In today’s competitive business landscape, securing funding can be a major hurdle. But what if you could leverage your intellectual property (IP) to unlock a powerful source of capital? This is precisely what ‘Use Intellectual Property to Secure Debt and Equity Based Funding’ explores, delving into the world of turning your innovative ideas into a tangible asset for financing.
Think of it as unlocking the hidden value within your patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. By understanding how to structure deals, value your IP, and navigate the legal intricacies, you can open doors to debt and equity financing that traditional methods might not offer. This approach can be a game-changer for startups, established businesses, and even individuals with groundbreaking ideas.
Understanding Intellectual Property as Collateral
In the realm of finance, securing debt and equity funding is crucial for businesses to expand, innovate, and achieve their goals. While traditional assets like real estate and equipment have long served as collateral, intellectual property (IP) is increasingly recognized as a valuable asset that can be leveraged for financing.
This section explores the nuances of using IP as collateral, delving into the types of IP that can be used, the legal and practical considerations involved, and real-world examples of successful IP-backed funding.
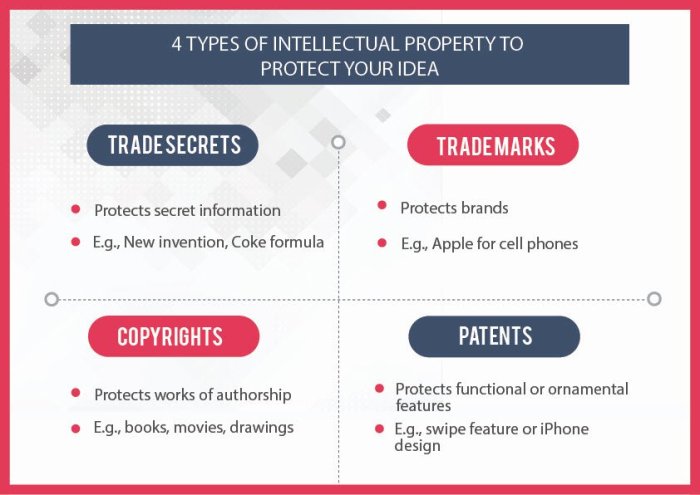
Types of Intellectual Property as Collateral
Understanding the various forms of IP that can be used as collateral is essential for businesses seeking funding. Different types of IP have varying degrees of value and require different approaches for securing financing.
- Patents: Patents protect inventions, providing exclusive rights to the inventor for a specific period. Patents can be used as collateral for financing, particularly for companies developing innovative products or technologies. The value of a patent as collateral depends on factors such as the strength of the patent, the market potential of the invention, and the patent’s remaining term.
- Trademarks: Trademarks protect brand names, logos, and other identifying marks. They can be used as collateral for financing, particularly for companies with established brands and strong market presence. The value of a trademark as collateral depends on the brand’s recognition, market share, and potential for future growth.
- Copyrights: Copyrights protect original works of authorship, such as books, music, and software. Copyrights can be used as collateral for financing, especially for companies in the creative industries. The value of a copyright as collateral depends on the work’s popularity, commercial potential, and the copyright’s remaining term.
- Trade Secrets: Trade secrets are confidential information that gives a business a competitive edge. While trade secrets are not typically registered, they can be used as collateral for financing, particularly for companies with valuable proprietary processes or formulas. The value of a trade secret as collateral depends on its confidentiality, the cost of its reproduction, and the economic value it provides to the business.
Legal and Practical Considerations
While using IP as collateral can be beneficial, it’s crucial to understand the legal and practical implications involved.
- Valuation: Determining the value of IP for collateral purposes can be challenging. Experienced IP valuation professionals can help estimate the fair market value of IP assets, considering factors such as market demand, competition, and potential revenue streams.
- Legal Protection: It’s essential to ensure that IP is properly protected before using it as collateral. This involves obtaining appropriate registrations, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, and maintaining confidentiality for trade secrets.
- Enforcement: Lenders need to be confident in their ability to enforce their rights over the IP collateral in case of default. This may involve obtaining appropriate security agreements and ensuring that the IP rights are transferable.
- Risk Assessment: Lenders will carefully assess the risks associated with using IP as collateral. Factors such as the maturity of the technology, the competitive landscape, and the strength of the IP protection will be considered.
Examples of Successful IP-Backed Funding
Several companies have successfully used IP as collateral to secure funding.
- Spotify: The music streaming giant secured early funding based on its patent for a music recommendation system, demonstrating the potential of using IP to attract investors.
- Tesla: The electric vehicle manufacturer has used its extensive patent portfolio as collateral for loans, highlighting the role of IP in financing growth for technology-driven companies.
- Genentech: The biotechnology company secured funding based on its patents for groundbreaking drugs, showcasing the potential of using IP to finance innovation in the healthcare industry.
Valuation of Intellectual Property: Use Intellectual Property To Secure Debt And Equity Based Funding
Valuing intellectual property (IP) for financing purposes is a crucial step in securing debt or equity funding. Investors and lenders need to understand the potential value of your IP to assess its worth as collateral or to determine the equity stake they are willing to acquire. This section explores various methods used to value IP, their suitability for different types of IP, and the challenges associated with valuing intangible assets.
Methods for Valuing Intellectual Property
Several methods are used to value IP for financing purposes. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the most appropriate approach depends on the specific IP being valued and the intended use of the valuation.
- Cost Approach: This method calculates the value of IP by estimating the cost of creating or acquiring the IP. It is often used for valuing newly developed IP or IP that is similar to existing assets. For example, the cost approach could be used to value a new patent by estimating the cost of research, development, and legal fees associated with obtaining the patent.
- Market Approach: This method compares the IP to similar IP that has been recently sold or licensed in the marketplace. It relies on finding comparable transactions to determine the value of the IP. For example, the market approach could be used to value a trademark by comparing it to similar trademarks that have been recently licensed.
- Income Approach: This method estimates the value of IP based on the future income it is expected to generate. It considers factors such as the expected sales of products or services incorporating the IP, the expected royalty rates, and the expected lifespan of the IP. For example, the income approach could be used to value a software program by estimating the future revenue it is expected to generate from sales and licensing.
- Hybrid Approach: This method combines elements of two or more of the other valuation methods. It is often used when no single method provides a comprehensive valuation. For example, a hybrid approach could combine the cost approach and the market approach to value a new patent.
Suitability of Valuation Methodologies
The suitability of a particular valuation methodology depends on several factors, including the type of IP, the stage of development, and the intended use of the valuation.
- Patents: The cost approach is often used to value patents, as it can be difficult to find comparable transactions. The income approach can also be used, but it is more challenging to estimate the future income from a patent.
- Trademarks: The market approach is often used to value trademarks, as there are many comparable transactions available. The income approach can also be used, but it is more challenging to estimate the future income from a trademark.
- Copyrights: The cost approach is often used to value copyrights, as it can be difficult to find comparable transactions. The income approach can also be used, but it is more challenging to estimate the future income from a copyright.
- Trade Secrets: The cost approach is often used to value trade secrets, as it can be difficult to find comparable transactions. The income approach can also be used, but it is more challenging to estimate the future income from a trade secret.
Challenges of Valuing Intangible Assets, Use intellectual property to secure debt and equity based funding
Valuing intangible assets like IP can be challenging due to their unique characteristics. These challenges include:
- Difficulty in Measuring Value: Intangible assets are not physical assets and cannot be easily measured or quantified. Their value is often based on subjective factors, such as market demand, brand recognition, and future potential.
- Lack of Market Data: There is often limited market data available for intangible assets, making it difficult to find comparable transactions.
- Uncertainty of Future Income: Estimating the future income from intangible assets can be difficult due to the uncertainty of future market conditions and competition.
- Subjectivity of Valuation: The valuation of intangible assets is often subjective and can vary significantly depending on the valuation methodology used and the assumptions made.
Strategies for Overcoming Valuation Challenges
Despite the challenges, several strategies can be used to overcome them and arrive at a more accurate and reliable valuation.
- Engage Qualified Professionals: It is essential to engage qualified professionals with experience in valuing intangible assets. These professionals can use their expertise and knowledge to apply appropriate valuation methodologies and make informed assumptions.
- Gather Relevant Data: It is crucial to gather as much relevant data as possible to support the valuation. This data may include market research, financial statements, industry reports, and legal documents.
- Use Multiple Valuation Methods: Using multiple valuation methods can help to provide a more comprehensive and robust valuation. Comparing the results from different methods can also help to identify any potential biases or inconsistencies.
- Consider the Intended Use of the Valuation: The intended use of the valuation should be considered when selecting the appropriate valuation methodology and making assumptions. For example, a valuation for financing purposes may require different assumptions than a valuation for tax purposes.
Structuring Debt and Equity Financing with IP Collateral
Leveraging intellectual property (IP) as collateral opens up unique avenues for securing both debt and equity financing. IP-backed financing can be a game-changer for companies with valuable intangible assets, enabling them to access capital that might otherwise be unavailable.
Debt Financing Structures
Various debt financing structures can be implemented to leverage IP as collateral. These structures provide a means for companies to access capital while retaining ownership of their IP.
- IP-Secured Loans: This is a straightforward approach where the lender provides funds based on the value of the borrower’s IP. The loan agreement Artikels the terms of repayment, including interest rates and collateralization provisions. In case of default, the lender has the right to seize the IP.
- Royalty-Based Financing: Instead of a fixed repayment schedule, the borrower makes payments to the lender based on a percentage of revenue generated from the IP. This structure aligns the interests of both parties, as the lender benefits from the success of the IP.
- IP-Backed Bonds: Companies can issue bonds backed by their IP, allowing investors to purchase debt securities that are secured by the IP assets. This structure offers a potential for higher returns for investors while providing the company with a source of long-term capital.
Equity Financing Structures
Equity financing structures involve the sale of ownership in the company in exchange for capital. This structure allows companies to raise funds without taking on debt.
- IP-Licensing Agreements: A company can grant a license to use its IP to another entity in exchange for equity in the licensee’s company. This structure can be particularly beneficial for early-stage companies with strong IP but limited resources.
- IP-Based Joint Ventures: Companies can form joint ventures where the IP is shared and used to develop and commercialize new products or services. The equity stake in the joint venture is typically determined based on the value of the IP contributed by each partner.
- IP-Backed Venture Capital: Venture capitalists often invest in companies with strong IP potential, providing capital in exchange for equity. The valuation of the IP is a key factor in determining the terms of the investment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IP-Backed Financing
Each financing structure has its advantages and disadvantages. It’s important to weigh these factors carefully when deciding on the best approach for a particular situation.
Advantages
- Access to Capital: IP-backed financing provides companies with access to capital that might otherwise be unavailable, particularly for early-stage companies or those with limited tangible assets.
- Preservation of Ownership: Debt financing structures, such as IP-secured loans, allow companies to retain ownership of their IP while accessing capital.
- Alignment of Interests: Structures like royalty-based financing and IP-based joint ventures can align the interests of the lender or investor with the success of the IP.
Disadvantages
- Valuation Challenges: Valuing IP can be complex and subjective, making it difficult to determine the appropriate amount of financing.
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Structuring IP-backed financing involves navigating legal and regulatory frameworks that can be complex and vary by jurisdiction.
- Risk of Default: In case of default on debt financing, lenders have the right to seize the IP, which can have significant consequences for the company.
Key Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Structuring IP-backed financing requires careful consideration of legal and regulatory frameworks.
- IP Rights: It’s essential to ensure that the IP rights are valid, enforceable, and properly documented.
- Collateralization: The IP being used as collateral must be clearly defined and properly secured.
- Contractual Agreements: All agreements related to IP-backed financing, including loan agreements, licensing agreements, and joint venture agreements, must be carefully drafted to protect the interests of all parties.
- Tax Implications: The tax implications of IP-backed financing should be carefully considered, as these can vary depending on the structure and jurisdiction.
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies must comply with all relevant laws and regulations governing IP, financing, and securities.
Future Trends and Innovations
The use of intellectual property (IP) as collateral for financing is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing market dynamics. Emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI), are transforming how IP is valued, protected, and leveraged for financing.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on IP Valuation and Financing
The emergence of new technologies is significantly influencing the valuation and financing of intellectual property. AI, for instance, can analyze vast datasets of IP-related information, such as patent filings, market trends, and competitor activities, to provide more accurate and comprehensive valuations. AI-powered tools can also automate various aspects of IP valuation, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
AI-powered tools can automate various aspects of IP valuation, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Moreover, AI can help identify and assess the potential commercial value of intangible assets, including trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. This can be particularly valuable for startups and small businesses that may struggle to obtain traditional financing due to a lack of tangible assets.
The Role of Blockchain in Securing IP-Backed Financing
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing and tracking intellectual property rights. By recording IP ownership and licensing agreements on a decentralized ledger, blockchain can enhance the security and authenticity of IP assets.
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for managing and tracking intellectual property rights.
Blockchain can also facilitate the creation of new financing models for IP-backed assets. For example, fractional ownership of IP rights can be tokenized and traded on blockchain platforms, enabling investors to access a wider range of investment opportunities.
Fractional ownership of IP rights can be tokenized and traded on blockchain platforms, enabling investors to access a wider range of investment opportunities.
This could lead to a more liquid market for IP assets, making it easier for businesses to secure funding based on their intellectual property.
Ultimately, using intellectual property as collateral for financing is about strategic thinking and a deep understanding of the market. It’s about recognizing the potential of your ideas and finding creative ways to translate them into a financial advantage. This approach can be a powerful tool for entrepreneurs and businesses looking to accelerate growth, expand operations, and achieve their goals.
Securing debt and equity-based funding for your innovative venture? Don’t forget to leverage your intellectual property! It’s not just about the tech, but also about the potential impact. Just like how techcrunch space true anomaly and rocket lab will make big moves on orbit literally , your IP can be a powerful tool to attract investors and fuel your growth.
So, make sure your IP is strong and well-defined, ready to launch your business into orbit!
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News