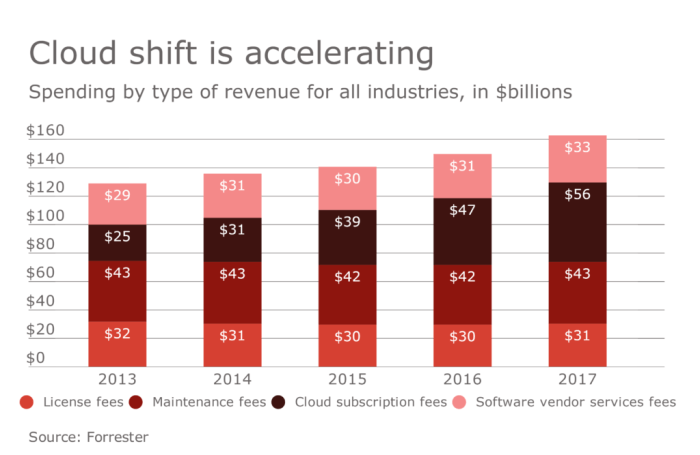
The market is forcing cloud vendors to relax data egress fees, and it’s a game-changer for businesses. Data gravity, the force that pulls data towards its source, is becoming increasingly powerful. This means businesses are looking for ways to keep their data close to where it’s used, regardless of where it’s stored. But traditional data egress fees, which charge for moving data out of a cloud provider’s infrastructure, can make this expensive and inconvenient. The market is responding, and cloud vendors are starting to offer more flexible and affordable options for data movement. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for data mobility and the desire for cost-effective solutions.
Cloud vendors are realizing that they need to offer more competitive pricing and flexible data management options to attract and retain customers. This has led to a number of strategies, including offering free or discounted egress, providing alternative data storage options, and developing new data mobility tools. These changes are benefiting businesses by giving them more control over their data and reducing their costs.
The Rise of Data Gravity
The world is drowning in data. As businesses generate more information than ever before, the sheer volume and complexity of this data are making it increasingly difficult to manage. This has led to a growing trend: businesses are moving away from centralized cloud storage and processing, opting instead to store and process data closer to its source. This shift is driven by the concept of data gravity, which describes the force that attracts data to its point of origin.
Impact of Data Gravity on Cloud Vendor Strategies
Data gravity has a significant impact on cloud vendor strategies. To address the increasing demand for distributed data processing, cloud providers are adapting their offerings. This includes:
- Expanding Edge Computing Capabilities: Cloud vendors are investing heavily in edge computing, which allows businesses to process data closer to its source, reducing latency and improving performance. This strategy directly addresses the challenges posed by data gravity.
- Developing Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Hybrid cloud solutions combine the benefits of public and private clouds, enabling businesses to maintain control over their data while leveraging the scalability and flexibility of public cloud services. This approach allows businesses to manage data gravity effectively by maintaining a balance between centralized and distributed data processing.
- Offering Data Egress Fee Flexibility: Cloud providers are becoming more flexible with their data egress fees, recognizing the need for businesses to move data freely across different locations and platforms. This move is a direct response to the challenges of data gravity, which can make it expensive to transfer data to centralized locations.
Egress Fees
Data egress fees are a common practice among cloud providers, representing charges levied for transferring data out of their cloud environments. These fees can significantly impact businesses, especially those dealing with large datasets or frequent data transfers.
Calculating Egress Fees
Egress fees are typically calculated based on the volume of data transferred, the destination of the data, and the type of transfer. Cloud providers often have tiered pricing structures, where the cost per GB decreases as the volume of data transferred increases. For instance, transferring data to a different cloud provider might be more expensive than transferring it to an on-premises location.
Egress fees are typically calculated based on the volume of data transferred, the destination of the data, and the type of transfer.
Examples of Egress Fees Impact
Here are some examples of how egress fees can impact businesses:
- Data Migration: A company migrating a large database from one cloud provider to another could incur substantial egress fees for transferring the data. For example, migrating a 10TB database at a rate of $0.10 per GB could result in $1,000 in egress fees.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly backing up data to an on-premises location or a different cloud provider can lead to recurring egress fees. If a company backs up 1TB of data daily at a rate of $0.05 per GB, the annual cost would be $18,250.
- Data Analytics: Companies performing data analytics on large datasets might need to transfer data to a different cloud provider or an on-premises environment for processing. Egress fees can significantly impact the cost of such operations. For example, a company analyzing a 50TB dataset at a rate of $0.08 per GB would incur $4,000 in egress fees.
Market Pressures for Change
The cloud computing market is a dynamic and competitive landscape, with major players constantly vying for market share. This fierce competition, coupled with evolving customer demands, is driving significant changes in the way cloud vendors approach data egress fees.
The Competitive Landscape
The cloud computing market is dominated by a handful of major players, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These vendors are constantly innovating and expanding their offerings to attract and retain customers. As a result, they are increasingly focused on providing cost-effective and flexible solutions, including re-evaluating their data egress pricing models.
Customer Demand for Data Mobility and Cost-Effective Solutions
Customers are demanding more flexibility and control over their data, driving the need for cost-effective solutions for data movement. Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, which involve moving data between different cloud environments and on-premises infrastructure. This necessitates efficient and affordable data egress solutions.
Cloud Vendor Responses
Faced with growing pressure from businesses seeking more flexible and cost-effective data management solutions, cloud vendors are responding to the challenge of data egress fees in a variety of ways. They are implementing strategies to alleviate the burden on users while also maintaining their own business models.
Free or Discounted Egress
Some cloud providers are recognizing the need to make data movement more affordable, particularly for specific use cases. They are offering free or discounted data egress for certain types of data transfers, such as:
- Data transfers to other cloud providers: This strategy aims to attract customers who might be considering migrating their data to a different cloud platform. By removing the cost barrier, cloud vendors hope to retain existing customers and attract new ones.
- Data transfers for disaster recovery and backup: Recognizing the importance of data protection, some providers offer free or discounted egress for transferring data to secondary locations for backup and disaster recovery purposes. This encourages users to rely on their cloud services for critical data management needs.
- Data transfers for specific industry applications: Cloud vendors are increasingly tailoring their offerings to meet the needs of specific industries. For example, they might offer free or discounted egress for data transfers related to healthcare, finance, or research, recognizing the unique data requirements of these sectors.
Alternative Data Storage Options
Another approach cloud vendors are taking is to offer alternative data storage options that minimize the need for data egress in the first place. These options can include:
- Regional data centers: By expanding their data center footprint to various regions, cloud providers can reduce the need for data transfers across vast distances. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with geographically dispersed operations or those seeking to comply with data residency regulations.
- Edge computing: This approach brings computation and data storage closer to users, reducing the need for data to travel long distances to centralized cloud infrastructure. This can be particularly advantageous for applications requiring low latency, such as real-time analytics or IoT data processing.
- Data lakes and data warehouses: These centralized data storage solutions allow businesses to consolidate data from multiple sources within the cloud, reducing the need for frequent data transfers between different cloud services. This can simplify data management and analytics workflows while minimizing egress costs.
Data Mobility Tools
Cloud vendors are also developing new tools and services to facilitate data mobility between cloud environments and on-premises systems. These tools can help users:
- Optimize data transfer processes: These tools can analyze data transfer patterns and identify opportunities to optimize data movement, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred and minimizing egress costs.
- Automate data transfer tasks: By automating data transfer tasks, these tools can streamline the process and reduce the manual effort required, potentially leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Ensure data integrity during transfer: Data mobility tools can help guarantee data integrity during transfer, ensuring that data is transferred accurately and securely between different environments.
Impact on Businesses
The relaxation of data egress fees by cloud vendors presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses. While lower egress fees can significantly reduce costs, companies must also consider the implications for their data management strategies and security. This shift in the cloud landscape opens doors for businesses to optimize their data handling and potentially unlock new avenues for growth and innovation.
Benefits for Businesses, The market is forcing cloud vendors to relax data egress fees
The reduced cost of transferring data out of the cloud offers businesses a range of benefits, allowing them to:
- Reduce Data Transfer Costs: Lower egress fees directly translate to cost savings for businesses that frequently transfer data out of the cloud, particularly for tasks like data analysis, reporting, and backups.
- Unlock New Data-Driven Initiatives: Businesses can now more readily explore data-intensive projects that were previously hindered by high egress fees. This could include leveraging external data sources, conducting large-scale data analysis, or training machine learning models on larger datasets.
- Enhance Data Portability: The reduction in egress fees promotes data portability, allowing businesses to move their data more easily between different cloud providers or on-premises systems. This enhances flexibility and reduces vendor lock-in.
- Simplify Hybrid Cloud Strategies: With lower egress fees, businesses can seamlessly integrate cloud-based services with on-premises infrastructure, facilitating hybrid cloud deployments and optimizing data management across multiple environments.
Challenges for Businesses
While the relaxation of egress fees brings numerous advantages, businesses must also navigate potential challenges:
- Data Security Considerations: Lower egress fees might encourage businesses to move data out of the cloud more frequently, potentially increasing the risk of data breaches if security measures are not adequately implemented.
- Data Management Complexity: As businesses embrace hybrid cloud strategies and data movement becomes more prevalent, managing data across different environments can become more complex, requiring robust data governance and management practices.
- Potential for Vendor Lock-in: While increased data portability is a benefit, businesses must still be mindful of potential vendor lock-in, especially if they rely heavily on a single cloud provider’s services.
Leveraging Data Management Strategies
Businesses can leverage the changes in data egress fees to optimize their data management strategies and achieve significant cost reductions. Here are some key considerations:
- Data Optimization: Implement data optimization techniques, such as data compression and deduplication, to minimize the amount of data transferred, thereby reducing egress fees.
- Data Locality: Strategically locate data closer to where it is used, minimizing the need for data transfer. This could involve storing data in edge locations, using cloud regions closer to data consumers, or leveraging content delivery networks (CDNs).
- Data Governance: Establish robust data governance policies to ensure that data is only transferred when necessary and that data movement adheres to compliance regulations.
- Cloud Provider Selection: Carefully evaluate cloud providers based on their egress fee structures, data security policies, and overall value proposition. Consider leveraging multiple cloud providers to achieve optimal cost and flexibility.
Future Trends: The Market Is Forcing Cloud Vendors To Relax Data Egress Fees
The landscape of data egress fees and cloud vendor strategies is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting market dynamics. The future holds several intriguing possibilities, shaped by the interplay of emerging technologies, evolving regulations, and evolving business needs.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rise of edge computing and decentralized data storage technologies is poised to significantly impact data egress fees.
- Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to users, reducing the need to transfer data to centralized cloud data centers. This could lead to a decrease in data egress fees as data movement becomes less frequent.
- Decentralized data storage, exemplified by blockchain and distributed ledger technologies, allows data to be stored across multiple nodes, potentially eliminating the need for centralized cloud storage altogether. This could drastically reduce data egress fees as data transfers become less necessary.
These emerging technologies could fundamentally alter the traditional cloud storage model, potentially leading to a shift in the balance of power between cloud vendors and businesses.
The market is evolving rapidly, and cloud vendors are adapting to the changing needs of businesses. As data gravity continues to grow, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions for managing data movement. This will lead to greater flexibility, affordability, and control for businesses of all sizes. The future of data management is looking bright, with cloud vendors taking steps to make it easier and more cost-effective to move data where it needs to be.
The market is definitely shifting, with cloud vendors feeling the pressure to loosen their grip on data egress fees. This move, driven by the need to stay competitive, aligns with the growing demand for flexible data management. Meanwhile, Instagram expands its creator marketplace to 10 new countries , signaling a shift towards supporting creative talent and content distribution on a global scale.
This expansion, combined with the evolving landscape of data egress fees, suggests a future where accessibility and content creation take center stage.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News