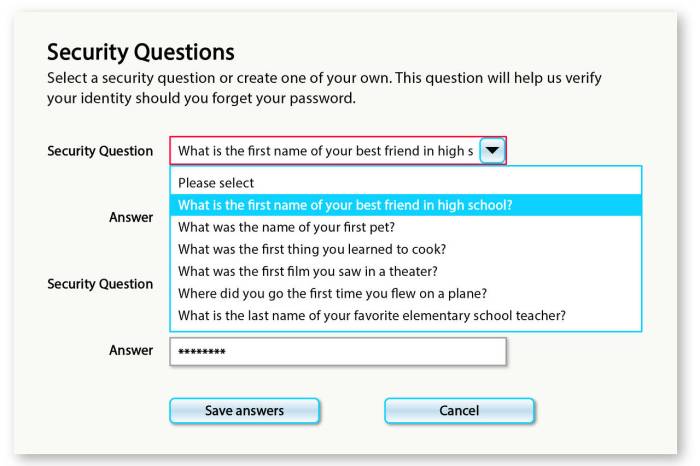
Security questions not secure? That’s a common misconception. While they’re intended to protect your accounts, the reality is, these questions can be surprisingly easy to crack. Think about it: your mother’s maiden name, your first pet’s name, or your favorite childhood book—all easily accessible through social media, public records, or even just a quick Google search. This makes your accounts vulnerable to social engineering and data breaches, leaving your sensitive information exposed.
This vulnerability stems from the fact that security questions are often based on easily accessible personal information. Attackers can exploit this by using social engineering techniques to gather information about individuals through various online sources. Once they have this information, they can easily bypass security questions and gain access to your accounts. And it’s not just about your personal accounts; data breaches can expose security questions across multiple services, putting all your online accounts at risk.
The Problem of Predictable Security Questions: Security Questions Not Secure
Security questions are meant to be a safety net, a last line of defense against unauthorized access to your accounts. But in many cases, these questions are anything but secure. They’re often based on easily accessible personal information, making them predictable and easily guessable by hackers.
The Problem of Easily Accessible Information
Security questions often rely on information that is readily available to others. This includes details like your mother’s maiden name, your first pet’s name, or your favorite childhood toy. These are often shared with friends, family, and even posted on social media platforms. Hackers can easily find this information through social media, public records, or even through simple online searches.
“If you can easily answer a security question, it’s likely a hacker can too.”
Examples of Common Security Questions and How They Can Be Easily Guessed
Here are some common security questions and how they can be easily guessed:
- What is your mother’s maiden name? This information is often found on public records, marriage certificates, or even social media profiles.
- What is the name of your first pet? Many people share stories and photos of their pets online, making this information readily available.
- What is your favorite book? This information can be found on social media, book reviews, or even online forums.
- What is your favorite color? This is a very common piece of information that is often shared on social media and other online platforms.
- What is your favorite food? This information can be easily found on social media, restaurant reviews, or even online food blogs.
Social Engineering and Security Questions
Security questions, often used as a second line of defense in online accounts, are not as secure as they seem. While they are intended to verify your identity, attackers can exploit them through social engineering techniques.
Social Engineering Techniques
Social engineering is the art of manipulating people into revealing confidential information. Attackers use various techniques to gain access to your personal details, including security questions. These techniques often involve exploiting human psychology and trust.
Gathering Information About Individuals
Attackers can gather information about individuals through various methods, including:
- Social Media: Attackers can browse your social media profiles to learn about your hobbies, interests, relationships, and significant dates, which can be used to answer security questions.
- Public Records: Information like your birthdate, address, and previous employment history can be found in public records, providing attackers with valuable clues to answer security questions.
- Online Sources: Attackers can use search engines and online databases to find information about you, including your online activities, affiliations, and even your social security number.
Examples of Social Engineering Attacks, Security questions not secure
- Phishing: Attackers may send emails or messages pretending to be legitimate companies or individuals, asking for personal information, including security questions.
- Pretexting: Attackers may create a believable story to trick you into revealing your information. They may pretend to be a bank representative or a friend in need, asking you to answer a security question to verify your identity.
- Shoulder Surfing: Attackers may watch you type in your password or answer security questions in public places, such as coffee shops or libraries.
Data Breaches and Security Question Compromise
Data breaches are a serious threat to online security, and they can have devastating consequences for individuals and businesses alike. One of the most concerning aspects of data breaches is the potential for security questions to be compromised, leading to the hijacking of user accounts.
When hackers gain access to a database, they often steal sensitive information, including usernames, passwords, and security question answers. This stolen data can then be used to compromise accounts on other websites or services where the user has chosen the same security questions.
Data Breaches and Security Question Compromise Examples
Data breaches involving the theft of security question answers have become increasingly common in recent years. Here are some notable examples:
- In 2017, the credit reporting agency Equifax suffered a massive data breach that exposed the personal information of over 147 million people. This breach included security question answers, which could have been used to compromise accounts on other websites.
- In 2018, the social media platform Facebook was hit by a data breach that exposed the personal information of over 50 million users. This breach also included security question answers, which could have been used to compromise accounts on other websites.
- In 2019, the hotel chain Marriott International suffered a data breach that exposed the personal information of over 500 million guests. This breach included security question answers, which could have been used to compromise accounts on other websites.
These are just a few examples of data breaches that have involved the theft of security question answers. As data breaches become more frequent and sophisticated, it is essential to take steps to protect your security questions and minimize the risk of account compromise.
Alternatives to Traditional Security Questions
Traditional security questions, despite their widespread use, have proven vulnerable to various security threats. The inherent predictability and susceptibility to social engineering make them an unreliable authentication method. Fortunately, several alternative approaches offer enhanced security and user experience.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a security practice that requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access to an account. This approach significantly enhances security by adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Knowledge-based factors: These are traditional security questions, passwords, or PINs that require users to recall specific information.
- Possession-based factors: These involve physical objects, such as a security token, smartphone, or hardware key, that users must possess to authenticate.
- Inherence-based factors: These factors rely on unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning, to verify identity.
By combining two or more authentication factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Even if an attacker compromises one factor, they will still be unable to gain access without the other.
“Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security measure that requires users to provide two or more forms of authentication before granting access to an account. This adds an extra layer of security by making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.”
Biometrics
Biometrics leverages unique biological characteristics to verify identity. These methods are generally more secure than traditional security questions because they are difficult to forge or steal.
- Fingerprint scanning: This method analyzes the unique patterns on a user’s fingerprints to authenticate identity. Fingerprint scanners are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and access control systems.
- Facial recognition: This technology uses facial features to identify individuals. It is becoming increasingly popular for unlocking smartphones, accessing secure areas, and verifying identity in various applications.
- Iris scanning: This method analyzes the unique patterns in the iris of a user’s eye for authentication. Iris scanning is considered highly secure due to the complexity of the patterns and the difficulty of replicating them.
Best Practices for Choosing Secure Security Questions
Security questions, while intended to protect your accounts, can be vulnerable if chosen poorly. This is why it’s crucial to understand how to select secure questions that are difficult to guess but easy for you to remember.
Choosing Secure Security Questions
Choosing strong security questions is paramount to protecting your accounts. Here’s a table outlining different question types, examples, their security strength, and recommendations for choosing secure questions:
| Question Type | Example Question | Security Strength | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Information | What is your mother’s maiden name? | Weak | Avoid easily accessible information like names, birthplaces, or school names. |
| Trivia | What is the capital of France? | Weak | These questions are easily found online and can be answered by anyone with access to a search engine. |
| Unique Memory | What was the name of your first pet? | Strong | Choose memories that are personal and unique to you. |
| Combination | What is the first three-letter word in the first book you read in high school? | Strong | Combine elements of your life, like a specific book title and a word within it. |
Strong security questions should be personal, unique, and difficult to guess.
- Avoid common information: Stay away from publicly available details like your birthdate, address, or phone number. These are easily accessible to potential attackers.
- Be creative: Think outside the box and use questions that are unique to your experiences. This makes it harder for attackers to guess your answers.
- Use a combination of elements: Combine different aspects of your life to create complex questions. For example, you could use a childhood memory, a favorite book, and a specific detail from that book.
- Don’t rely on common knowledge: Avoid questions that can be easily answered through a quick Google search. Focus on memories and details that are personal to you.
- Choose questions you can easily remember: While security is crucial, you should also be able to recall the answers to your questions. If you struggle to remember, your security question is not effective.
The Future of Security Questions
The era of traditional security questions, with their inherent vulnerabilities, is drawing to a close. As technology evolves, so too do the methods of authentication, paving the way for a more secure and user-friendly online experience. The future of security questions lies in the integration of innovative technologies, such as AI and machine learning, that can adapt to the changing landscape of online threats.
New Authentication Methods
The rise of new authentication methods is a direct response to the shortcomings of traditional security questions. These innovative approaches aim to enhance security while simplifying the user experience.
- Biometric Authentication: This method utilizes unique biological traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, to verify identity. It offers a high level of security, as these traits are difficult to forge or steal.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This method combines multiple authentication factors, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile app, to strengthen security. By requiring users to provide more than one piece of information, MFA makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
- Passwordless Authentication: This emerging technology eliminates the need for passwords altogether, relying instead on secure methods like security keys or biometrics. Passwordless authentication offers a streamlined and more secure approach, eliminating the risk of password compromise.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming the security landscape, playing a crucial role in enhancing authentication methods.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can analyze user behavior patterns and identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. This allows for real-time detection and prevention of unauthorized access attempts.
- Adaptive Security: Machine learning enables security systems to adapt to evolving threats by continuously learning from past experiences and identifying emerging patterns. This proactive approach helps stay ahead of cybercriminals and strengthen defenses against new attack vectors.
- Personalized Security: AI can personalize security measures based on individual user behavior and risk profiles. This allows for a more tailored and effective security approach, providing a balance between security and user convenience.
Predictions about the Future of Security Questions
As technology advances, the reliance on traditional security questions will continue to diminish. Here are some predictions about the future of security questions:
- Increased Adoption of Biometrics: Biometric authentication is expected to become increasingly prevalent, as it offers a high level of security and user convenience. This trend is already evident in smartphones and other devices, and it is likely to extend to other online services.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will play a more prominent role in authentication, enhancing security measures and personalizing user experiences. These technologies will enable more sophisticated fraud detection, adaptive security, and personalized security solutions.
- Shift towards Passwordless Authentication: Passwordless authentication is expected to gain significant traction, offering a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional passwords. As the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see a gradual shift away from passwords and towards passwordless authentication.
The future of security is moving away from traditional security questions and towards more secure authentication methods. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometrics, and advanced AI-powered security measures are all playing a crucial role in enhancing online security. While security questions may still have a place in some contexts, it’s essential to be aware of their limitations and to adopt stronger authentication methods to protect your online identity. By understanding the vulnerabilities of security questions and embracing more secure alternatives, we can all contribute to a safer digital world.
We all know those security questions are supposed to be tough, but let’s be real, most of us could probably answer them in our sleep. It’s like they’re designed to be easily guessed, which is why a recent story about a hostage sending an SOS message through the Pizza Hut app hostage sends sos message via pizza hut app is so wild.
It just goes to show that sometimes the most unexpected places can be the key to getting help, especially when security questions fail us.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News