Steam’s Response to the Attack: Steam Hit By Ddos Attacks Hackers Claim Responsibility
The recent DDoS attack on Steam, which caused widespread disruption to the platform’s services, prompted a swift and decisive response from Valve, the company behind Steam. Valve’s immediate actions aimed to mitigate the attack’s impact, restore service for its users, and bolster the platform’s security to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Measures Taken to Mitigate the Attack
Valve’s response to the DDoS attack was multifaceted, focusing on containing the attack, restoring service, and ensuring user safety. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps they took:
- Traffic Filtering and Routing Optimization: Valve implemented traffic filtering mechanisms to identify and block malicious traffic originating from the attacker’s network. They also optimized network routing to minimize the impact of the attack on legitimate users.
- Increased Server Capacity: To handle the surge in traffic and ensure smooth service delivery, Valve significantly increased server capacity. This move helped to absorb the attack’s impact and prevent system overload.
- Collaboration with Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Valve collaborated with ISPs to identify and block the attack’s source, effectively disrupting the attacker’s ability to send malicious traffic to Steam’s servers.
- Communication with Users: Valve kept its users informed about the attack’s progress and the steps being taken to resolve it. They communicated through official channels like the Steam website and social media platforms, ensuring transparency and building trust.
Measures Implemented to Prevent Future Attacks
To prevent similar attacks in the future, Valve implemented several proactive measures:
- Enhanced Security Infrastructure: Valve invested in strengthening its security infrastructure, including upgrading firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security tools to better detect and prevent DDoS attacks.
- Advanced Threat Intelligence: Valve implemented advanced threat intelligence systems to proactively identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. These systems analyze data from various sources to detect and respond to emerging attack patterns.
- Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Valve continuously monitors its systems for vulnerabilities and proactively updates its security measures to stay ahead of evolving attack techniques. This proactive approach ensures the platform’s resilience against future threats.
- Partnerships with Security Experts: Valve collaborates with leading security experts and organizations to gain insights into the latest threats and best practices for protecting online platforms. This collaboration ensures that Valve’s security measures are informed by the latest industry knowledge.
Effectiveness of Steam’s Response in Protecting Users
Steam’s response to the DDoS attack was generally effective in protecting its users. The swift and decisive action taken by Valve minimized the attack’s impact on user experience, and the measures implemented to prevent future attacks have significantly enhanced the platform’s security posture.
Comparison to Similar Attacks on Other Gaming Platforms
Steam’s response to the DDoS attack is comparable to how other major gaming platforms, like PlayStation Network and Xbox Live, have responded to similar attacks. These platforms have also implemented robust security measures, including traffic filtering, server capacity enhancements, and threat intelligence systems, to mitigate and prevent DDoS attacks. However, the specific strategies employed by each platform might vary depending on their infrastructure, target audience, and attack vectors.
Security Implications and Future Concerns
The recent DDoS attack on Steam, while disruptive, serves as a stark reminder of the growing vulnerabilities in the online gaming industry. The attack highlights the need for robust security measures to protect gaming platforms and players from malicious actors. This incident has broader security implications for the entire gaming industry, underscoring the escalating threat of DDoS attacks and the need for proactive security strategies.
The Growing Threat of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks, which overwhelm servers with traffic, are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent, posing a significant threat to online gaming platforms. The attack on Steam demonstrates the potential for these attacks to disrupt gaming services, impacting players’ ability to connect and play. The attackers can leverage botnets, networks of compromised computers, to generate massive amounts of traffic, making it difficult for gaming platforms to handle legitimate requests.
Potential Vulnerabilities Exploited by Attackers
Attackers often exploit vulnerabilities in gaming platforms to launch DDoS attacks. These vulnerabilities could include:
- Weak network security: Lack of proper firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation can make it easier for attackers to infiltrate and disrupt services.
- Unpatched software: Outdated software with known security flaws can be exploited by attackers to gain access to systems.
- Poorly configured servers: Misconfigured servers with default settings or weak security protocols can be easily targeted.
- Lack of DDoS mitigation: Gaming platforms without proper DDoS mitigation strategies are more vulnerable to attacks.
Security Measures to Prevent Future Attacks
To mitigate the risk of future DDoS attacks, gaming platforms should implement a comprehensive security strategy that includes:
- Strengthening network security: Implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation to prevent unauthorized access and traffic.
- Regular software updates: Regularly patching software to address known vulnerabilities and security flaws.
- Secure server configuration: Properly configuring servers with strong passwords, encryption, and security protocols to minimize vulnerabilities.
- DDoS mitigation strategies: Implementing DDoS mitigation solutions to absorb and filter malicious traffic.
- Threat intelligence and monitoring: Staying informed about emerging threats and monitoring network activity for suspicious patterns.
- Incident response plan: Developing a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively address and contain attacks.
User Impact and Reactions
The DDoS attack on Steam caused significant disruption and frustration for millions of users worldwide. The attack impacted users’ ability to access and play games, leading to widespread complaints and concerns about the security of the platform. This event also raised questions about the long-term impact on user trust in Steam.
Impact on Gaming Experiences, Steam hit by ddos attacks hackers claim responsibility
The attack primarily affected users’ ability to access and play games. During the attack, many users experienced connection issues, lag, and disconnections, rendering their gaming experiences unplayable. Some users reported being unable to log into their accounts, while others were unable to download or update games. This widespread disruption caused significant frustration among users, who were unable to enjoy their favorite games during the peak hours.
User Complaints and Concerns
The attack sparked a wave of complaints and concerns from users. Many users expressed frustration over the lack of communication from Valve during the attack. Some users questioned the effectiveness of Steam’s security measures, while others expressed concerns about the potential for future attacks.
“It’s frustrating to be locked out of my games during peak hours because of a DDoS attack. Valve needs to do a better job of protecting its users.” – A Steam user on Reddit.
“I’m worried about the security of my account after this attack. I hope Valve takes steps to improve security and prevent this from happening again.” – A Steam user on Twitter.
Long-Term Impact on User Trust
The attack could potentially have a long-term impact on user trust in Steam. While Valve responded quickly to mitigate the attack, the disruption and frustration caused by the event could lead some users to question the platform’s reliability. If similar attacks occur in the future, it could further erode user trust and potentially drive users to alternative gaming platforms.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks, short for Distributed Denial of Service attacks, are a type of cyberattack aimed at disrupting the normal functioning of a website, online service, or network by overwhelming it with a flood of traffic from multiple sources. These attacks are designed to make the target resource unavailable to legitimate users, causing significant disruptions and potential financial losses.
Common Methods and Tools
DDoS attacks employ various methods and tools to achieve their goal of overwhelming the target. The most common methods include:
- SYN Flood: This attack exploits the three-way handshake process used in TCP connections. The attacker sends a large number of SYN (synchronization) packets to the target server, which then allocates resources to handle the incoming connections. However, the attacker never sends the ACK (acknowledgment) packet, leaving the server with a backlog of half-open connections, consuming resources and preventing legitimate users from connecting.
- UDP Flood: Similar to the SYN flood, this attack utilizes the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to overwhelm the target server with a large number of UDP packets. Unlike TCP, UDP is connectionless, meaning the server doesn’t have to allocate resources for each connection. This allows attackers to send a massive number of UDP packets, overloading the server’s processing power and causing it to crash.
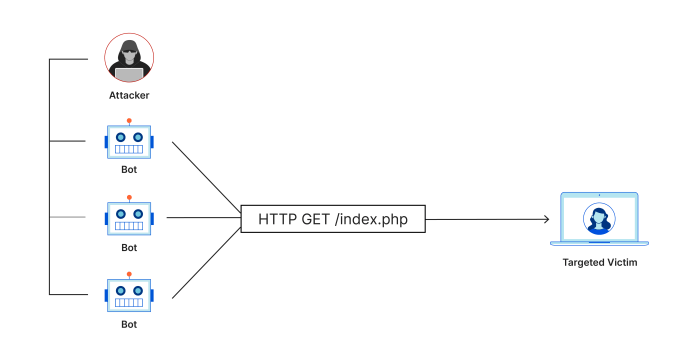
- HTTP Flood: This attack targets web servers by sending a large number of HTTP requests, overwhelming the server’s capacity to handle legitimate requests. Attackers can use various techniques, such as sending malformed requests, spamming the server with GET requests, or exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to amplify the attack.
Attackers use various tools to execute DDoS attacks, including:
- Botnets: These networks of compromised computers, often infected with malware, are controlled by attackers and used to launch DDoS attacks. The botnet’s large size and distributed nature make it difficult to trace and stop the attack.
- DDoS-as-a-Service (DDoSaaS): This service allows individuals or organizations to rent botnets or other resources for launching DDoS attacks. DDoSaaS platforms make it easier for anyone to launch an attack without having the technical expertise or infrastructure.
- Stressers: These are online services that allow users to send traffic to a target website or server for a fee. Stressers are often used by individuals or small groups to launch small-scale DDoS attacks.
Types of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks can be categorized into different types based on the methods used and the impact they have on the target:
- Volume-based attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm the target server with a massive volume of traffic, exhausting its bandwidth and resources.
- Protocol-based attacks: These attacks target specific network protocols, such as TCP or UDP, to disrupt communication and service availability.
- Application-layer attacks: These attacks target specific web applications, such as web servers, databases, or APIs, by sending malicious requests or exploiting vulnerabilities in the application’s code.
Defense Mechanisms
Defending against DDoS attacks requires a multi-layered approach, involving a combination of technologies and strategies:
| Defense Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) | These systems monitor network traffic for malicious patterns and block suspicious connections, preventing DDoS attacks from reaching the target server. |
| Firewalls | Firewalls act as a barrier between the target network and the outside world, filtering traffic based on predefined rules. They can help mitigate DDoS attacks by blocking malicious traffic at the network edge. |
| Rate Limiting | This technique limits the number of requests that can be made from a single IP address or source within a specific time frame. This helps prevent attackers from overwhelming the server with a large number of requests. |
| Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) | CDNs distribute content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing the load on the origin server and providing a more resilient infrastructure. |
| Cloud-based DDoS Protection | Cloud providers offer DDoS protection services that use a variety of techniques to mitigate attacks, such as traffic scrubbing, rate limiting, and traffic redirection. |
| Blackholing | This technique involves dropping all traffic from a specific IP address or network range, preventing the attack from reaching the target server. |
| Traffic Shaping | This technique prioritizes legitimate traffic over malicious traffic, ensuring that critical services remain available during an attack. |
Steam hit by ddos attacks hackers claim responsibility – The DDoS attack on Steam serves as a wake-up call for the gaming industry. The growing sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates a proactive approach to security. Gaming platforms must invest in robust security measures to protect their users and their data. As the gaming world becomes increasingly reliant on online platforms, the need for strong security measures is paramount. This attack underscores the importance of ongoing vigilance and innovation in the fight against cybercrime.
Looks like the digital world is under attack, with Steam getting hit by DDoS attacks and hackers claiming responsibility. It’s almost like a game of digital whack-a-mole, where one problem pops up while another one gets fixed. Just last week, Apple confirmed an issue where iTunes music libraries were being deleted, but they’ve promised safeguards to prevent it from happening again – you can read more about that here.
Hopefully, Steam can get things back to normal soon, but in the meantime, it’s a good reminder that our digital lives are more vulnerable than we think.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News