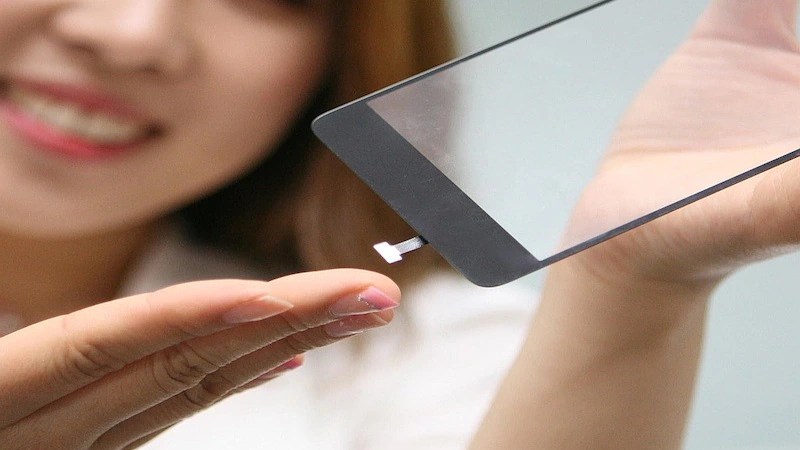
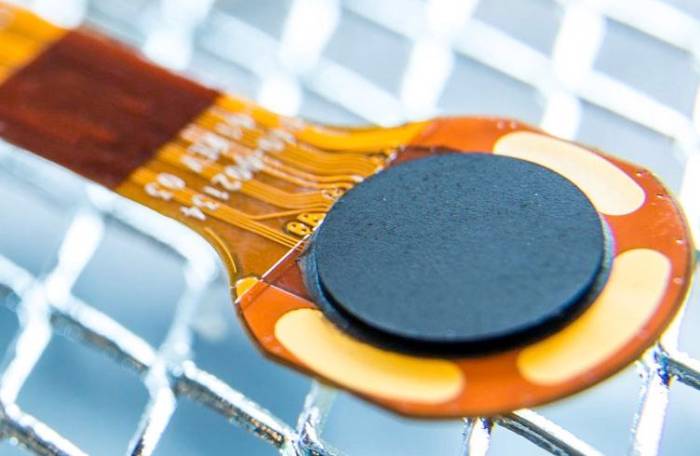
Introduction to Synaptics in-Display Fingerprint Sensors
In the realm of smartphone security, fingerprint sensors have become ubiquitous, offering a convenient and reliable way to authenticate users. While traditional fingerprint sensors were mounted on the phone’s back or side, a new era of security emerged with the introduction of in-display fingerprint sensors. These sensors, seamlessly integrated beneath the smartphone’s display, revolutionized the user experience by eliminating the need for separate hardware buttons. Synaptics, a leading innovator in human interface solutions, has played a pivotal role in shaping this technological advancement.
The Evolution of In-Display Fingerprint Sensors
The journey of in-display fingerprint sensors began with the development of optical fingerprint sensors. These sensors utilize light to capture a user’s fingerprint image. While they were the first to be integrated into displays, they faced challenges in terms of accuracy and speed, particularly when dealing with wet or dirty fingers.
In response to these limitations, Synaptics introduced its Clear ID™ technology, which employed capacitive sensing. This technology relies on the electrical properties of a user’s fingerprint to create a unique digital signature. Clear ID™ sensors are renowned for their high accuracy, responsiveness, and ability to function reliably even in challenging environments.
- Optical Fingerprint Sensors: These sensors utilize light to capture a user’s fingerprint image. While they were the first to be integrated into displays, they faced challenges in terms of accuracy and speed, particularly when dealing with wet or dirty fingers.
- Capacitive Fingerprint Sensors: These sensors, including Synaptics’ Clear ID™ technology, rely on the electrical properties of a user’s fingerprint to create a unique digital signature. Clear ID™ sensors are renowned for their high accuracy, responsiveness, and ability to function reliably even in challenging environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synaptics Sensors: Synaptics In Display Fingerprint Sensor
Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors have become a popular choice for smartphone manufacturers, offering a convenient and secure way to unlock devices. However, like any technology, they have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. This section will delve into the key strengths and weaknesses of Synaptics sensors, comparing their performance to other fingerprint sensor technologies.
Advantages of Synaptics Sensors
Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors offer several advantages over traditional fingerprint sensors, making them an attractive option for smartphone manufacturers and users. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Seamless Integration: Synaptics sensors are embedded directly beneath the display, offering a seamless and aesthetically pleasing design. Unlike traditional fingerprint sensors, they don’t require a separate physical button or a dedicated area on the device, allowing for a more streamlined and immersive user experience.
- Enhanced Security: Synaptics sensors utilize advanced algorithms and technologies to ensure secure authentication. They are resistant to spoofing attempts and offer a high level of protection against unauthorized access.
- Faster Recognition: Synaptics sensors are known for their fast and accurate fingerprint recognition capabilities. They can quickly identify and verify fingerprints, enabling a smooth and efficient unlocking process.
- Durability: Synaptics sensors are designed to withstand the rigors of everyday use. They are protected beneath the display glass, making them less susceptible to scratches, dust, and other environmental factors.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other in-display fingerprint sensor technologies, Synaptics sensors are generally more cost-effective, making them a viable option for a wider range of smartphone models.
Disadvantages of Synaptics Sensors
While Synaptics sensors offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
- Performance Variability: The performance of Synaptics sensors can vary depending on factors such as the type of display, the thickness of the glass, and the user’s fingerprint. Some users may experience occasional issues with recognition accuracy or speed.
- Sensitivity to Moisture: Synaptics sensors can be sensitive to moisture, and wet fingers may not be recognized as easily. This can be a drawback in certain environments or weather conditions.
- Limited Functionality: Unlike some other fingerprint sensor technologies, Synaptics sensors may not be able to support features such as gesture recognition or heart rate monitoring.
- Potential for False Positives: Although Synaptics sensors are designed to be secure, there is always a possibility of false positives, where an unauthorized individual might be able to gain access to the device. However, this risk is generally considered low.
Comparison with Other Fingerprint Sensor Technologies
Synaptics sensors compete with other fingerprint sensor technologies, such as ultrasonic sensors and capacitive sensors.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Ultrasonic sensors are known for their high accuracy and ability to work through thicker glass. However, they are generally more expensive than Synaptics sensors. For example, the Qualcomm 3D Sonic Sensor found in the Samsung Galaxy S22 series is a popular ultrasonic sensor.
- Capacitive Sensors: Capacitive sensors are typically found in traditional fingerprint sensors on the back or side of the device. They are generally less expensive than ultrasonic sensors, but they may not be as accurate or as secure as Synaptics sensors.
Applications of Synaptics in-Display Fingerprint Sensors
Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors are a game-changer in the world of mobile technology. They offer a seamless and secure way to unlock your device, making them a popular choice for manufacturers. Let’s delve into the diverse applications of these sensors, exploring their use across various devices and scenarios.
Smartphones
The primary application of Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors is in smartphones. They are integrated directly into the display, eliminating the need for a separate sensor on the front or back of the device. This integration results in a more aesthetically pleasing design, allowing for a larger screen-to-body ratio.
- Unlocking the Device: The most common application is unlocking the smartphone. Users can simply place their finger on the display to unlock the device, providing a secure and convenient way to access their data.
- Secure Payment Authentication: These sensors can be used for secure payment authentication. Many banking apps and online payment platforms support fingerprint authentication, adding an extra layer of security to financial transactions.
- App Security: Some apps can be configured to require fingerprint authentication for access, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Laptops
Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors are also finding their way into laptops, enhancing security and user experience.
- Secure Login: These sensors enable secure login to the laptop. Users can simply place their finger on the touchpad to log in, eliminating the need for passwords or PINs.
- Enhanced Security: The integration of fingerprint sensors in laptops adds an extra layer of security, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Tablets
Similar to smartphones, Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors are also being integrated into tablets.
- Secure Access: These sensors allow users to unlock their tablets quickly and securely, using their fingerprints.
- Improved User Experience: The seamless integration of the sensor into the display enhances the overall user experience, providing a more intuitive and user-friendly interface.
Smart Home Appliances
The applications of Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors extend beyond smartphones, laptops, and tablets. They are increasingly being integrated into smart home appliances, enhancing security and user convenience.
- Smart Locks: These sensors can be used in smart locks to grant access to authorized individuals. This eliminates the need for physical keys, providing a more secure and convenient way to manage access to your home.
- Smart Refrigerators: Some smart refrigerators are equipped with Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors for secure access to the refrigerator’s settings and features.
Real-World Examples, Synaptics in display fingerprint sensor
- Samsung Galaxy S10: The Samsung Galaxy S10 was one of the first smartphones to feature an in-display fingerprint sensor from Synaptics. The sensor was integrated into the display, allowing users to unlock their device with a simple touch.
- Apple MacBook Pro: Apple has also integrated Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors into their MacBook Pro laptops, providing a secure and convenient way for users to log in to their devices.
- Lenovo Yoga 9i: Lenovo’s Yoga 9i laptop features an in-display fingerprint sensor that is seamlessly integrated into the touchpad, enhancing the overall user experience.
Future Trends and Developments
The in-display fingerprint sensor technology is continuously evolving, driven by the pursuit of enhanced security, user experience, and integration with emerging technologies. This section delves into the potential future directions of this technology, analyzing the impact of emerging technologies on Synaptics sensors and exploring advancements in security and usability.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The convergence of in-display fingerprint sensors with emerging technologies presents exciting possibilities. One notable trend is the integration of these sensors with artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms can enhance the accuracy and speed of fingerprint recognition, enabling more robust security measures and personalized user experiences. For instance, AI can analyze fingerprint patterns to detect potential spoofing attempts, providing an extra layer of security.
Advancements in Security and Usability
The future of in-display fingerprint sensors lies in enhancing both security and usability. Advancements in sensor technology are leading to increased accuracy and faster recognition times. For example, the use of 3D fingerprint scanning can significantly improve security by capturing the unique three-dimensional structure of a fingerprint. Furthermore, advancements in display technology are enabling the integration of larger, more responsive fingerprint sensors, enhancing user experience.
Enhanced Security Features
In-display fingerprint sensors are expected to play a crucial role in securing sensitive data and transactions. Future developments include the integration of advanced security features such as:
- Biometric Fusion: Combining fingerprint recognition with other biometric modalities, such as facial recognition or iris scanning, can create a multi-layered security system. This approach significantly reduces the risk of spoofing and enhances security.
- Secure Enclave: Integrating fingerprint sensors with secure enclaves, dedicated hardware components that protect sensitive data, can further strengthen security. This approach ensures that fingerprint data is processed and stored securely, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Dynamic Fingerprint Authentication: This technique involves analyzing the unique characteristics of a fingerprint’s movement and pressure during authentication. By incorporating dynamic fingerprint authentication, the security of in-display sensors can be significantly enhanced.
Improved User Experience
Future in-display fingerprint sensors are expected to offer a seamless and intuitive user experience. Advancements in this area include:
- Larger Sensing Area: Increasing the sensing area of in-display fingerprint sensors will improve the accuracy and speed of recognition, particularly for users with larger fingers.
- Improved Display Technology: Advancements in display technology, such as the use of flexible OLED displays, can enable the integration of more sophisticated and responsive fingerprint sensors.
- Haptic Feedback: Incorporating haptic feedback into in-display fingerprint sensors can provide users with real-time confirmation of successful authentication, enhancing the user experience.
Comparative Analysis of Synaptics Sensors
Synaptics offers a range of in-display fingerprint sensor models, each with unique features and specifications. Understanding the differences between these models is crucial for manufacturers and consumers to make informed decisions. This section provides a comparative analysis of Synaptics sensors, focusing on their performance, speed, accuracy, and security aspects.
Performance Comparison
Performance is a key factor in evaluating in-display fingerprint sensors. Synaptics sensors are known for their fast and accurate fingerprint recognition capabilities. However, there are variations in performance between different models. For example, the Synaptics Clear ID FS9500 series boasts a high recognition rate and low false rejection rate. This translates to a smoother and more reliable user experience.
Speed and Accuracy
Speed and accuracy are interconnected aspects of fingerprint sensor performance. Faster sensors typically achieve higher accuracy. Synaptics sensors utilize advanced algorithms and hardware to achieve high recognition speed and accuracy. The Synaptics Clear ID FS9800 series, for instance, is designed to provide lightning-fast recognition speeds while maintaining high accuracy.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in fingerprint sensor technology. Synaptics sensors incorporate robust security features to protect user data. These features include advanced anti-spoofing technology, which prevents unauthorized access using fake fingerprints. The Synaptics Clear ID FS9600 series, for example, incorporates multi-layer security features, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to bypass the system.
Key Features and Specifications
The following table summarizes the key features and specifications of various Synaptics sensors:
| Model | Features | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Synaptics Clear ID FS9500 | High recognition rate, low false rejection rate, advanced anti-spoofing technology | Recognition speed: 0.5 seconds, Accuracy: 99.9%, Security level: High |
| Synaptics Clear ID FS9800 | Lightning-fast recognition speed, high accuracy, multi-layer security features | Recognition speed: 0.2 seconds, Accuracy: 99.99%, Security level: Very High |
| Synaptics Clear ID FS9600 | Advanced anti-spoofing technology, multi-layer security features, low power consumption | Recognition speed: 0.3 seconds, Accuracy: 99.9%, Security level: High |
Technical Specifications and Design Considerations
Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors are intricate devices that require careful consideration of technical specifications and design factors for optimal performance and integration into devices. This section delves into the technical specifications of Synaptics sensors, the design considerations for seamless integration, and the influence of display technology on sensor performance.
Technical Specifications
Synaptics sensors are designed with various technical specifications that define their functionality and performance. These specifications are crucial for understanding the sensor’s capabilities and limitations.
- Resolution: Synaptics sensors offer high resolution, typically ranging from 500 to 1000 DPI (dots per inch), enabling accurate fingerprint detection and matching. Higher resolution translates to more detailed fingerprint data, improving accuracy and security.
- Sensor Size: The sensor size varies depending on the specific model, typically ranging from 4mm x 4mm to 10mm x 10mm. Smaller sensors are more compact and suitable for smaller devices, while larger sensors provide a larger area for fingerprint placement, potentially improving accuracy.
- Sensitivity: Synaptics sensors are highly sensitive to subtle fingerprint details, allowing for accurate fingerprint recognition even with dry or wet fingers. This sensitivity is crucial for reliable performance in various environmental conditions.
- Response Time: The response time, or the time it takes for the sensor to read and process a fingerprint, is a crucial factor for user experience. Synaptics sensors typically have response times under 0.5 seconds, ensuring a fast and seamless authentication process.
- False Acceptance Rate (FAR): FAR represents the probability of the sensor incorrectly accepting an unauthorized fingerprint. Synaptics sensors have a low FAR, typically below 0.01%, ensuring high security and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- False Rejection Rate (FRR): FRR represents the probability of the sensor incorrectly rejecting a legitimate fingerprint. Synaptics sensors have a low FRR, typically below 1%, ensuring a smooth user experience and minimizing the inconvenience of repeated authentication attempts.
- Power Consumption: Synaptics sensors are designed to be energy-efficient, consuming minimal power during operation. This minimizes battery drain and extends device runtime.
Design Considerations for Integration
Integrating Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors into devices requires careful design considerations to ensure seamless functionality and optimal performance.
- Display Type: The type of display used in the device significantly impacts sensor performance. OLED displays offer superior light transmission compared to LCD displays, allowing for better fingerprint recognition and reduced signal interference.
- Display Thickness: The thickness of the display panel influences the sensor’s depth and integration. Thinner displays can pose challenges for sensor placement and signal transmission.
- Cover Glass: The cover glass protecting the display can affect the sensor’s sensitivity and signal transmission. Some cover glass materials can hinder fingerprint recognition or cause signal distortion.
- Sensor Placement: The sensor’s position within the display is crucial for user convenience and optimal performance. Ideally, the sensor should be located in a position that is easily accessible and allows for natural finger placement.
- Integration with System-on-a-Chip (SoC): The sensor needs to be seamlessly integrated with the device’s SoC for data processing and communication. This integration ensures efficient data transfer and secure authentication.
Impact of Display Technology
The display technology used in a device plays a crucial role in the performance of Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors. Different display technologies have varying levels of light transmission, signal interference, and optical properties, which can significantly impact sensor performance.
“OLED displays offer superior light transmission compared to LCD displays, allowing for better fingerprint recognition and reduced signal interference.”
- OLED Displays: OLED displays offer high light transmission, allowing for better fingerprint recognition and reduced signal interference. The absence of a backlight in OLED displays minimizes light scattering, enhancing sensor accuracy.
- LCD Displays: LCD displays typically have lower light transmission compared to OLED displays, potentially leading to reduced sensor accuracy and increased signal interference. The backlight in LCD displays can cause light scattering, affecting fingerprint recognition.
Security and Privacy Implications
In-display fingerprint sensors, while offering convenience, raise significant security and privacy concerns. The integration of fingerprint scanning technology directly into the display screen presents unique vulnerabilities that require careful consideration.
Data Breaches and Spoofing Attacks
Data breaches and spoofing attacks pose significant threats to in-display fingerprint sensors. Unauthorized access to the stored fingerprint data could compromise user security, enabling identity theft and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Spoofing attacks involve using fake fingerprints or other methods to bypass the sensor’s authentication process.
These attacks can exploit vulnerabilities in the sensor’s software or hardware, potentially enabling unauthorized access to devices.
Measures Taken by Synaptics to Ensure User Privacy
Synaptics employs various measures to mitigate security and privacy risks associated with in-display fingerprint sensors.
- Secure Enclave: Synaptics uses a secure enclave, a protected area within the device’s processor, to store and process fingerprint data. This isolation helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Encryption: Fingerprint data is encrypted both during storage and transmission, further enhancing security and protecting against unauthorized access.
- Anti-Spoofing Technology: Synaptics incorporates advanced anti-spoofing technology to detect and reject fake fingerprints, such as 3D printed replicas or silicone molds.
- Limited Data Collection: Synaptics collects only the necessary fingerprint data for authentication purposes, minimizing the amount of sensitive information stored on the device.
Synaptics in display fingerprint sensor – The integration of Synaptics in-display fingerprint sensors has undeniably transformed the landscape of device security, offering a convenient and secure method of authentication. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and secure fingerprint sensors, further blurring the lines between physical and digital security. The future of in-display fingerprint sensors is brimming with exciting possibilities, promising a seamless and secure user experience.
Synaptics, a leading provider of display fingerprint sensors, is facing some challenges. The recent Apple Watch shipping estimates hinting at supply constraints might be a sign of broader industry issues, impacting the availability of key components like those used in Synaptics’ sensors. This could potentially lead to delays and production bottlenecks for manufacturers incorporating their technology, creating a ripple effect throughout the tech ecosystem.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News