ULA aims to launch Astrobotic lunar lander on Christmas Eve, marking a significant milestone in lunar exploration. This mission, a collaboration between ULA and Astrobotic, will send a lander carrying scientific instruments to the Moon, aiming to conduct groundbreaking research and gather valuable data about our celestial neighbor. The launch is scheduled for Christmas Eve, adding a unique holiday twist to this ambitious endeavor.
This mission signifies a pivotal moment in the ongoing pursuit of lunar exploration. It represents the culmination of years of research, development, and collaboration between ULA, Astrobotic, and other key players in the space industry. The launch is not only a technological achievement but also a testament to the enduring human fascination with the Moon and the potential it holds for scientific discovery and future exploration.
ULA’s Role in Lunar Exploration
United Launch Alliance (ULA) is a leading American launch services provider with a long history of successfully launching spacecraft into orbit. They have been instrumental in sending missions to the Moon, playing a crucial role in lunar exploration.
ULA’s History and Contributions to Lunar Missions
ULA’s journey began in 2006 with the merger of Lockheed Martin and Boeing’s launch services divisions. Since then, ULA has consistently delivered reliable and powerful launch vehicles, contributing significantly to space exploration, including lunar missions.
ULA’s Launch Vehicles and Capabilities for Lunar Missions
ULA boasts a fleet of powerful and versatile launch vehicles, including the Atlas V and Delta IV, specifically designed to launch payloads to the Moon. These rockets have proven capabilities for lunar missions, with a high degree of reliability and precision.
Atlas V
The Atlas V is a two-stage rocket with a solid-propellant first stage and a liquid-propellant second stage. It has a proven track record of successfully launching various payloads to the Moon, including robotic spacecraft and scientific probes.
Delta IV
The Delta IV is a three-stage rocket, also designed for heavy-lift launches. It is known for its exceptional performance and reliability, capable of delivering large payloads to lunar orbit.
ULA’s Partnership with Astrobotic
ULA has partnered with Astrobotic Technology, a leading provider of lunar delivery services, to support their mission to land payloads on the Moon. This collaboration is crucial for advancing lunar exploration and scientific research.
Significance of the Partnership
This partnership brings together ULA’s expertise in launch services and Astrobotic’s lunar delivery capabilities, creating a powerful combination for successful lunar missions. It demonstrates the importance of collaboration in space exploration, bringing together diverse skills and resources to achieve common goals.
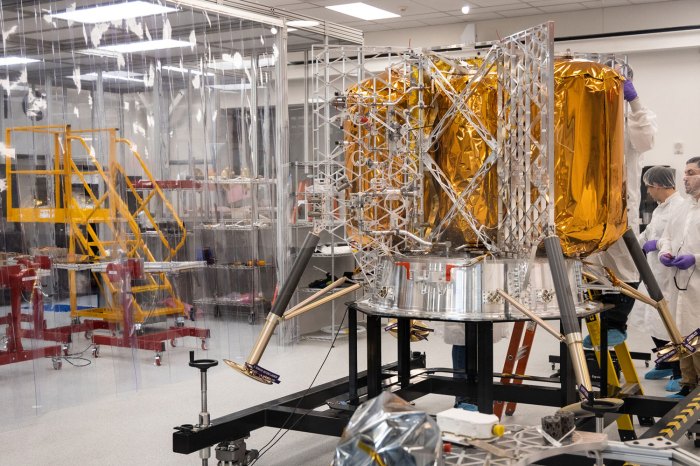
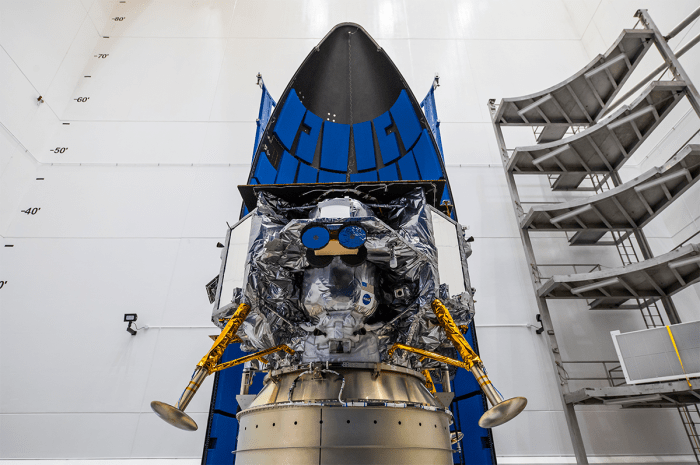
Astrobotic’s Lunar Lander
Astrobotic Technology, a leading company in lunar exploration, has developed a state-of-the-art lunar lander designed to deliver payloads to the Moon’s surface. This lander, known as the Peregrine Lunar Lander, is a crucial component of Astrobotic’s mission to enable commercial access to the Moon and facilitate scientific research.
Design and Features
The Peregrine Lunar Lander is a robust and versatile spacecraft designed for safe and precise lunar landings. Its design incorporates several key features, including:
* Autonomous Landing System: The lander is equipped with an advanced autonomous landing system that allows it to navigate and land safely on the Moon’s surface without human intervention. This system uses sophisticated sensors and algorithms to analyze terrain and adjust its trajectory for a successful landing.
* Versatile Payload Bay: The Peregrine Lunar Lander boasts a spacious payload bay capable of carrying a variety of scientific instruments and experiments. This allows for a diverse range of scientific research to be conducted on the lunar surface.
* Communication Systems: The lander is equipped with robust communication systems that enable it to transmit data and images back to Earth. This ensures that scientists can monitor the mission and receive valuable data from the lunar surface.
* Power System: The lander is powered by a high-performance solar array that provides reliable energy for its operations. This ensures that the lander can function effectively throughout its mission on the Moon.
Payload Capacity and Scientific Instruments
The Peregrine Lunar Lander has a significant payload capacity, allowing it to carry a diverse range of scientific instruments and experiments. The lander’s payload bay can accommodate up to 150 kg of scientific instruments, enabling a wide range of research objectives.
The Peregrine Lunar Lander will carry a variety of scientific instruments, including:
* Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC): This instrument will capture high-resolution images of the lunar surface, providing valuable data for geological studies.
* Lunar Dust Experiment (LDEX): This experiment will study the composition and behavior of lunar dust, which is a significant factor in the design of future lunar habitats.
* CubeSat Deployment System: The lander will deploy several CubeSats, miniature satellites that can conduct a variety of scientific investigations.
* Other Instruments: The Peregrine Lunar Lander will also carry other scientific instruments, such as spectrometers and magnetometers, to study the lunar environment and composition.
Mission Objectives and Scientific Research
Astrobotic’s mission with the Peregrine Lunar Lander is to advance scientific knowledge about the Moon and pave the way for future lunar exploration. The mission objectives include:
* Scientific Research: The lander will conduct a wide range of scientific research, including geological studies, lunar dust analysis, and environmental monitoring.
* Technology Demonstration: The mission will demonstrate the capabilities of the Peregrine Lunar Lander, providing valuable data for future lunar exploration missions.
* Commercial Access to the Moon: Astrobotic aims to establish commercial access to the Moon, providing a platform for private companies and organizations to conduct research and develop new technologies.
The scientific research conducted by the Peregrine Lunar Lander is expected to provide valuable insights into the Moon’s history, geology, and environment. This information will be crucial for future lunar exploration missions and the development of lunar resources.
The Christmas Eve Launch: Ula Aims To Launch Astrobotic Lunar Lander On Christmas Eve
Launching a lunar lander on Christmas Eve is a unique and symbolic event, adding a festive touch to the already exciting endeavor of lunar exploration. It signifies the arrival of a new era in space exploration, where private companies like Astrobotic are playing a significant role. This launch is a testament to human ingenuity and the pursuit of scientific knowledge, even during the holiday season.
Launch Timeline and Mission Duration
The launch timeline for the Astrobotic lunar lander is meticulously planned, taking into account various factors like weather conditions and the precise launch window. The launch is scheduled for Christmas Eve, with a specific time slot determined by the mission’s trajectory and the alignment of celestial bodies. The mission’s duration is expected to be several months, during which the lander will perform its scientific experiments and data collection on the lunar surface.
Comparison with Previous Lunar Missions
This launch stands out from previous lunar missions in several ways. First, it marks the first time a private company is sending a lander to the moon, demonstrating the growing role of commercial space exploration. Second, the mission aims to land in a previously unexplored region of the moon, expanding our understanding of the lunar surface. Third, the lander is equipped with advanced scientific instruments, capable of collecting data that will contribute significantly to our knowledge of the moon’s geology, composition, and history.
Implications for Future Lunar Exploration
This launch marks a significant step forward in the global effort to return to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence there. The success of this mission will not only provide valuable scientific data but also pave the way for future lunar missions, including crewed landings and the development of lunar infrastructure.
Potential Scientific and Technological Advancements
The Astrobotic lander carries a diverse payload of scientific instruments designed to study various aspects of the lunar environment. These instruments will collect data on the Moon’s surface composition, geology, and potential resources. The mission will also test new technologies for lunar navigation, communication, and landing, which will be crucial for future missions.
- Resource Mapping: The mission will provide detailed maps of the lunar surface, identifying potential resources such as water ice and rare earth elements. This information is essential for planning future lunar settlements and industrial activities.
- Lunar Geology: The lander’s instruments will analyze the composition of lunar rocks and regolith, providing insights into the Moon’s formation and evolution. This data will contribute to our understanding of the early solar system.
- Lunar Environment: The mission will collect data on the lunar radiation environment, dust storms, and other factors that could affect human exploration and infrastructure development.
- Technological Advancements: The mission will test new technologies for landing, navigation, and communication, paving the way for more sophisticated lunar missions in the future.
Public Interest and Engagement
The launch of Astrobotic’s lunar lander on Christmas Eve is a momentous occasion, capturing the public’s imagination and igniting a renewed interest in lunar exploration. This mission signifies a pivotal step towards a future of sustained human presence on the Moon, driving public curiosity and engagement.
The public’s interest in lunar exploration is deeply rooted in humanity’s innate fascination with the cosmos. Witnessing the Apollo missions in the 1960s and 1970s sparked a generation’s passion for space exploration, leaving a lasting impact on our collective consciousness. Today, with advancements in technology and the emergence of private companies like Astrobotic, the dream of returning to the Moon feels more attainable than ever.
Resources for Public Engagement
The public’s enthusiasm for lunar exploration is evident in the widespread interest in this mission. To further fuel this passion and provide valuable information, various resources are available for the public to learn more about the mission and its objectives.
- Astrobotic Website: The official website of Astrobotic provides comprehensive information about the mission, including technical details, mission objectives, and updates on the launch and landing.
- NASA Website: NASA’s website features extensive resources on lunar exploration, including information about past missions, current projects, and future plans.
- Social Media: Astrobotic and NASA maintain active social media accounts, providing regular updates, behind-the-scenes glimpses, and engaging content about the mission.
- Educational Resources: Several educational institutions and organizations offer resources for the public to learn more about lunar exploration, including articles, videos, and interactive exhibits.
Visual Representation of the Mission, Ula aims to launch astrobotic lunar lander on christmas eve
A compelling visual representation of the mission’s journey from launch to landing on the Moon can effectively communicate the complexities of the endeavor and engage the public’s interest. The graphic could depict the following key elements:
- Launch: The graphic should showcase the powerful ULA rocket lifting off from the launchpad, carrying the Astrobotic lander into space.
- Trajectory: The graphic should illustrate the lander’s trajectory as it travels through space, highlighting the Earth and the Moon in the background.
- Lunar Orbit: The graphic should depict the lander entering lunar orbit, showcasing its maneuvering capabilities as it prepares for landing.
- Landing: The graphic should highlight the lander’s descent to the lunar surface, emphasizing the precision and control required for a successful landing.
“This mission represents a significant milestone in lunar exploration, paving the way for future scientific discoveries and potential human settlements on the Moon.”
The launch of the Astrobotic lunar lander on Christmas Eve is a testament to the ongoing advancements in space exploration technology and the growing international collaboration in lunar research. This mission will contribute valuable data and insights, propelling us closer to a deeper understanding of the Moon and its potential for future human presence. As we eagerly await the launch and the scientific discoveries that will follow, this mission serves as a reminder of the boundless possibilities that lie within the vast expanse of space.
ULA’s Christmas Eve launch of the Astrobotic lunar lander is a major milestone for space exploration. Meanwhile, on Earth, a different kind of innovation is happening – check out here are the 30 startups showcasing at haxs may 1 demo day for a glimpse into the future of tech. As we look to the stars, we also need to remember the ground-breaking work happening right here on our planet.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News