Uhg change healthcare ransomware compromised credentials mfa – UHG Data Breach: Ransomware, Compromised Credentials, and MFA – Imagine a world where your medical records, financial details, and personal information are all at risk. This isn’t a dystopian novel, but a reality for millions affected by the recent UHG data breach. This breach, fueled by a ransomware attack, highlights a growing trend in the healthcare industry: cybercriminals are increasingly targeting vulnerable systems, exploiting weaknesses like compromised credentials to steal sensitive data and disrupt critical services. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the need for robust cybersecurity measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to protect patient information and ensure the integrity of our healthcare system.
The UHG data breach is a prime example of the vulnerabilities within the healthcare system. It exposed millions of patient records, including sensitive information like medical histories, financial details, and personal identifiers. This breach, attributed to a ransomware attack, serves as a stark reminder of the growing threat of cyberattacks in the healthcare industry. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities like weak passwords, outdated software, and inadequate security measures to gain access to sensitive data and disrupt critical services. The consequences of such breaches can be devastating, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage and compromised patient trust.
The UHG Data Breach
The UHG data breach, which occurred in 2023, is a significant cybersecurity incident that impacted a major healthcare provider and its patients. This event highlights the vulnerabilities of healthcare systems to cyberattacks and the potential consequences for both organizations and individuals.
Timeline of the UHG Data Breach
The timeline of the UHG data breach provides a detailed account of the events that transpired, from the initial attack to the aftermath.
- September 2023: The initial attack occurred, but the details of the attack, including the specific methods used by the attackers, were not publicly disclosed.
- October 2023: UHG discovered the data breach and initiated an investigation. The investigation confirmed that sensitive patient data had been compromised.
- November 2023: UHG notified affected patients about the breach and began to implement measures to mitigate the impact of the incident.
- December 2023: UHG continued to provide support to affected patients and to work with law enforcement to investigate the breach.
Data Compromised in the UHG Breach
The data compromised in the UHG data breach included sensitive information about patients, which could be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious purposes.
- Patient health information: This included medical records, diagnoses, treatment plans, and other sensitive health data.
- Financial data: This included credit card numbers, bank account information, and other financial details.
- Personal information: This included names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, and other personal identifiers.
Impact of the UHG Data Breach
The UHG data breach had a significant impact on the organization, its patients, and the healthcare industry as a whole.
- UHG: The breach resulted in reputational damage, legal costs, and increased cybersecurity expenses.
- Patients: Affected patients faced an increased risk of identity theft, financial fraud, and other security threats. They also experienced anxiety and stress due to the breach.
- Healthcare industry: The breach highlighted the vulnerabilities of healthcare systems to cyberattacks and the need for stronger cybersecurity measures. It also raised concerns about patient privacy and data security in the healthcare sector.
The Role of Compromised Credentials in Healthcare Breaches
Healthcare data is incredibly sensitive, containing personal and medical information that can be misused for identity theft, financial fraud, and other harmful purposes. Compromised credentials, such as stolen passwords and usernames, are a major vulnerability that attackers exploit to gain access to healthcare systems and steal this valuable data.
Methods Used to Obtain Compromised Credentials
Attackers employ various tactics to acquire compromised credentials, targeting both individuals and organizations.
- Phishing Attacks: These involve sending deceptive emails, text messages, or social media messages that appear to be from legitimate sources, like a healthcare provider or insurance company. They often contain links or attachments that lead to fake websites designed to steal login credentials.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can be installed on computers and mobile devices through various means, including clicking on infected links, opening malicious attachments, or visiting compromised websites. Once installed, malware can steal passwords, keystrokes, and other sensitive information.
- Social Engineering: This involves manipulating individuals into revealing sensitive information or granting access to systems. Attackers may use phone calls, emails, or even in-person interactions to trick users into providing their credentials or bypassing security measures.
Examples of Compromised Credentials in Healthcare Breaches
Compromised credentials have been used in numerous healthcare breaches, leading to significant consequences.
- Anthem Inc. (2015): This breach affected over 78.8 million individuals, exposing their personal and medical information. The attackers gained access to the company’s systems through compromised credentials, likely obtained through a phishing attack.
- Premera Blue Cross (2014): This breach exposed the personal and medical information of over 11 million individuals. The attackers used stolen credentials to access the company’s network and steal data.
The Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Uhg Change Healthcare Ransomware Compromised Credentials Mfa
In the wake of high-profile data breaches, such as the one affecting UnitedHealth Group (UHG), the need for robust security measures in healthcare has become more critical than ever. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) emerges as a crucial element in bolstering security against credential theft and unauthorized access to sensitive patient information.
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access to an account or system. This means that even if an attacker manages to obtain a user’s password, they will still be unable to gain access without the additional authentication factor.
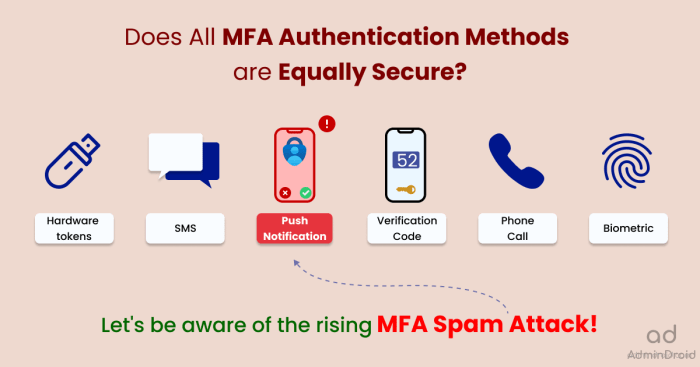
Different Types of MFA Methods
Different MFA methods offer varying levels of security and convenience. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method is essential for healthcare organizations to choose the most appropriate options for their specific needs.
- SMS Codes: This method involves sending a one-time code to the user’s mobile phone via SMS. While convenient, SMS codes can be vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks, where attackers gain control of the user’s phone number.
- Push Notifications: Push notifications are sent to the user’s mobile device and require the user to approve the login attempt. This method is generally considered more secure than SMS codes, as it does not rely on the user’s phone number.
- Hardware Tokens: Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate unique codes, typically based on time-based algorithms. These tokens are generally considered the most secure MFA method, as they are not susceptible to phishing attacks or SIM swapping.
Best Practices for Implementing MFA in Healthcare Organizations
Implementing MFA effectively requires careful planning and execution. Healthcare organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Select Appropriate MFA Methods: The choice of MFA methods should be based on a risk assessment that considers the sensitivity of the data being protected, the potential threats, and the organization’s budget and resources.
- Provide Comprehensive Staff Training: Training staff on the importance of MFA and how to use it effectively is crucial. This training should cover different MFA methods, security best practices, and procedures for reporting suspicious activity.
- Enforce MFA for All Sensitive Accounts: MFA should be mandatory for all accounts that have access to sensitive patient data, including administrative accounts, clinical systems, and electronic health records (EHRs).
- Monitor and Review MFA Effectiveness: Regularly monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of MFA implementation is essential. This includes analyzing login attempts, detecting anomalies, and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
Strategies for Preventing and Responding to Healthcare Breaches
Healthcare data breaches are a significant threat to patient privacy and safety, and they can have devastating consequences for organizations. Ransomware attacks, in particular, can cripple healthcare systems, disrupting critical operations and putting lives at risk. Fortunately, healthcare organizations can take proactive steps to prevent breaches and develop robust response plans to mitigate the damage if a breach occurs.
Preventive Measures for Healthcare Breaches
Proactive measures are essential for safeguarding sensitive healthcare data and minimizing the risk of breaches. Implementing a multi-layered security approach is crucial to address vulnerabilities at every stage of the data lifecycle.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems and networks. These audits should include assessments of access controls, network security, and data encryption practices. Regular audits help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure their security posture remains strong.
- Employee Training: Train employees on security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and data handling procedures. Regular training sessions help employees recognize and avoid common phishing scams, understand the importance of strong passwords, and practice secure data handling techniques. This minimizes the risk of human error, which is often a major factor in data breaches.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Encrypting data across all systems and networks ensures that even if a breach occurs, the stolen data will be useless to attackers.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile device. This makes it much more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies, including minimum length requirements, complexity rules, and regular password changes. Strong password policies help prevent attackers from guessing passwords or using stolen credentials to gain access to systems.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches. Software updates often contain critical security fixes that address vulnerabilities exploited by attackers.
- Network Segmentation: Segment the network into different zones with varying levels of security. This helps contain the spread of malware and limits the impact of a breach.
- Security Awareness Programs: Implement ongoing security awareness programs to educate employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices. Regular security awareness programs help employees stay informed about evolving threats and reinforce the importance of security practices.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that Artikels steps to be taken in the event of a breach. This plan should include procedures for identifying and containing the breach, notifying affected individuals, and reporting the incident to relevant authorities.
Responding to a Healthcare Breach
A robust response plan is critical for minimizing the impact of a breach and ensuring the safety of patient data. A well-defined plan helps organizations manage the situation effectively and efficiently.
- Identify and Contain the Breach: The first step is to identify the source of the breach and isolate the affected systems. This involves analyzing logs, monitoring network traffic, and identifying any suspicious activity.
- Assess the Impact: Determine the scope of the breach and identify the data that has been compromised. This assessment is crucial for determining the appropriate response and notifying affected individuals.
- Notify Affected Individuals: Notify individuals whose data has been compromised in a timely and transparent manner. This notification should include details about the breach, the type of data affected, and steps individuals can take to protect themselves.
- Report the Breach to Authorities: Report the breach to relevant authorities, such as the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Reporting requirements vary by jurisdiction, but healthcare organizations are generally required to notify authorities of breaches involving sensitive patient data.
- Remediate the Breach: Take steps to remediate the breach and prevent future attacks. This may involve patching vulnerabilities, updating security systems, and implementing additional security measures.
- Provide Support to Affected Individuals: Provide support to individuals whose data has been compromised. This may include credit monitoring services, identity theft protection, and counseling.
- Document the Incident: Document the entire incident, including the steps taken to identify, contain, and remediate the breach. This documentation is important for future incident response efforts and regulatory compliance.
Key Stakeholders in Breach Response
Effective breach response requires coordination among multiple stakeholders. Each stakeholder plays a critical role in managing the incident and ensuring a swift and effective resolution.
| Stakeholder | Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| IT Security Team | Identify and contain the breach, analyze logs, and implement security measures. | Identify the source of the breach, isolate affected systems, and assess the impact of the breach. |
| Legal Counsel | Provide legal guidance, advise on regulatory compliance, and handle communications with authorities. | Ensure compliance with privacy laws, advise on notification requirements, and coordinate with relevant authorities. |
| Public Relations Team | Manage communication with the public, media, and affected individuals. | Develop and disseminate communication strategies, respond to media inquiries, and provide updates to stakeholders. |
| Human Resources Team | Provide support to employees, handle employee communications, and implement security awareness training. | Ensure employees are informed about the breach, provide support and resources, and reinforce security best practices. |
| Senior Management | Provide oversight and leadership, make critical decisions, and ensure resources are available for breach response. | Approve incident response plans, allocate resources, and provide guidance to stakeholders. |
The Future of Healthcare Security
The healthcare industry faces a constantly evolving threat landscape, demanding innovative solutions to safeguard sensitive patient data and ensure the continuity of care. Emerging technologies and evolving security strategies offer promising avenues for enhancing healthcare security in the years to come.
Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and healthcare is no exception. AI can play a pivotal role in bolstering healthcare security by automating threat detection and response, improving risk assessment, and optimizing security operations.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including network traffic, security logs, and patient records, to identify suspicious patterns and potential threats in real-time. This enables proactive threat detection and prevention, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can automate incident response procedures, such as isolating infected systems, containing malware spread, and restoring compromised data. This reduces the time and resources required to respond to security incidents, minimizing potential damage.
- Risk Assessment and Prioritization: AI can analyze historical data and identify vulnerabilities and risks within healthcare systems. This allows security teams to prioritize security efforts and allocate resources effectively, focusing on the most critical areas.
Blockchain for Secure Data Management
Blockchain technology, known for its immutability and transparency, offers a promising solution for secure data management in healthcare. Blockchain can enhance data integrity, streamline data sharing, and improve patient privacy.
- Data Integrity and Auditability: Blockchain’s decentralized and tamper-proof nature ensures data integrity, making it virtually impossible to alter or corrupt records. This enhances trust in data and provides an auditable trail of all data modifications.
- Secure Data Sharing: Blockchain enables secure and efficient data sharing between healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders. It allows authorized parties to access and share data without compromising its security or privacy.
- Patient Privacy and Control: Blockchain can empower patients to control their medical data, allowing them to grant or revoke access to their records as needed. This enhances patient autonomy and privacy.
Zero-Trust Security Models
Traditional security models rely on a “castle and moat” approach, where perimeter defenses are the primary line of defense. However, the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks and the prevalence of remote access have rendered these models ineffective. Zero-trust security models shift the focus from perimeter security to user and device authentication, assuming that no user or device can be trusted by default.
- Strict Authentication and Authorization: Zero-trust models require rigorous authentication and authorization for all users and devices, regardless of their location. This ensures that only authorized individuals and devices have access to sensitive data and systems.
- Continuous Monitoring and Verification: Zero-trust models involve continuous monitoring and verification of user and device activity, detecting and responding to suspicious behavior in real-time. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Least Privilege Access: Zero-trust models grant users only the minimum access privileges necessary to perform their job functions. This limits the potential impact of a compromised account and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Evolving Threat Landscape, Uhg change healthcare ransomware compromised credentials mfa
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with attackers becoming more sophisticated and finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Healthcare organizations must stay vigilant and adapt their security strategies to counter emerging threats.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks continue to be a significant threat to healthcare organizations, with attackers demanding large sums of money to unlock encrypted data. The sophistication of ransomware attacks has increased, with attackers using more advanced techniques to evade detection and bypass security controls.
- Targeted Attacks: Healthcare organizations are increasingly targeted by nation-state actors and organized criminal groups seeking to steal sensitive patient data or disrupt healthcare operations. These attacks are often highly sophisticated and require specialized knowledge and resources.
- Emerging Attack Vectors: Attackers are constantly exploring new attack vectors, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in medical devices, social engineering tactics, and supply chain attacks. Healthcare organizations must be aware of these emerging threats and implement appropriate safeguards.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
Healthcare organizations must proactively invest in security infrastructure and ongoing education for staff to stay ahead of the curve in terms of cybersecurity.
- Investment in Security Infrastructure: Healthcare organizations should invest in robust security infrastructure, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security solutions. They should also consider implementing advanced security technologies such as AI, blockchain, and zero-trust security models.
- Ongoing Staff Education: Regular security awareness training for all staff is crucial to combat phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Staff should be educated on best practices for handling sensitive data, recognizing suspicious emails and websites, and reporting security incidents.
- Regular Security Audits and Assessments: Regular security audits and assessments are essential to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in healthcare systems. This allows organizations to address security gaps and implement corrective measures before they can be exploited by attackers.
The UHG data breach is a wake-up call for the healthcare industry. It underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect patient data and ensure the integrity of our healthcare system. Organizations must prioritize investments in security infrastructure, implement multi-factor authentication, and educate employees on best practices to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks and data breaches. The future of healthcare security lies in proactive measures, constant vigilance, and a commitment to protecting patient information at all costs. The UHG data breach serves as a cautionary tale, urging us to strengthen our defenses and safeguard the sensitive data entrusted to us.
The recent UHG healthcare ransomware attack, highlighting the vulnerability of compromised credentials and the importance of MFA, underscores the need for robust cybersecurity solutions. While this incident serves as a stark reminder of the threats facing the healthcare industry, it’s encouraging to see innovation in action, as showcased by the 30 startups presenting at HAX’s May 1 Demo Day.
These startups are developing cutting-edge solutions that could potentially help healthcare organizations better protect themselves against future attacks, like the one that impacted UHG.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News