What we learned from the indictment of lockbits mastermind – What We Learned From the LockBit Mastermind Indictment: The indictment of the alleged mastermind behind the LockBit ransomware operation sends a powerful message to cybercriminals and serves as a valuable lesson for cybersecurity professionals. This case sheds light on the intricate workings of a sophisticated ransomware group, revealing their tactics, techniques, and the devastating impact they have on victims.
The indictment provides a detailed account of the alleged activities of the LockBit mastermind, including their role in developing and distributing the ransomware, targeting victims, and orchestrating the extortion schemes. This case is a significant development in the ongoing battle against ransomware, highlighting the importance of international cooperation, robust cybersecurity measures, and proactive threat intelligence.
The LockBit Ransomware Operation
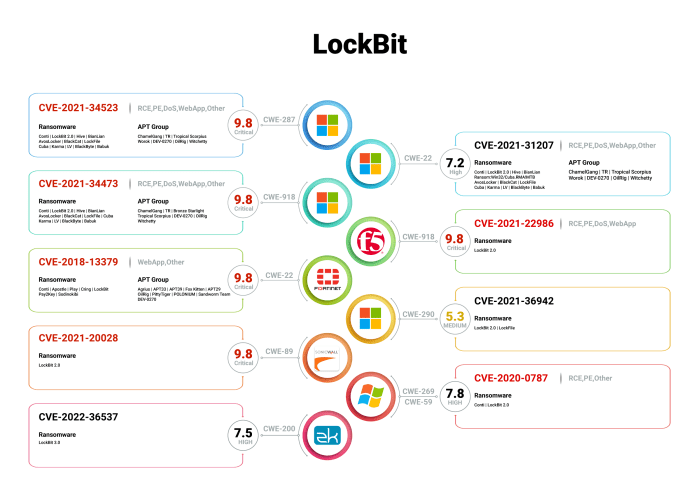
The LockBit ransomware operation is a sophisticated and highly organized criminal enterprise that has inflicted significant damage on businesses and individuals worldwide. Its history spans several years, marked by continuous evolution and adaptation to evade detection and maximize its impact. Understanding the evolution of LockBit, its tactics, and its consequences is crucial for mitigating the threat it poses to global cybersecurity.
History and Evolution
LockBit’s history can be traced back to 2019, when the first version, known as LockBit 1.0, emerged. This initial iteration was characterized by its relatively simple design and limited functionality. However, the ransomware quickly gained notoriety for its aggressive encryption techniques and the large ransom demands it levied on victims. LockBit 1.0 was followed by several subsequent versions, each introducing new features and enhancements that made the operation more resilient and challenging to counter.
LockBit 2.0, released in 2020, incorporated advanced features like data exfiltration, enabling attackers to steal sensitive information from victims’ networks in addition to encrypting their files. This development significantly increased the pressure on victims to pay ransoms, as the threat of data leaks added a new dimension to the extortion scheme. The introduction of the LockBit 3.0 variant in 2021 marked a further evolution, introducing a more robust command-and-control infrastructure and a sophisticated affiliate program. This program incentivized individuals to participate in the LockBit operation, expanding its reach and attack capabilities.
The continuous evolution of LockBit has been driven by the relentless pursuit of profitability and the desire to stay ahead of security measures. The ransomware operation has demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt to changing security landscapes, incorporating new techniques and technologies to circumvent defenses and maintain its effectiveness.
Tactics and Techniques
LockBit operators employ a wide range of tactics and techniques to infiltrate networks and execute their ransomware attacks. These methods include:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: LockBit actors often exploit vulnerabilities in software applications and operating systems to gain initial access to target networks. This can involve leveraging known vulnerabilities or discovering zero-day exploits.
- Phishing and social engineering: Attackers use phishing emails, malicious websites, and social engineering tactics to trick users into downloading malware or revealing sensitive credentials, providing a pathway into target networks.
- Remote desktop protocol (RDP) brute-forcing: LockBit operators may attempt to gain access to networks by brute-forcing weak or default RDP credentials. This involves systematically trying different password combinations until a successful login is achieved.
- Malware distribution: LockBit actors can distribute malware through various channels, including malicious attachments in emails, compromised websites, or exploit kits. Once installed, the malware can provide a backdoor for attackers to access the network and deploy the ransomware.
- Lateral movement: Once inside a network, LockBit operators employ techniques like credential harvesting and privilege escalation to gain access to sensitive data and systems. This allows them to spread the ransomware throughout the network and maximize their impact.
- Data exfiltration: LockBit actors often steal sensitive data from victims’ networks before encrypting their files. This stolen data is used as leverage to pressure victims into paying ransoms, threatening to release the information publicly if the ransom is not met.
- Ransomware deployment: The final stage involves deploying the LockBit ransomware payload onto victim systems. This payload encrypts files using strong cryptographic algorithms, rendering them inaccessible to the victim.
Impact of LockBit Attacks
LockBit attacks have had a significant impact on victims and the global cybersecurity landscape.
- Financial losses: LockBit attacks have resulted in substantial financial losses for victims, both from the cost of paying ransoms and from the disruption of business operations.
- Data breaches: LockBit’s data exfiltration capabilities have led to numerous data breaches, exposing sensitive information such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Reputational damage: LockBit attacks can severely damage the reputation of affected organizations, eroding public trust and impacting brand image.
- Increased cybersecurity awareness: LockBit attacks have heightened awareness of the ransomware threat and the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
- Cybersecurity industry response: The emergence of LockBit has spurred significant research and development efforts in the cybersecurity industry to develop new technologies and strategies for combating ransomware.
The Indictment and its Implications
The indictment of the LockBit mastermind, a significant event in the fight against ransomware, sheds light on the inner workings of this notorious cybercrime operation. The indictment Artikels a detailed picture of the mastermind’s role in orchestrating the LockBit ransomware attacks, providing valuable insights into the operation’s structure, tactics, and potential vulnerabilities.
Key Charges Against the LockBit Mastermind
The indictment Artikels a range of charges against the LockBit mastermind, reflecting the breadth of their alleged criminal activities. These charges highlight the individual’s alleged involvement in the LockBit operation, ranging from leadership and organization to technical expertise and financial gain. The indictment provides a comprehensive legal framework for understanding the mastermind’s role within the LockBit ransomware ecosystem.
- Conspiracy to Commit Computer Fraud and Abuse: This charge alleges that the mastermind conspired with others to access and damage computer systems without authorization, causing significant financial harm to victims. This charge underscores the mastermind’s alleged role in directing and facilitating the ransomware attacks.
- Conspiracy to Commit Wire Fraud: This charge focuses on the mastermind’s alleged involvement in the financial aspect of the LockBit operation. It suggests that the mastermind conspired with others to defraud victims by demanding ransom payments through wire transfers. This charge emphasizes the financial motivation behind the LockBit attacks.
- Money Laundering: This charge relates to the mastermind’s alleged efforts to conceal and disguise the proceeds of the LockBit ransomware attacks. The indictment suggests that the mastermind engaged in financial transactions designed to obscure the origin of the ransom payments. This charge highlights the mastermind’s alleged involvement in the financial infrastructure of the LockBit operation.
Legal and Technical Evidence Presented in the Indictment
The indictment presents a compelling case against the LockBit mastermind, relying on a combination of legal and technical evidence. This evidence demonstrates the alleged involvement of the mastermind in the LockBit operation, highlighting the depth of the investigation and the meticulous efforts to gather evidence. The indictment offers a glimpse into the investigative techniques employed to unravel the intricate web of the LockBit ransomware network.
- Communication Records: The indictment likely includes communication records, such as emails, instant messages, and online forum posts, to establish the mastermind’s connection to the LockBit operation. These records may provide insights into the mastermind’s role in coordinating attacks, managing affiliates, and communicating with victims.
- Financial Transactions: The indictment may rely on financial transaction records, such as bank statements, cryptocurrency transactions, and money transfers, to trace the flow of ransom payments. These records can demonstrate the mastermind’s involvement in the financial aspect of the LockBit operation, including the collection, laundering, and distribution of ransom funds.
- Technical Evidence: The indictment may include technical evidence, such as malware analysis, network logs, and forensic data, to link the mastermind to the LockBit ransomware attacks. This evidence can demonstrate the mastermind’s role in developing, deploying, and controlling the LockBit ransomware, highlighting their technical expertise and involvement in the operation’s infrastructure.
Potential Consequences of the Indictment for the LockBit Operation
The indictment of the LockBit mastermind carries significant implications for the LockBit operation and its members. It signifies a major blow to the operation, potentially disrupting its leadership, communication, and financial infrastructure. The indictment serves as a strong deterrent to other ransomware operators, highlighting the risks and consequences associated with these criminal activities.
- Disruption of Leadership: The indictment of the mastermind can disrupt the leadership structure of the LockBit operation, potentially causing internal turmoil and weakening its ability to coordinate attacks. This disruption can hinder the operation’s ability to recruit new members, manage affiliates, and develop new ransomware strains.
- Impact on Communication: The indictment can impact the communication channels used by the LockBit operation, making it harder for members to coordinate attacks, share information, and communicate with victims. This disruption can make it more difficult for the operation to maintain its network and operate effectively.
- Financial Disruption: The indictment can disrupt the financial infrastructure of the LockBit operation, making it harder for members to collect ransom payments, launder money, and manage their finances. This disruption can make it more difficult for the operation to sustain its activities and reward its members.
- Deterrence and Increased Pressure: The indictment can serve as a deterrent to other ransomware operators, highlighting the risks and consequences associated with these criminal activities. It can also increase pressure on law enforcement agencies to pursue investigations and bring perpetrators to justice.
Lessons Learned for Cybersecurity Professionals: What We Learned From The Indictment Of Lockbits Mastermind
The indictment of the LockBit mastermind offers valuable insights for cybersecurity professionals, highlighting vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware operators and emphasizing the importance of proactive security measures. Understanding the tactics used by LockBit can help organizations strengthen their defenses against similar threats and minimize the risk of falling victim to ransomware attacks.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Defenses
The LockBit indictment underscores the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks. These measures should encompass various aspects of cybersecurity, including:
- Network Segmentation: Implementing network segmentation can limit the impact of a ransomware attack by isolating critical systems and data from compromised areas. This strategy helps prevent lateral movement of malware and reduces the potential for widespread damage. For instance, separating production environments from development and testing environments can limit the spread of an attack.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access to sensitive systems and data. This significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access and helps prevent ransomware operators from gaining control of critical systems.
- Regular Security Audits: Organizations should conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ransomware operators. These audits should include assessments of network security, user access controls, and software patching practices. For example, identifying outdated software with known vulnerabilities and patching them promptly can significantly reduce the risk of a successful ransomware attack.
- Employee Training: Training employees on cybersecurity best practices is crucial to prevent them from falling victim to social engineering attacks. Ransomware operators often use phishing emails and other social engineering techniques to trick employees into granting access to their systems. Training employees to recognize and report suspicious emails and attachments can significantly reduce the risk of a ransomware attack.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implementing a robust data backup and recovery plan is essential for organizations to minimize the impact of a ransomware attack. Regular backups of critical data should be stored offline and securely protected to ensure that data can be restored even if the primary systems are compromised.
The Future of Ransomware and Cybersecurity
The indictment of the LockBit mastermind serves as a stark reminder of the evolving nature of ransomware and the persistent threat it poses to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. Understanding the future trajectory of ransomware attacks is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies and mitigating potential damage.
The Evolving Nature of Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, targeting critical infrastructure, utilizing advanced evasion techniques, and exploiting vulnerabilities in software and human behavior. This evolution demands a proactive approach to cybersecurity, encompassing robust security measures, constant vigilance, and ongoing adaptation to emerging threats.
- Increased Targeting of Critical Infrastructure: Ransomware actors are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure, such as healthcare, energy, and transportation, recognizing the potential for significant disruption and financial gain. For example, the 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack, which crippled a major fuel pipeline in the United States, highlighted the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to ransomware attacks.
- Advanced Evasion Techniques: Ransomware actors are employing sophisticated evasion techniques, such as using malware that can bypass traditional security measures, encrypting data in multiple layers, and using steganography to hide malicious code. These techniques make it increasingly difficult to detect and respond to ransomware attacks.
- Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities: Ransomware actors are actively exploiting vulnerabilities in software, often targeting unpatched systems and outdated software. The recent Log4j vulnerability, which affected a wide range of software applications, demonstrated the potential for widespread exploitation of software vulnerabilities by ransomware actors.
- Social Engineering and Phishing: Ransomware actors are increasingly using social engineering and phishing tactics to gain access to systems. These techniques often involve sending malicious emails or messages that trick users into clicking on links or opening attachments that contain malware.
International Cooperation in Combating Ransomware Threats, What we learned from the indictment of lockbits mastermind
International cooperation is essential to effectively combat ransomware threats. Sharing information, coordinating law enforcement efforts, and developing joint cybersecurity strategies are crucial steps in mitigating the global impact of ransomware.
- Information Sharing: Sharing information about ransomware attacks, tactics, and indicators of compromise (IOCs) is essential for early detection and response. This includes sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and incident response plans.
- Law Enforcement Cooperation: Close collaboration between law enforcement agencies is vital for investigating and prosecuting ransomware actors. This includes sharing evidence, coordinating raids, and extraditing suspects.
- Joint Cybersecurity Strategies: Developing joint cybersecurity strategies that encompass national and international efforts is crucial for addressing the global nature of ransomware. This includes developing common standards, best practices, and frameworks for cybersecurity.
Hypothetical Scenario of a Successful LockBit Attack
Imagine a scenario where a LockBit ransomware attack successfully compromises a major financial institution. The attackers encrypt critical data, including customer records, financial transactions, and internal systems. The institution faces a significant disruption of operations, causing widespread financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal ramifications.
- Operational Disruption: The institution’s operations are severely disrupted, with critical systems offline, customer service unavailable, and financial transactions halted. This can lead to significant financial losses, including lost revenue, customer churn, and increased operational costs.
- Data Loss and Recovery: The institution faces the potential loss of critical data, including customer information, financial records, and internal documents. Recovering this data can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially requiring specialized data recovery services and forensic investigations.
- Reputational Damage: A successful LockBit attack can significantly damage the institution’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust, negative media coverage, and potential regulatory scrutiny. This reputational damage can have long-lasting consequences, impacting future business opportunities and customer relationships.
- Legal and Regulatory Ramifications: The institution may face legal and regulatory ramifications, including fines, lawsuits, and investigations by regulatory agencies. These consequences can further exacerbate the financial and reputational impact of the attack.
The indictment of the LockBit mastermind is a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat posed by ransomware. It underscores the importance of constant vigilance, proactive cybersecurity measures, and international collaboration in combating this global menace. By understanding the tactics employed by ransomware groups and leveraging lessons learned from this case, organizations can strengthen their defenses and mitigate the risk of becoming victims. As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, it’s crucial to stay informed, adapt to new threats, and work together to create a safer digital world.
The LockBit indictment showed us that even the most sophisticated cybercriminals can be brought down, highlighting the importance of collaboration and intelligence sharing. It also reminded us that the success of any endeavor, be it dismantling a criminal enterprise or achieving an NBA championship, relies on teamwork. And speaking of teamwork, NBA champion Kyle Kuzma looks to bring his team mentality to Scrum Ventures , a venture capital firm focused on supporting the next generation of tech startups.
Just like the FBI’s takedown of LockBit, Kuzma’s approach emphasizes the power of collaboration and a shared vision to achieve success.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News