Waymo’s Milestone: 4 Million Miles
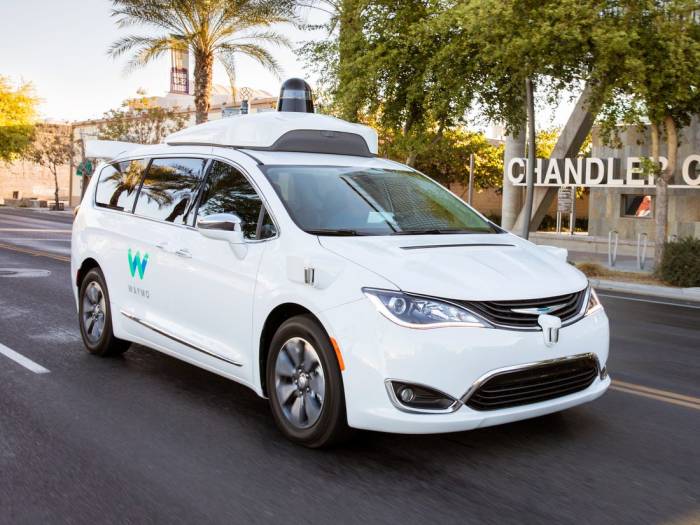
Waymo, a leading company in autonomous driving technology, has achieved a significant milestone by accumulating 4 million miles of self-driving experience. This achievement underscores the company’s dedication to advancing autonomous driving technology and its commitment to safety and reliability.
This milestone represents a significant leap forward in the development of self-driving technology. It allows Waymo to gather valuable data and refine its algorithms, leading to continuous improvement in the performance and safety of its autonomous vehicles.
Comparison to Other Self-Driving Companies
The 4 million miles mark positions Waymo as a frontrunner in the self-driving car industry. While other companies are also making progress, Waymo’s extensive testing experience sets it apart. For instance, Cruise, another prominent player in the autonomous driving space, has accumulated over 2 million miles of self-driving experience. However, Waymo’s 4 million miles signify a significant lead in terms of real-world driving data.
Locations and Environments
Waymo’s autonomous vehicles have driven millions of miles across diverse locations and environments, including:
- Phoenix, Arizona: Waymo has been operating a self-driving taxi service in Phoenix since 2017, providing rides to the public in a designated area. This real-world testing in a bustling urban environment has provided Waymo with valuable insights into navigating complex traffic patterns, pedestrian interactions, and various weather conditions.
- San Francisco, California: Waymo has expanded its operations to San Francisco, a city known for its dense traffic and challenging driving conditions. Testing in this environment allows Waymo to refine its autonomous driving algorithms to handle tight spaces, narrow streets, and unpredictable pedestrian behavior.
- Other Locations: Waymo has also conducted testing in other locations, including Mountain View, California, and Austin, Texas. These diverse locations expose Waymo’s vehicles to a range of road types, traffic patterns, and weather conditions, further enhancing the robustness of its technology.
Technology and Innovation
Waymo’s journey to 4 million miles of autonomous driving is a testament to the company’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology. This milestone reflects the culmination of years of dedicated research and development, resulting in a sophisticated suite of technologies that power their self-driving cars.
Waymo self driving cars 4m miles – At the core of Waymo’s autonomous driving system lies a complex interplay of hardware and software, each playing a crucial role in enabling safe and reliable navigation.
Sensors and Perception
Waymo’s self-driving cars are equipped with a comprehensive suite of sensors that provide a 360-degree view of their surroundings. These sensors gather real-time data, allowing the vehicles to perceive and understand their environment.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR emits laser beams to create a detailed 3D map of the environment, measuring distances and identifying objects with high accuracy.
- Cameras: Multiple cameras capture images from various angles, providing a comprehensive view of the surroundings. These cameras are used for lane detection, traffic light recognition, and pedestrian detection.
- Radar: Radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects and measure their distance and speed, even in low-visibility conditions. This technology is particularly useful for identifying moving objects like other vehicles and pedestrians.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors emit sound waves to detect objects in close proximity, providing crucial information for parking maneuvers and avoiding collisions at low speeds.
Software and Algorithms
The collected sensor data is then processed by sophisticated software algorithms, which interpret the information and make decisions about vehicle navigation. These algorithms are constantly learning and improving, enabling the cars to adapt to different driving scenarios and make increasingly accurate predictions.
- Perception Algorithms: These algorithms analyze the data from sensors to identify and track objects, including vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and road signs. They use machine learning techniques to recognize patterns and make predictions about the behavior of other road users.
- Path Planning and Control Algorithms: These algorithms determine the optimal path for the vehicle to follow, considering factors such as traffic conditions, road geometry, and obstacles. They also control the vehicle’s steering, acceleration, and braking to execute the planned path safely.
- Decision-Making Algorithms: These algorithms integrate information from various sources to make complex decisions, such as whether to change lanes, stop at a red light, or yield to pedestrians. They use sophisticated logic and reasoning to prioritize safety and comply with traffic laws.
Simulation and Testing
Waymo has invested heavily in simulation and testing to validate its autonomous driving technology. This process allows the company to create virtual environments that mimic real-world driving conditions, enabling them to test and refine their algorithms in a safe and controlled setting.
Waymo’s self-driving cars have clocked over 4 million miles on the road, showcasing their impressive progress in navigating the complexities of real-world driving. While Waymo focuses on autonomous vehicles, Apple is venturing into a different realm of technology with the anticipated release of their augmented reality headset in 2020, apples augmented reality headset release in 2020. This headset promises to revolutionize how we interact with the world, offering a glimpse into the future of immersive experiences.
Both Waymo and Apple are pushing the boundaries of innovation, shaping the technological landscape of tomorrow.
- Virtual Environments: Waymo uses sophisticated simulation software to create realistic virtual environments that include diverse road conditions, weather patterns, and traffic scenarios. This allows them to test their algorithms in a wide range of situations without the need for real-world driving.
- Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Testing: HIL testing involves integrating real-world sensors and actuators into a simulated environment. This allows the company to test the performance of their hardware and software in a controlled setting, ensuring compatibility and reliability.
- Real-World Testing: Waymo conducts extensive real-world testing in various locations, including cities, suburbs, and highways. These tests allow the company to gather real-world data and refine their algorithms to handle unexpected situations and complex driving scenarios.
Safety and Performance: Waymo Self Driving Cars 4m Miles
Waymo’s 4 million miles of autonomous driving represent a significant milestone in the development of self-driving technology. This extensive testing has provided valuable insights into the safety and performance of Waymo’s autonomous vehicles, paving the way for their eventual deployment on public roads.
Safety Record
Waymo’s safety record is a testament to the robust nature of its technology and its commitment to safety. During these 4 million miles, Waymo has consistently demonstrated its ability to navigate complex driving scenarios with minimal incidents.
- Waymo has publicly reported a low rate of disengagements, where a human safety driver needs to intervene. This data underscores the reliability of Waymo’s autonomous driving system, indicating that the technology is capable of handling most driving situations without human intervention.
- The company has also released statistics highlighting its low rate of accidents. These figures demonstrate that Waymo’s vehicles are involved in significantly fewer accidents than human-driven vehicles.
Comparison to Human Drivers
- Human error is a leading cause of accidents, and autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce this risk. Waymo’s technology is designed to eliminate human error, which can contribute to crashes caused by distractions, fatigue, or impaired judgment.
- Waymo’s autonomous driving system has been trained on millions of miles of real-world driving data, enabling it to identify potential hazards and react more quickly than a human driver. This capability has the potential to significantly reduce the number of accidents and improve overall road safety.
Role of Human Safety Drivers
While Waymo’s technology is highly advanced, human safety drivers play a crucial role during testing. These drivers are responsible for monitoring the vehicle’s performance and intervening in rare situations where the autonomous system may not be able to handle a particular scenario.
- The presence of human safety drivers provides an additional layer of safety during testing, ensuring that the vehicle can operate safely in a variety of driving conditions.
- As the technology continues to evolve, the role of human safety drivers is expected to diminish, with the ultimate goal being fully autonomous driving without human intervention.
Impact and Future Implications
Waymo’s 4 million miles of autonomous driving experience mark a significant milestone, not just for the company but for the future of transportation as a whole. This achievement signifies the potential of self-driving technology to revolutionize how we move around, offering a glimpse into a future where cars drive themselves, freeing us from the wheel and reshaping our cities and lives.
Impact on Urban Planning
The rise of autonomous vehicles presents a unique opportunity to reimagine urban planning. With self-driving cars, cities can be designed with a focus on pedestrian-friendly spaces, reducing reliance on personal vehicles and promoting alternative modes of transportation like walking and cycling. This can lead to more compact and efficient cities with less traffic congestion and improved air quality. For instance, cities can allocate more space for public parks and green areas, creating a more livable environment.
Implications for Traffic Congestion
One of the most significant implications of Waymo’s progress is the potential to alleviate traffic congestion. Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow and reducing accidents. By eliminating human error, self-driving cars can navigate roads more efficiently, leading to shorter commute times and less wasted time on the road. Studies have shown that autonomous vehicles can reduce traffic congestion by up to 30%, freeing up road space and improving overall efficiency.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Waymo’s technology has the potential to make transportation more accessible for people with disabilities and those who are unable to drive. Autonomous vehicles can provide door-to-door transportation, allowing individuals with limited mobility to travel independently. This can significantly enhance their quality of life and provide them with greater freedom and independence. Additionally, self-driving cars can offer transportation options for seniors who may no longer be able to drive themselves.
Waymo’s Vision for the Future, Waymo self driving cars 4m miles
Waymo envisions a future where autonomous vehicles are seamlessly integrated into our lives, providing safe, reliable, and convenient transportation. The company believes that self-driving technology will create a safer and more efficient transportation system, reducing accidents and improving overall mobility. Waymo aims to make autonomous vehicles accessible to everyone, transforming how we move around and creating a more sustainable and equitable future.
Public Perception and Acceptance
While Waymo has amassed an impressive amount of data and experience with its self-driving cars, public perception and acceptance remain crucial for widespread adoption. Public trust and confidence are essential for people to feel comfortable using and relying on this technology.
Key Concerns and Challenges
Public trust in self-driving cars is influenced by several factors, including safety concerns, ethical dilemmas, and the potential for job displacement.
- Safety Concerns: One of the primary concerns is the potential for accidents. While Waymo’s self-driving cars have demonstrated impressive safety records, there are still instances where accidents occur, raising questions about the reliability and robustness of the technology.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Self-driving cars face complex ethical dilemmas in situations where a collision is unavoidable. For example, how should the car decide who to prioritize in a potential accident? These ethical considerations raise concerns about the moral implications of autonomous vehicles.
- Job Displacement: The widespread adoption of self-driving cars could potentially displace jobs in industries like transportation and logistics. This raises concerns about the economic impact on workers and the need for retraining and social safety nets.
Strategies for Addressing Public Concerns
Waymo is actively working to address public concerns and build trust through various strategies:
- Transparency and Communication: Waymo emphasizes transparency by sharing information about its technology, safety protocols, and accident data. They also engage in open dialogue with the public to address concerns and provide reassurance.
- Public Demonstrations and Pilot Programs: Waymo conducts public demonstrations and pilot programs in select cities, allowing people to experience self-driving cars firsthand. This helps to build familiarity and trust in the technology.
- Collaboration with Regulators and Stakeholders: Waymo collaborates with government agencies, industry experts, and other stakeholders to develop comprehensive safety regulations and standards for autonomous vehicles. This fosters a sense of shared responsibility and builds public confidence in the technology.
- Educational Initiatives: Waymo invests in educational initiatives to inform the public about the benefits, limitations, and ethical considerations of self-driving cars. This helps to address misconceptions and build a better understanding of the technology.
Waymo’s 4 million miles is a milestone that signals a shift in the landscape of transportation. It’s a testament to the company’s dedication, the power of technology, and the potential for a future where autonomous vehicles become commonplace. This journey is far from over, but Waymo’s achievements demonstrate the possibilities of a world where cars drive themselves, and humans are free to focus on other things. As Waymo continues to refine its technology and navigate the complexities of public acceptance, the future of autonomous driving looks brighter than ever.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News