- Data Anonymization: When possible, anonymize or aggregate data to protect individual privacy. This involves removing personally identifiable information while retaining the essential insights for security analysis.
- Data Retention Policies: Establish clear data retention policies to ensure that data is stored only for as long as necessary and then securely deleted.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct regular audits and reviews of data collection and analysis practices to ensure compliance with privacy regulations and ethical standards.
Challenges and Opportunities in Behavioral Security
While behavioral security offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed for successful implementation. This section will explore these challenges and highlight opportunities for maximizing the effectiveness of behavioral security.
Potential Challenges
Implementing behavioral security effectively requires addressing potential challenges that can arise from various factors, including data bias, ethical concerns, and resistance to change.
- Data Bias: One major challenge is the potential for bias in the data used to train behavioral security systems. If the training data reflects existing biases, the system may perpetuate these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For instance, a system trained on data from a predominantly male workforce might misinterpret the behavior of women in the workplace, potentially leading to false alarms or unfair security measures.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of behavioral data raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding privacy and the potential for misuse. Individuals may feel uncomfortable with the collection and analysis of their behavioral data, especially if they are unaware of how this data is being used. It’s crucial to ensure transparency and obtain informed consent from individuals before collecting and analyzing their behavioral data.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing behavioral security can encounter resistance from employees, who may be skeptical of the technology or concerned about its impact on their privacy and autonomy. It’s important to address these concerns proactively through clear communication, education, and training programs to ensure buy-in and acceptance of behavioral security measures.
Potential Benefits
Despite the challenges, behavioral security offers significant benefits that can enhance security outcomes, improve customer experiences, and reduce costs.
- Improved Security Outcomes: By identifying potential threats based on behavioral patterns, behavioral security can significantly improve security outcomes. For example, by detecting unusual activity or suspicious behavior, security personnel can intervene proactively to prevent incidents before they escalate.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Behavioral security can contribute to a more positive customer experience by personalizing interactions and streamlining security processes. For example, by identifying frequent customers or loyal patrons, security personnel can provide more personalized attention and expedite security checks.
- Reduced Costs: By preventing security breaches and incidents, behavioral security can help organizations reduce costs associated with security incidents, such as damage to property, lost revenue, and legal expenses.
Strategies for Addressing Challenges and Maximizing Benefits
To address challenges and maximize the benefits of behavioral security, organizations can implement strategies such as:
- Data Governance and Bias Mitigation: Organizations should establish robust data governance practices to ensure data quality, accuracy, and fairness. This includes implementing mechanisms to detect and mitigate bias in training data, as well as ongoing monitoring of system performance to identify and address potential bias issues.
- Transparency and Ethical Considerations: Organizations must be transparent about their use of behavioral data and ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations. This includes obtaining informed consent from individuals, providing clear information about data collection and usage, and establishing mechanisms for data access and control.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Effective communication is essential to address concerns and gain acceptance for behavioral security measures. Organizations should engage with employees, customers, and other stakeholders to address their concerns, explain the benefits of behavioral security, and provide training and support to ensure successful implementation.
The Future of Behavioral Security
Behavioral security is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the increasing need to protect individuals and organizations from evolving threats. The future of behavioral security promises a more sophisticated and proactive approach to security, leveraging data analysis, predictive modeling, and real-time monitoring to identify and mitigate risks before they materialize.
Emerging Trends in Behavioral Security, Security company behavioral security
The integration of biometrics, sentiment analysis, and social media monitoring is transforming how security professionals understand and respond to potential threats. These technologies offer unprecedented insights into human behavior, allowing for more accurate risk assessments and targeted security interventions.
- Biometrics: The use of biometric technologies, such as facial recognition, iris scanning, and fingerprint analysis, is becoming increasingly prevalent in security applications. Biometric authentication systems offer a high level of accuracy and security, making them ideal for access control, identity verification, and fraud prevention.
- Sentiment Analysis: Sentiment analysis, also known as opinion mining, involves using natural language processing (NLP) techniques to extract and analyze subjective information from text and speech data. By understanding the emotional tone and sentiment expressed in communication, security professionals can identify potential threats, such as disgruntled employees or individuals expressing extremist views.
- Social Media Monitoring: Social media platforms have become a rich source of information about individuals and their activities. Security professionals are increasingly leveraging social media monitoring tools to track online conversations, identify potential threats, and monitor the activities of individuals of interest.
Innovative Technologies and Approaches
The future of behavioral security is being shaped by innovative technologies and approaches that are enhancing our ability to detect, analyze, and respond to security threats.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being used to develop sophisticated behavioral analytics tools that can detect anomalies and predict potential threats. These systems can analyze large datasets of behavioral data, identifying patterns and trends that might not be apparent to human analysts.
- Predictive Modeling: Predictive modeling uses historical data and statistical techniques to forecast future events. In the context of behavioral security, predictive models can be used to identify individuals at risk of engaging in violent or criminal behavior.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Real-time monitoring systems use sensors, cameras, and other technologies to collect and analyze data in real-time. This allows security professionals to identify and respond to threats as they occur, preventing potential incidents from escalating.
Potential Future Applications of Behavioral Security
Behavioral security has the potential to revolutionize security practices across various industries.
| Industry | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Fraud detection, insider threat mitigation, customer risk assessment |
| Healthcare | Patient safety, medication error prevention, staff behavior monitoring |
| Education | Student safety, bullying prevention, early intervention for at-risk students |
| Transportation | Passenger safety, terrorism prevention, transportation security |
| Retail | Loss prevention, shoplifting detection, employee theft prevention |
In the future of security, behavioral security is poised to become a game-changer. By embracing data-driven insights and understanding human behavior, security companies can move beyond reactive measures and embrace a proactive, preventative approach to safety. This shift will lead to more secure environments, enhanced customer experiences, and ultimately, a safer world for all.
Security companies are increasingly focusing on behavioral security, analyzing user patterns to identify potential threats. This approach can be particularly effective in combating adware and malware, which often rely on deceptive tactics to gain access to devices. A new adblock browser beta launched for Android devices is a welcome addition to the fight, offering a layer of protection against intrusive ads and potentially harmful content.
By integrating behavioral security into their strategies, security companies can help create a safer digital environment for users.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News