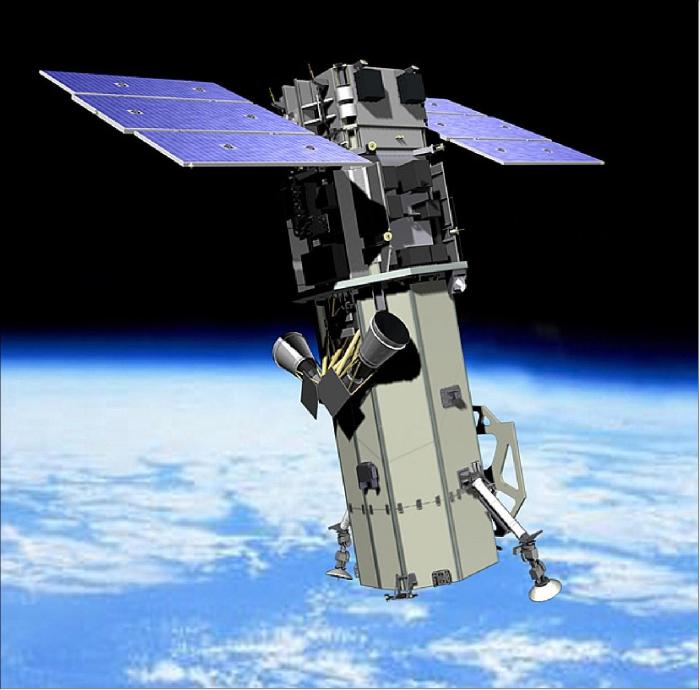
The WorldView-3 Telescope: Worldview 3 Telescope Sees In Great Detail
The WorldView-3 telescope is a marvel of modern technology, designed to capture high-resolution imagery of the Earth’s surface. It’s a vital tool for a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring and disaster response to military intelligence and scientific research.
Advanced Imaging Technologies
The WorldView-3 telescope is equipped with a suite of advanced imaging technologies that enable it to capture detailed images of the Earth. These technologies include:
- Panchromatic Imaging: This technology captures images in a single band of the electromagnetic spectrum, providing high-resolution black and white images. WorldView-3’s panchromatic sensor has a resolution of 31 cm (12.2 inches), allowing it to distinguish objects as small as a car.
- Multispectral Imaging: This technology captures images in multiple bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, allowing scientists to analyze different features of the Earth’s surface. WorldView-3’s multispectral sensor captures images in eight bands, ranging from visible light to near-infrared wavelengths. This allows scientists to distinguish between different types of vegetation, identify areas of pollution, and track changes in land cover over time.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This technology captures images in hundreds of narrow bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, providing detailed information about the chemical composition of objects on the Earth’s surface. WorldView-3’s hyperspectral sensor captures images in 12 bands, allowing scientists to identify minerals, map vegetation health, and monitor environmental changes.
Unveiling the World in High Detail
WorldView-3 is not just another satellite; it’s a high-resolution imaging marvel, capable of capturing the Earth’s surface with exceptional detail. This advanced technology allows us to see our planet in ways never before possible, revealing intricate details that were previously hidden from our view.
The Power of High Resolution
The WorldView-3 telescope’s high resolution is its most impressive feature. With the ability to capture images with a resolution of up to 30 centimeters (12 inches), it can distinguish objects as small as a picnic table or a parked car. This level of detail provides a level of clarity and accuracy that is unmatched by other imaging systems.
Understanding the World in Greater Depth
This incredible detail allows us to study our planet in unprecedented ways. We can now analyze land use patterns, track deforestation, monitor urban sprawl, and assess the impact of natural disasters. WorldView-3’s imagery provides valuable insights into various aspects of our environment, helping us to understand the complex interactions that shape our planet.
Applications of Detailed Imagery
The applications of WorldView-3’s detailed imagery are vast and diverse. Here are a few examples:
- Disaster Response: Following natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, WorldView-3’s imagery helps rescue teams quickly assess the damage and identify areas in need of immediate assistance. The detailed images can pinpoint the locations of survivors, damaged infrastructure, and blocked roads, enabling swift and efficient relief efforts.
- Agriculture: Farmers can utilize WorldView-3’s imagery to monitor crop health, identify areas of stress, and optimize irrigation and fertilization practices. This detailed information allows them to improve crop yields and maximize their farm’s productivity.
- Urban Planning: City planners use WorldView-3’s imagery to assess urban growth, identify potential infrastructure challenges, and optimize the use of land resources. The detailed images provide valuable insights into population density, traffic patterns, and the availability of green spaces, facilitating informed urban planning decisions.
- Environmental Monitoring: Environmental scientists rely on WorldView-3’s imagery to track changes in vegetation cover, monitor deforestation rates, and assess the impact of pollution. The detailed images help them understand the health of ecosystems and identify areas that require protection and conservation.
Applications of WorldView-3 Imagery
WorldView-3, with its exceptional resolution and multispectral capabilities, provides a wealth of data that can be utilized across various fields, offering valuable insights and solutions for a wide range of applications. From monitoring agricultural yields to assessing disaster damage, WorldView-3 imagery plays a crucial role in addressing real-world challenges.
Applications of WorldView-3 Imagery in Various Fields
WorldView-3 imagery finds diverse applications in various fields, enabling informed decision-making and effective problem-solving. The table below highlights some key applications in different sectors:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Crop monitoring, precision farming, yield estimation, disease detection, irrigation management |
| Urban Planning | Infrastructure development, city growth analysis, urban sprawl monitoring, population density estimation |
| Disaster Management | Damage assessment, rescue operations, flood mapping, earthquake impact analysis |
| Environmental Monitoring | Deforestation tracking, pollution detection, water quality assessment, coastal change monitoring |
| Military and Intelligence | Target identification, reconnaissance, surveillance, battlefield analysis |
| Oil and Gas Exploration | Pipeline monitoring, infrastructure inspection, environmental impact assessment |
Real-World Examples of WorldView-3 Imagery Applications
WorldView-3 imagery has been instrumental in solving real-world problems across diverse domains.
For instance, in the aftermath of Hurricane Harvey in 2017, WorldView-3 imagery was used to assess the extent of damage to infrastructure and homes in Houston, Texas. This information was crucial for coordinating rescue efforts and providing aid to affected communities.
In agriculture, WorldView-3 imagery has helped farmers optimize crop yields by providing detailed information about crop health, irrigation needs, and disease outbreaks. Farmers can use this data to make informed decisions about fertilizer application, irrigation schedules, and pest control measures.
In environmental monitoring, WorldView-3 imagery has been used to track deforestation rates in the Amazon rainforest, providing valuable data for conservation efforts. The imagery can also be used to monitor air and water quality, helping to identify and address environmental issues.
The Future of High-Resolution Earth Observation
WorldView-3 has ushered in a new era of high-resolution Earth observation, and its capabilities have inspired advancements that will shape the future of this field. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and powerful Earth observation systems to emerge, pushing the boundaries of what we can see and understand about our planet.
Advancements in Earth Observation Technology
WorldView-3’s success has paved the way for several exciting advancements in Earth observation technology. These advancements are driven by the desire to capture even more detailed information, improve the accuracy of data analysis, and expand the range of applications for Earth observation.
- Enhanced Spectral Resolution: Future Earth observation systems will likely feature an even wider range of spectral bands, allowing for more detailed analysis of specific features on the Earth’s surface. This will enable scientists to differentiate between different types of vegetation, identify mineral deposits, and monitor environmental changes with greater precision.
- Higher Spatial Resolution: The pursuit of higher spatial resolution is a key driver of innovation in Earth observation. Future telescopes may achieve resolutions of less than 10 centimeters, providing unprecedented detail for applications like urban planning, infrastructure monitoring, and disaster response.
- Advanced Data Processing: The sheer volume of data generated by high-resolution Earth observation systems requires sophisticated data processing techniques. Future systems will likely incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms to automatically analyze and interpret data, providing insights that were previously impossible to obtain.
Future Telescopes Surpassing WorldView-3
While WorldView-3 has set a new standard for high-resolution Earth observation, future telescopes are poised to surpass its capabilities in several ways. These advancements will be driven by ongoing research and development in areas such as optics, sensors, and data processing.
- Larger Aperture Telescopes: Larger aperture telescopes will collect more light, enabling them to capture images with higher resolution and clarity, even in low-light conditions. This will allow for more detailed observations of the Earth’s surface, particularly in areas with limited sunlight.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging captures data across a much wider range of spectral bands than traditional multispectral imaging. This allows for more detailed analysis of materials and objects on the Earth’s surface, leading to improved applications in fields like agriculture, geology, and environmental monitoring.
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): SAR technology allows for imaging through clouds and in darkness, making it ideal for monitoring weather patterns, mapping terrain, and detecting changes in land use. Future SAR systems are expected to offer higher resolution and wider coverage, further expanding their capabilities.
Impact of High-Resolution Imagery on Various Sectors, Worldview 3 telescope sees in great detail
High-resolution Earth observation imagery is already having a significant impact on various sectors, and this trend is only expected to accelerate in the coming years.
- Agriculture: High-resolution imagery can be used to monitor crop health, identify disease outbreaks, and optimize irrigation practices. This leads to increased agricultural productivity and reduced reliance on chemical inputs.
- Urban Planning: High-resolution imagery provides valuable insights for urban planners, enabling them to analyze population density, traffic patterns, and infrastructure development. This data helps in creating more sustainable and efficient urban environments.
- Disaster Management: High-resolution imagery plays a crucial role in disaster response by providing rapid assessments of damage, identifying areas of need, and guiding rescue efforts. This helps to save lives and minimize the impact of natural disasters.
- Environmental Monitoring: High-resolution imagery is essential for monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change. This data provides valuable insights for environmental policymaking and conservation efforts.
Worldview 3 telescope sees in great detail – The WorldView-3 telescope is a testament to human ingenuity and its potential to unlock new possibilities. It’s a window into the intricate details of our planet, providing a wealth of information that’s transforming industries and shaping our future. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated Earth observation tools, pushing the boundaries of what we can see and understand.
The James Webb Space Telescope, with its groundbreaking worldview 3 capabilities, allows us to see the universe in exquisite detail. This incredible feat of engineering is made possible by advancements in rocket technology, such as the new Vulcan rocket unveiled by the United Launch Alliance here. The Vulcan rocket, with its powerful engines and innovative design, will play a crucial role in launching future space missions, including those that will further expand our understanding of the cosmos through the lens of the James Webb Space Telescope.
 Standi Techno News
Standi Techno News