TSMC’s Role in Apple’s Chipset Production
TSMC, or Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, is a global leader in semiconductor foundry services. It plays a crucial role in the production of Apple’s A-series chips, which power iPhones, iPads, and other Apple devices.
TSMC’s advanced manufacturing capabilities are essential for Apple’s A-series chips, known for their exceptional performance and efficiency. TSMC’s expertise in manufacturing cutting-edge chips allows Apple to deliver high-performance devices with innovative features.
TSMC’s Advanced Technology Nodes
TSMC’s advanced technology nodes, such as 5nm and 3nm, enable the production of smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient chips. These nodes refer to the size of the transistors used in chip manufacturing. Smaller transistors allow for more transistors to be packed onto a chip, resulting in increased performance and reduced power consumption.
For example, Apple’s A16 Bionic chip, found in the iPhone 14 Pro models, is built on TSMC’s 4nm process technology. This allows for a significant performance increase compared to previous generations while maintaining energy efficiency.
The A9 and A9X Chipsets
Apple’s A9 and A9X chipsets are powerful processors that were at the heart of several of their devices in 2015 and 2016. These chipsets, manufactured by TSMC using a 16nm FinFET process, represent a significant leap in performance and efficiency compared to their predecessors.
The Key Differences Between the A9 and A9X Chipsets, Tsmc rumored to product 70 of apples a9a9x chipsets this year
The A9 and A9X chipsets share a common core architecture but differ in their configurations and performance capabilities. The A9X, designed for iPad Pro models, is essentially a beefed-up version of the A9, offering more processing power and graphics capabilities.
- Number of Cores: The A9 chipset features two CPU cores, while the A9X boasts three cores, providing a significant performance boost for demanding tasks.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The A9X’s GPU is significantly more powerful than the A9’s, offering enhanced graphics performance, particularly crucial for demanding tasks like gaming and video editing.
- Memory Bandwidth: The A9X chipset utilizes a higher memory bandwidth compared to the A9, enabling faster data access and improved performance for tasks that require large amounts of data processing.
Applications of the A9 and A9X Chipsets
The A9 and A9X chipsets were strategically deployed in Apple’s product lineup, catering to different performance requirements.
- A9 Chipset: The A9 chipset powered the iPhone 6s and iPhone 6s Plus, providing a significant performance improvement over previous generations. It also powered the iPad mini 4 and the first-generation iPad Pro (9.7-inch model).
- A9X Chipset: The A9X chipset was specifically designed for the first-generation iPad Pro (12.9-inch model) and was known for its exceptional graphics performance, enabling seamless and immersive gaming experiences and professional-level video editing capabilities.
Production Volume and Market Impact: Tsmc Rumored To Product 70 Of Apples A9a9x Chipsets This Year
The rumor of TSMC producing 70% of Apple’s A9 and A9X chipsets carries significant weight, potentially impacting Apple’s supply chain, product availability, and the broader semiconductor industry.
This high production volume indicates a strong partnership between TSMC and Apple, highlighting the importance of TSMC’s advanced manufacturing capabilities in meeting Apple’s demanding requirements.
Impact on Apple’s Supply Chain and Product Availability
This large-scale production could bolster Apple’s supply chain resilience, ensuring a steady supply of crucial components for its flagship devices.
A stable supply chain can lead to:
- Reduced risk of shortages and delays in product launches.
- Greater flexibility in managing production and meeting fluctuating demand.
- Potentially lower manufacturing costs due to economies of scale.
However, it’s important to note that relying heavily on a single manufacturer can create vulnerabilities.
For example, if TSMC experiences production issues, Apple could face significant challenges in meeting its production targets.
Impact on the Semiconductor Industry
TSMC’s dominance in producing Apple’s A9 and A9X chipsets can influence the overall semiconductor industry.
This high volume production could:
- Increase demand for advanced manufacturing equipment and materials, driving innovation and investment in the industry.
- Lead to increased competition among other foundries to secure similar contracts with major players like Apple.
- Potentially create pressure on other chip manufacturers to enhance their capabilities and technologies to remain competitive.
Additionally, TSMC’s success in producing high-performance chips for Apple could strengthen its position as a leading foundry, attracting more customers and solidifying its dominance in the market.
Competition and Market Dynamics
The semiconductor foundry market is a fiercely competitive landscape, with TSMC facing several formidable competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to assess TSMC’s position and potential for future growth.
Tsmc rumored to product 70 of apples a9a9x chipsets this year – The market share of TSMC and its competitors is constantly shifting, influenced by factors such as technological advancements, manufacturing capacity, customer relationships, and global economic conditions.
Key Competitors
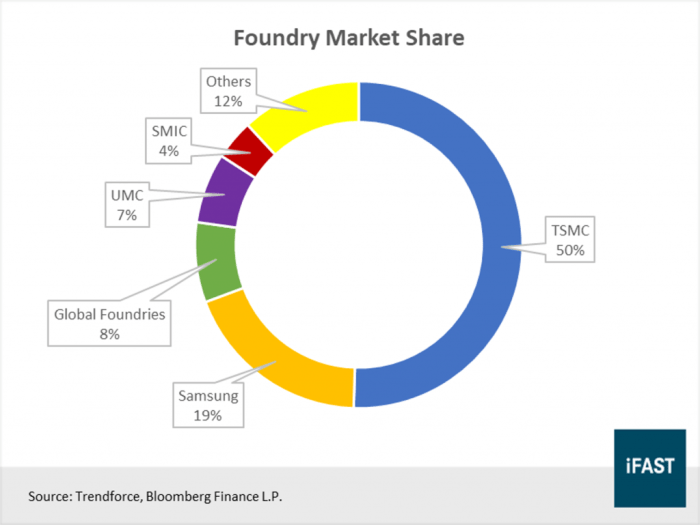
TSMC’s primary competitors in the semiconductor foundry market include:
- Samsung Foundry: A major player with advanced manufacturing capabilities, Samsung Foundry is a strong competitor to TSMC, particularly in the high-end logic node market.
- Intel: Although primarily known for its own chip designs, Intel also operates a foundry business, competing with TSMC in specific segments.
- GlobalFoundries: A leading foundry player with a focus on mature nodes, GlobalFoundries competes with TSMC in the automotive and industrial sectors.
- United Microelectronics Corporation (UMC): A significant player in the mature node market, UMC focuses on cost-effective solutions.
Comparison of Manufacturing Capabilities
TSMC, Samsung Foundry, and Intel are the leading players in advanced semiconductor manufacturing, competing in the cutting-edge nodes below 10nm. GlobalFoundries and UMC primarily focus on mature nodes (above 10nm), catering to different market segments.
| Foundry | Technology Leadership | Manufacturing Capacity | Customer Base |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSMC | Leading in advanced nodes (below 10nm) | Largest manufacturing capacity | Broad customer base, including Apple, Qualcomm, and NVIDIA |
| Samsung Foundry | Strong in advanced nodes, particularly for mobile devices | Significant manufacturing capacity | Strong ties with Samsung Electronics, also serving other customers |
| Intel | Advanced node capabilities, but primarily focused on its own designs | Limited foundry capacity compared to TSMC and Samsung | Focuses on its own products, but also serves select customers |
| GlobalFoundries | Strong in mature nodes (above 10nm) | Significant manufacturing capacity | Focuses on automotive, industrial, and other sectors |
| UMC | Specializes in mature nodes, offering cost-effective solutions | Large manufacturing capacity | Serves a wide range of customers in various industries |
The semiconductor foundry market is dynamic, with ongoing competition and technological advancements driving market share shifts.
- Emerging Technologies: Advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are creating new demand for specialized chips, which could lead to market share shifts.
- Geopolitical Factors: Trade tensions and geopolitical uncertainties can impact the semiconductor industry, potentially influencing market share dynamics.
- Investment and Capacity: Foundries are investing heavily in new facilities and technologies to maintain their competitiveness, which can influence market share.
Future Trends and Implications
The semiconductor industry, particularly for mobile devices, is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. The integration of emerging technologies like 5G and AI is profoundly impacting chip design and production, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. TSMC’s strategic partnership with Apple has been instrumental in driving innovation and shaping the future of mobile technology. This section explores the future trends and implications of these developments.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rise of 5G and AI is fundamentally changing the landscape of mobile devices. 5G networks offer significantly faster speeds and lower latency, enabling new applications and experiences. AI, on the other hand, is driving the development of more intelligent and personalized devices, requiring chips with greater processing power and efficiency. These technologies are driving demand for more sophisticated chips that can handle complex workloads and demanding tasks.
- 5G: 5G networks demand chips with higher bandwidth and lower latency to support the increased data flow and real-time responsiveness. This is driving the development of advanced chipsets with faster data processing capabilities, enabling seamless streaming, faster downloads, and enhanced gaming experiences. For example, the Qualcomm Snapdragon X55 modem supports 5G networks and provides high-speed data connectivity for mobile devices.
- AI: AI applications, such as facial recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning, require significant processing power and specialized hardware. This has led to the development of AI-specific chips, like Apple’s Neural Engine, which are optimized for machine learning tasks. These chips are designed to handle complex calculations and algorithms efficiently, enabling more sophisticated AI features in mobile devices.
TSMC’s Long-Term Implications
TSMC’s partnership with Apple has been a strategic move for both companies, creating a symbiotic relationship that has propelled innovation in the semiconductor industry. TSMC’s advanced manufacturing capabilities have enabled Apple to develop cutting-edge chipsets for its devices, while Apple’s demand for high-performance chips has incentivized TSMC to invest heavily in research and development.
- For Apple: TSMC’s manufacturing expertise and technological prowess have been crucial for Apple’s success in developing powerful and efficient chipsets. This partnership has allowed Apple to maintain its competitive edge in the mobile device market by offering superior performance and user experience.
- For TSMC: Apple’s significant orders have contributed to TSMC’s revenue and profitability, solidifying its position as a leading semiconductor manufacturer. This relationship has also provided TSMC with valuable insights into the needs and trends in the mobile device market, enabling it to develop more advanced and innovative technologies.
The potential impact of TSMC’s dominance in Apple’s chipset production is a topic that will continue to be debated and analyzed in the coming months and years. The implications for both companies, the semiconductor industry, and the wider tech landscape are far-reaching and will likely shape the future of the mobile device market. As the demand for advanced semiconductors continues to grow, TSMC’s role in Apple’s supply chain will likely become even more critical, further cementing its position as a leading player in the global semiconductor industry. This development could also have significant implications for Apple’s competitive advantage, as the company seeks to maintain its position as a leader in the mobile device market.
While TSMC is rumored to be cranking out 70 million of Apple’s A9A9X chipsets this year, the tech world is also buzzing about a different kind of fruit: New Line Cinema has secured the rights to a Fruit Ninja movie. It’s a reminder that even in the world of high-tech, sometimes the simplest ideas can become the biggest hits.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News